A credit card grace period is the days between the billing date and the due date. During this period, no interest is charged on purchases if you pay your balance in full.
The grace period is typically given to newly purchased products rather than to services such as cash advances and transfers. For any of these purchases, interest will be charged from the date of occurrence unless they qualify for a particular 0 percent APR tease.
What is a Credit Card Grace Period?
The Credit Card Grace Card refers to the period between the issuance of a credit card statement and the due date, during which the consumer bears no interest for any purchase made on the card.
The grace period is the time that elapses between the time a consumer makes purchases through his/her credit card in the previous billing cycle and the time he/she is required to pay interest on the outstanding balance made during the current billing cycle.
It is only applicable if the consumer cleared his or her last credit card balance in full and timely and did not roll over a balance for any part of the preceding billing cycle.
Note: It is advisable to read the terms and conditions of your credit card and find out if it has a grace period.
How Long is a Typical Grace Period for a Credit Card?
A grace period normally ranges from 21 days to 55 days. Remember that having a credit card grace period does not mean that you have more time until the due date.
When you make partial payments, fail to make the necessary minimum payment on your credit card, or pay your bill after the due date, your credit card company will start charging interest on your balance.
In addition, you will incur late penalties if you fail to make a payment or make it after the due date.
To prevent interest payments, you must pay off your credit card balance in full before the payment due date. At the absolute least, you must make the minimum payment, and you will then be charged interest on any balance carried over to the next month.
| Tip: To maintain your grace period, make sure to pay your bills in full and on time each month. If you pay in full for some months but not others, you may lose your grace period for the month in which you do not pay in full and the following month. |
If you pay off your credit card amount every month during this grace period, you will avoid incurring interest on your purchases. However, the grace period usually only applies to new purchases, not cash advances, balance transfers, or special promotional deals.
Example of Credit Card Grace Period
| Let’s understand this with an example: If your billing cycle ends on May 31, your credit card statement detailing the amount due is issued on the same day. Assuming a 30-day grace period, your payment due date would be June 30. By paying the full balance within this timeframe, you can avoid any interest charges. |
How Long is the Grace Period On Credit Card?
Credit card lenders or companies must send cardholders their bills at least 21-25 days before payment is due. Sometimes, some credit cards consider those 21 days, as well as the time between when you made your purchases inside the billing cycle, to be a grace period if you have paid your previous balance in full. This means grace periods might last nearly two months.
How Does the Credit Card Grace Period Work?
To fully enjoy a grace period, you must understand the credit card’s billing cycle, the expense of carrying a debt, and how the lender charges interest on your purchases.
These key concepts assist in clarifying how grace periods work:
- Billing Cycle
Your credit card company establishes a billing cycle, which is typically one month long. Finally, your purchases are totaled and presented in a statement.
- Statement Generation
Your credit card provider generates a statement of your purchases at the end of each billing cycle that summarises the transactions completed during that time.
- Grace Period
The grace period begins on the day your statement is generated and normally lasts 21-25 days, depending on the credit card provider.
- Interest Fee
If you pay off your credit card amount in full by the due date during the grace period, you will not be charged interest on your transactions.
- Interest on Unpaid Balances
If you fail to pay the entire balance by the due date, the remaining balance will start to accrue inte
How Can Credit Card Grace Periods Save you Money?

If you are keen on maintaining your credit card balance, it is very important to make the most out of the grace period. If done with some thought, one can manage their cash flow and make the right usage of the credit card.
Here’s how to get the most out of your grace period:
1. Pay Your Full Balance On Time
The simplest way to avoid interest charges is to always make full payments for the amount charged on your statement by the due date. If you are unable to contribute the total amount, ensure that you contribute at least the minimum.
The balance will then attract an interest rate, as will any other purchase made after this. If you transfer lesser balances, then the interest you will be charged will also be reduced.
Example:
If your statement balance is $500 and your due date is the 25th of the month, by the due date, you must pay $500. Thus, you avoid interest charges that could come along the way if you have a line of credit.
However, if you pay only $250, interest will be charged on that amount and all purchases made after the date of the statement.
2. Buy at the Right Time to Gain Most Benefits
To maximize your grace period further, make your purchases at the start of a billing cycle. However, if you want to take much more time, you will have a full cycle with interest and a grace period.
For bigger purchases, this strategy could allow you to go up to two months without accruing interest.
Example:
Your account’s billing cycle ends on the 10th of the following month. If you purchase $200 and have the records that it reflects in your statement, the purchase attracts an interest-free period of 25 days from the 5th to the 30th.
For example, if you make the same $200 purchase on the 20th, those will count in your next cycle, and you get a full month + the interest grace period.
3. Set a Budget
Having a budget will allow you to control your purse strings well, enabling you to manage your credit card balance correctly. It is best to think of your credit card as an interest-free loan.
If the grace period is understood correctly, complete payment should be made on the statement balance before the grace period expires.
Example:
Let’s assume that you have $500 that you can spend as you please in a month. Thus, tracking your expenses allows you to use your credit card only for purchases within this limit and make a payment in full before the due date.
For instance, when you buy groceries worth $100 using your credit card, and you buy 200 worth of gas, you will be charged $300 in a statement, which can be paid by the due date to minimize interest charges.
4. Avoid Carrying a Balance
The key to making good use of the grace period is paying your bill in full every month. Even if you continue into the next month with a balance remaining, you may lose your grace period, and thus, interest will be added to any new purchases.
That only happens when you pay off your balance, which lets you retain the grace period you negotiated on your credit card.
Example:
Let’s say your statement balance is $300, but you manage to pay $100; the remaining balance is $200, which will be carried over to the next month. This balance will start incurring interest, and you will lose your grace period for new purchases.
On the other hand, paying up to $300 in full means that in the next cycle, you will not incur any additional interest on the balance or new products.
5. Effectively Manage your Credit Card for Expected Expenses
If you cannot control your urge to spend, it would be ideal to only use your credit card in situations where you already know you can pay up before the due date.
By sticking to the planned amount for each category, you will maximize your payments, ensuring they clear their balance, and you will not be charged any interest.
Example:
For instance, you might be considering a $400 plane ticket at the beginning of the month and are aware that you can afford to pay for it on the due date.
This enables its holder to charge any item that he or she wants on the credit card and make the full and timely repayment before the due date, hence avoiding any interest.
However, if you use the card to make random purchases, as you do not need to, your chances of repaying it in full may be strained.
6. Set Up Automatic Payments
To avoid being devoid of a grace period, it is prudent to make arrangements for auto payments of your statement balance.
This ensures that you pay your outstanding amount in full every month, even if you forget or are occupied.
Example:
If you know your statement balance is $400 and your due date is the 25th, automatic payment means that your card issuer will pay the stated balance before the due date.
This prevents you from forgetting to make a payment, so there is no need to incur extra interest charges.
How Can Grace Periods Maximize Your Credit Card Rewards?
The grace period comes between 21 to 25 days from the last date of your billing cycle and allows you to clear your balance before it starts to attract interest charges.
Here’s how you can use this feature to your advantage:
- Don’t Charge and Optimize Profit
Paying off your balance in full if you have the cash during the grace period helps prevent interest charges from devaluing your rewards.
For example, utilizing an incentive card like the Chase Sapphire Preferred® Card, which pays 3X points on Dining and 2X Points on Travel, earns you valuable points while keeping your spending interest-free if you pay off the balance before the due date.
- Time Big Purchases Wisely
Whenever you are planning a big purchase, try to time it until the billing cycle commences. This gives you the maximum time to pay it off within the grace period. This basically assists in giving the maximum time within the grace period to pay off what has been borrowed.
More easily, using credit cards like the Citi® Double Cash Card, which offers 2% cash back, 1% when you buy, and 1% when you pay, could double the rewards when using this strategy.
- Link Grace Periods with introductory APR Offers
Some cards, like the Wells Fargo Active Cash® Card, have no annual fees and include 0% APR introductory periods.
You also get 2% back on every purchase. By following the grace period curve to ensure the introductory APR has ended, you can always reap from those points without being charged interest.
- Optimize Category Rewards
Cards with bonus categories that change each quarter, such as the Discover it® Cash Back, enable their holders to charge up to 5% on certain items, such as groceries, gas, or even dining.
No value erodes for these rewards through interest charges when your balance is paid fully within the grace period.
- Redeem Points From Daily Purchases
Merchant purchases, such as food and electricity bills, can also contribute to the accrual of rewards, and charges apply if they settle before the grace period.
The Blue Cash Preferred® Card offers an enrollment bonus of $150 once you spend $1,000 in the first three months of opening the account. It also offers the following rewards: 6% cash back on up to $6,000 per year at US supermarkets.
This way, it becomes possible to protect all those bonuses, remain profitable, and pay the balance on time.
Who is Eligible for Credit Card Grace Periods?
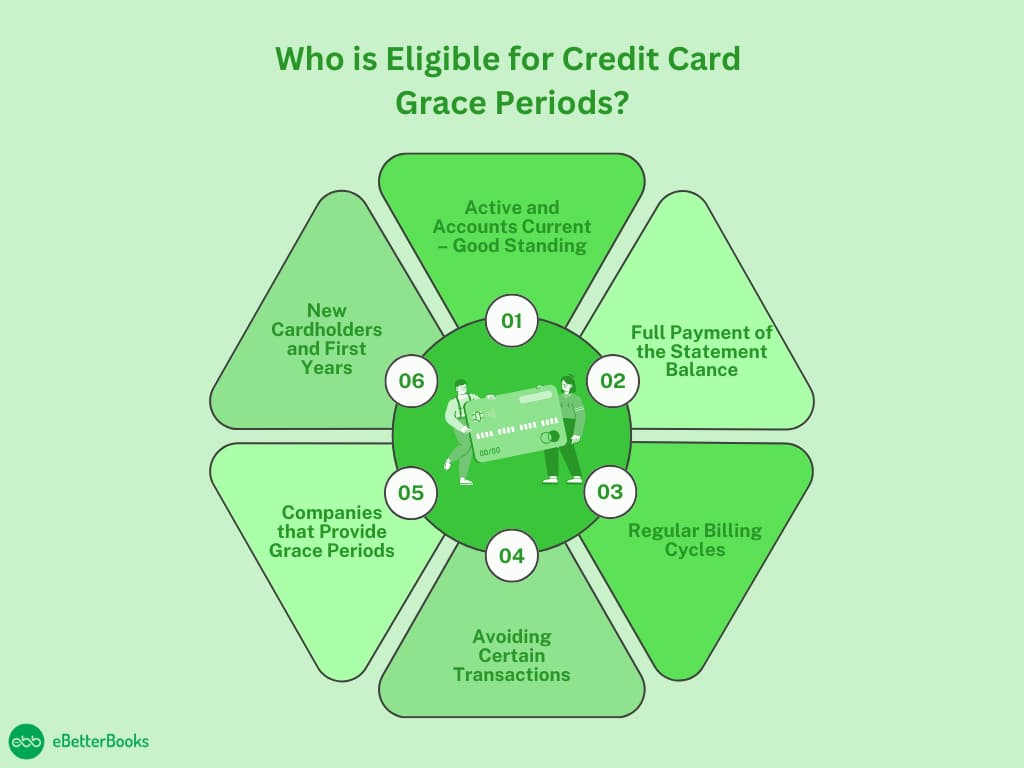
A credit card grace period is one of the privileges that enable users to make purchases without accruing interest on the purchases so long as they pay the amounts owed before the due date. However, only some people are entitled to this kind of benefit right away. Not all cards are issued with a grace period, and here are factors that will determine if you are a beneficiary or not:
1. Active and Accounts Current – Good Standing
The first qualification for eligibility is that the credit card account you are qualifying must be open and not in default. As a result, you have to maintain an active, unblocked credit card with no overdue payments or complications, including chargebacks or defaults.
In this case, if your card is suspended or closed, for instance, due to non-payment or other issues, you are eliminated from accessing the grace period. It is also very important that you don’t go overboard with spending over your credit limit.
2. Full Payment of the Statement Balance
To be eligible for the grace period, you need to make your minimum statement balance payment by the stated date. The grace period only kicks in if you start a billing cycle with a $0 balance on your account.
If you leave any balance unpaid, you forfeit your grace period right, and interest begins to be charged on new purchases as soon as they are made. The consequence of paying only the minimum amount or of keeping a balance over the month will be interest charges.
3. Regular Billing Cycles
Most credit card companies go for monthly statements, and where your specific card operates within these regular cycles, you are allowed the grace period.
An ideal billing cycle is between 28 and 31 days, and from the close of the cycle, you are afforded some grace period between 21 and 25 days, within which you should pay your bill before incurring interest.
This is a supremacy of most credit card companies mandated by federal statute, though it is only valid when one does not carry over a balance from the previous cycle.
4. Avoiding Certain Transactions
It’s important to remember that grace periods do not include balance transfers, cash advances, or any other special occasions. Many of these transactions begin charging interest immediately while you are still in the grace period on new cash advances.
If you transfer a balance or get a cash advance, interest will be charged from the date of the transaction or the date the card was issued. Any grace period you may have for new purchases will not apply to this.
5. Companies that Provide Grace Periods
It is important to note that some credit cards do not allow a grace period. This feature, however, is not universal: most major credit card issuers offer it; however, some specific types of cards, like high-risk or secure credit cards, do not.
So, it’s wise to go through the terms and conditions of any credit card that you wish to apply for some time and check to ascertain whether the Credit card offers a grace period.
If the card does not have this feature, interest starts to be charged on the purchase as soon as one is made.
6. New Cardholders and First Years
Most consumers are eligible for the grace period when they sign up for a new credit card, but they should review the disclosures of introductory periods. Certain card companies are likely to provide an initial 0% APR on purchases for a set amount of months, in which you would not be charged any interest.
Yet the rules change after the first month, and as with any other credit card, the standard grace period applies. During this period, one must make a complete payment of the balance to avoid interest.
Here are the types of transactions and the grace period eligibility criteria…
| Types of Transactions | Eligible for Grace Period | Notes |
| New Purchase | Yes | There is no interest if the full balance is paid on time. |
| Cash Advance | No | Interest starts immediately. |
| Balance Transfer | No | It often has its own interest rates. |
| Special Promotion | Card Specific | Check specific terms. |
What Can Cause You to Lose Your Grace Period?
There are several reasons you may lose eligibility for a grace period, including:
- Carrying a Balance: If you can’t clear the amount in full, the grace period is removed, and any new purchases will attract interest charges immediately.
- Late Payments: Failure to make the payment or paying an amount below the minimal required sum initiates the grace period and penalties, such as fees for lateness.
- Certain Transactions: It is important to note that balance transfers, cash advances, and similar operations do not usually qualify for this grace period, and they attract interest from the day the transfer is made.
The Impact of Grace Periods on Other Debt
Grace periods are useful for many types of debt because they imply that the debtor has a certain period during which he/she does not need to make payments.
These periods allow borrowers more time to make the payments without attracting penalties or having their credit rating affected. However, they may be different, as they depend on the kind of debt one has and the policies of the credit company.
Student Loans
Grace Period: 6 months (for federal loans usually)
Details: Federal student loans allow, for example, a grace period of six months after graduation. Indeed, during this period, borrowers do not have to pay back any loans. This time provides an opportunity for graduates to get a job or make other preparations before starting to pay back the loans. Nevertheless, interest may continue to be charged on certain loans (such as unsubsidized federal loans).
Mortgages
Grace Period: 10-15 days
Details: Most mortgage creditors offer a brief period of forbearance, which ranges between 10 and 15 days after the due date. This means that if a mortgage payment is made during this period, no penalty charge is added. Nonetheless, the borrower should be cautious that even during the grace period, interest continues to build up, and payments in default after the grace period are deemed past due.
Auto Loans
Grace Period: 10-15 days
Details: Like mortgages, auto loans are normally accompanied by a brief grace period. Borrowers can be offered a grace period of 10 to 15 days before they are charged for late payment. Although this may help, it slows, and interest keeps piling up. Once the grace period is over, the loan is deemed past due.
Personal Loans
Grace Period: 15-30 days
Details: A personal loan may also include a grace period, usually 15 – 30 days, depending on the nature of the loan. If a payment is made during this period, no penalty fee is incurred. However, interest does not cease to grow, and the grace period is aimed only at sparing borrowers from immediate consequences.
Payday Loans
Grace Period: Varies (may offer extensions)
Details: Some payday lenders allow the borrower to roll over the loan or give extra time to pay it. However, such extensions always attract other costs in addition to having a relatively high interest rate. Payday loans are often short-term, and if the amount borrowed is not repaid at the agreed-upon time, then the lender will roll it over, but this will be at a higher interest rate.
Situations Where Your Credit Card Grace Period Pays You Off!
| Situations | Example | How the Grace Period Works |
Buying Smart for Large Purchases | If you buy a $1200 laptop during the start of the billing bicycle, you have a 25-day grace period to pay off your bill. | The grace period here helps you pay off your laptop bill in 2 months so that you can avoid interest and allow extra time to gather funds. |
Managing a Tight Month | The bills for the month are higher than expected, and you need to wait until the next month’s paycheck. | The 25-day grace period allows you to cover immediate needs now and pay next month, avoiding interest and maintaining flexibility for urgent expenses. |
Covering Emergency Expenses | Your car was hit by an accident, and you need an emergency fund of $700 for replacement purposes. | The grace period lets you cover the repair now and pay off the balance by the due date, avoiding stress and interest on an unexpected expense. |
Maximizing Cash Flow | You booked a $1000 vacation during the billing cycle, and then you have 25 days of grace period. | This allows you to pay off the vacation cost after you return, giving you nearly two months to enjoy your trip and budget without immediate out-of-pocket costs. |
The Bottom Line
It is important to be aware of how grace periods and credit card rewards are useful so that you can take advantage of some key benefits. Paying your balance in full within that grace period means that you can avoid interest charges while getting reward points for charges.
This strategy not only adds more value to the rewards you offer but also plays an important role in improving your creditworthiness.
The golden rule when using the card is to avoid hasty payments and take full advantage of the grace period to understand your debts on the credit card.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if you don’t pay your entire balance?
If you are unable to make the whole payment by the due date, you must make at least the minimum payment—or more, if possible. If you lose the grace period, you have to pay interest, but you won’t pay a late fee.
How long is the grace period for your credit card?
The grace period for a credit card typically lasts from 21 days to 25 days. You can ask for your grace period by checking your cardholder agreement. The grace period duration comes with the fee and annual percentage rate (APR). Apart from checking your agreement, you can also call your lender’s helpline and ask about the grace period directly.
Does a grace period work with credit card cash advances?
The credit card grace period is only applicable with purchases. Cash advances do not qualify for the grace period. Cash advances can incur with the interest immediately when in use.
Which credit card does have a grace period?
Whether it is the major credit card issuer or the smaller one, it gives you a grace period at the time of paying your statement balance in full by the due date. This is mandatory to provide a grace period to the cardholder.
-
How to Record A Donation in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
This guide helps nonprofit organizations efficiently record and track donations in QuickBooks, ensuring accurate financial management and compliance. It covers cash, in-kind, and product/service donations,…
-
How to Record k-1 Income in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Accurately recording K-1 income, which represents a share of profits or losses from pass-through entities like partnerships or S-Corporations, is essential for maintaining financial compliance…
-
How to Record A Chargeback in QuickBooks Desktop/Online?
This article provides a clear guide on how to record chargebacks in QuickBooks, which are crucial for managing disputes, fraud, or errors in transactions. By…
-
How to Record an ACH Payment in QuickBooks Desktop/Online – Learn the Process
Recording Automated Clearing House, or ACH, payments accurately in QuickBooks Desktop and Online is crucial for maintaining clean financial records and optimizing cash flow. The…
-
How to Record S-Corp Distribution in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
To properly manage S-Corp distributions in QuickBooks, you must create and track specialized accounts for equity, shareholder distributions, and retained earnings. Accurate setup ensures tax…
-
How to Record Expenses in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Accurate recording and strategic management of business expenses are fundamental to maintaining precise accounts, maximizing tax deductions, and ensuring healthy cash flow. This detailed resource…
-
How To Record A Loan in QuickBooks Online and Desktop – Learn the Process
Accurate tracking of business debt and lending activity is mandatory for sound financial management. This resource provides expert, step-by-step guidance on how to establish and…
-
How to Record Depreciation in QuickBooks Online/Desktop – Learn the Process
Recording asset depreciation in QuickBooks is vital for accurate financial reporting and tax compliance, as it allocates the cost of a fixed asset over its…
-
How Do You Record Credit Card Payments in QuickBooks Online/Desktop – Learn the Process
The provided content is highly accurate and aligned with the latest QuickBooks and accounting best practices. The validation confirms the core workflows for both QuickBooks…
-
How to Record Credit Card Processing Fees in QuickBooks Online and Desktop?
Accurate recording of credit card processing fees is a mandatory accounting task for any business utilizing QuickBooks Online or QuickBooks Desktop, ensuring financial reports are…
-
How to Record Deposits in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Accurate deposit recording in QuickBooks Desktop and Online is centered on correctly handling the flow of funds from a Payment to a Deposit, utilizing the…
-
How To Record A Refund in QuickBooks Online and Desktop – Learn the Process
Accurately recording customer and vendor refunds in QuickBooks Desktop and Online relies on choosing the correct transaction type and ensuring proper account linking to maintain…
-
How to Record Things in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
QuickBooks provides comprehensive solutions for managing financial transactions, including refunds, deposits, credit card payments, and sales tax payments. It helps businesses track various processes such…
-
Peachtree to QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
eBetterBooks offers a seamless migration service from Peachtree to QuickBooks Online, ensuring accurate and hassle-free data transfer. With expert guidance, your financial data is safely…
-
Wave to QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Transition from Wave to QuickBooks Online seamlessly with expert-guided data conversion services, ensuring accurate and efficient migration of financial data. QuickBooks Online offers advanced features…
-
Migrate from Sage 50 to QuickBooks Online
Seamlessly migrate from Sage 50 to QuickBooks Online with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. Experience hassle-free, secure, and accurate data migration, ensuring minimal disruption to…
-
How to add Bank Accounts to QuickBooks?
Connecting your bank or credit card account to QuickBooks streamlines your financial management by automating transaction downloads, reducing manual data entry, and providing real-time insights.…
-
Learn How to Add an Accountant to QuickBooks
Connecting an accountant to QuickBooks is a critical step for small business owners seeking expert financial management, allowing the accountant to view, correct, and prepare…
-
Effortlessly migrate your business data from Microsoft Dynamics NAV (Navision) to QuickBooks with eBetterBooks. Our expert conversion service ensures smooth, accurate data transfer—preserving critical records…
-
Sage MAS 200 to QuickBooks Desktop
Migrating from Sage MAS 200 to QuickBooks offers businesses a more user-friendly, scalable, and cost-effective solution for managing finances. This transition simplifies financial management with…
-
Great Plains to QuickBooks Data Conversion
Effortlessly transition from Microsoft Dynamics Great Plains to QuickBooks with eBetterBooks. This service addresses the complexities of financial data migration, offering a seamless, accurate, and…
-
Sage 200 to QuickBooks Data Conversion – An Ultimate Guide
Easily transition from Sage 200 to QuickBooks with eBetterBooks’ seamless data conversion services. Unlock advanced features like enhanced reporting, robust inventory management, and third-party app…
-
How to Import Accountant’s Changes in QuickBooks? – DIY Solutions
This guide helps QuickBooks users import their accountant’s changes to ensure accurate and organized financial records. It explains how to use QuickBooks’ Import Accountant’s Changes…
-
How to Delete QuickBooks Desktop & Online Account? – Step by Step Process
This guide provides clear, step-by-step instructions for deleting your QuickBooks account, whether using QuickBooks Desktop or QuickBooks Online. It helps users safely remove accounts, ensuring…
-
Convert Sage 300 Construction to QuickBooks
Easily migrate from Sage 300 Construction to QuickBooks with our expert data conversion services. We ensure accurate and seamless transfer of your financial data, including…
-
Convert Oracle to QuickBooks
This article addresses businesses seeking a smooth transition from Oracle to QuickBooks, highlighting a comprehensive and efficient data conversion process. It ensures accurate migration of…
-
QuickBooks Data Conversion: Migrate From Omega to QuickBooks Desktop
Switch from Omega to QuickBooks Pro, Premier, or Enterprise with eBetterBooks for seamless data migration. This service helps automate processes, streamline invoicing, manage inventory, track…
-
Convert from Adagio to QuickBooks
If you’re looking to move from Adagio to QuickBooks, this guide will help streamline the transition. QuickBooks offers advanced features, integrations, and enhanced reporting capabilities,…
-
How to Move from AccountEdge to QuickBooks?
Switching from AccountEdge to QuickBooks offers small to large businesses a more robust solution for advanced reporting, integrations, and improved security. This transition ensures seamless…
-
Convert from Microsoft Access to QuickBooks
Transition seamlessly from Microsoft Access to QuickBooks with eBetterBooks’ data conversion services. Solve performance and scalability limitations of Microsoft Access by upgrading to QuickBooks’ advanced…
-
Convert Sage MAS 90 to QuickBooks
Transition effortlessly from Sage MAS 90 to QuickBooks to overcome limitations like complexity and high costs. QuickBooks offers advanced features, automation, and scalability tailored to…
-
Convert Cougar Mountain to QuickBooks
Transitioning from Cougar Mountain to QuickBooks simplifies accounting by integrating advanced tools like payroll, expense tracking, and invoicing into a user-friendly, scalable platform. Addressing limitations…
-
Sage MAS 500 to QuickBooks Data Conversion
Seamlessly migrate your financial data from Sage MAS 500 to QuickBooks with eBetterBooks. Our service ensures accurate, secure, and efficient data conversion, enhancing your business’s…
-
Switch from Epicor to QuickBooks
Switching from Epicor to QuickBooks simplifies financial management and streamlines business operations. QuickBooks offers a user-friendly interface, advanced reporting, and extensive third-party integrations, making it…
-
Move from DacEasy to QuickBooks
Transition seamlessly from DacEasy to QuickBooks to overcome DacEasy’s limitations like outdated features, limited reporting, and lack of mobility. QuickBooks offers advanced integration, industry-specific tools,…
-
Sage Intacct To QuickBooks Data Conversion Services
Sage Intacct to QuickBooks Data Conversion Get your existing financial data migrated stress free from Intacct to QuickBooks Pro, Premier or Enterprise with eBetterBooks. Migrate…
-
Sage HRMS to QuickBooks Conversion Services
If you’re looking to smoothly migrate from Sage HRMS to QuickBooks, this service ensures a fast and accurate conversion of your financial data, including chart…
-
Convert Wave to QuickBooks Desktop – Learn the process
Transition seamlessly from Wave to QuickBooks to overcome scalability limitations and streamline financial processes. QuickBooks offers advanced tools like invoicing, payroll, and reporting, catering to…
-
Complete Guide to Migrate From QuickBooks Online to Desktop
This article guides businesses on migrating from QuickBooks Online to QuickBooks Desktop, addressing limitations in customization, offline access, and scalability that many users face with…
-
Microsoft Excel to QuickBooks Data Conversion
Effortlessly transition from Excel to QuickBooks with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. Solve the challenge of manual financial management by adopting QuickBooks’ advanced tools, automated…
-
Learn How To Switch from XERO to QuickBooks – A User Guide
Switch from Xero to QuickBooks to unlock advanced accounting features and seamless financial management tailored to your business needs. This process solves the challenges of…
-
How to Convert Data From MYOB to QuickBooks?
Converting from MYOB to QuickBooks simplifies your accounting with better invoicing, payroll, and inventory management features. QuickBooks offers advanced automation, seamless third-party integrations, and customizable…
-
Convert QuickBooks Premier To Enterprise (Desktop)
eBetterBooks offers seamless migration from QuickBooks Premier to QuickBooks Enterprise, ensuring your business data is converted efficiently with minimal disruption. Gain access to enhanced features…
-
Convert QuickBooks Pro to Enterprise (Desktop) – Complete Process
Switch from QuickBooks Pro to QuickBooks Enterprise for advanced financial management with industry-specific solutions. Get enhanced inventory control, customizable reporting, and scalable options to meet…
-
Migrate from Sage 100 Contractor to QuickBooks Desktop
Seamlessly migrate from Sage 100 Contractor to QuickBooks with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. Ensure accurate, hassle-free transitions of customer, vendor, and financial data while…
-
Upgrading QuickBooks Desktop in a Few Simple Steps
Upgrading to the latest version of QuickBooks ensures your business stays productive and secure with enhanced features like customized payment receipts, real-time invoice tracking, and…
-
Migrate from SageCRM to QuickBooks Desktop
Switching from Sage CRM to QuickBooks improves your business’s financial management by offering an intuitive interface and comprehensive accounting tools. QuickBooks supports small to medium-sized…
-
Sage CRM to QuickBooks Data Conversion
Switch from SageCRM to QuickBooks effortlessly with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. We ensure seamless migration of key business data, including customer lists, transactions, and…
-
How to Fix Issues When Converting from QuickBooks Desktop to Online?
Migrating financial data from QuickBooks Desktop (QBDT) to QuickBooks Online (QBO) often encounters critical technical barriers related to data volume, file accessibility, and platform differences.…
-
Switch Sage 100 to QuickBooks Desktop/Online – User Guide
Switching from Sage 100 to QuickBooks offers businesses a more user-friendly, scalable accounting solution. QuickBooks enhances efficiency with its intuitive design, seamless integrations, and various…
-
Switch from Sage300 ERP to QuickBooks Desktop or Online
Migrating from Sage300 ERP to QuickBooks Desktop simplifies your accounting, offering improved productivity, ease of use, and advanced features. QuickBooks provides an intuitive interface, robust…
-
Sage300 ERP to QuickBooks Data Conversion Services
eBetterBooks offers seamless and cost-effective Sage300 ERP to QuickBooks data conversion services, ensuring accurate migration of essential data like customer lists, transactions, payroll, and more.…
-
Switch from NetSuite to QuickBooks Desktop or Online
Migrating from NetSuite to QuickBooks can streamline your business’s accounting by improving customization, integration, and usability. This process involves evaluating your specific needs, converting and…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2011 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
This page provides the necessary downloads for QuickBooks Desktop 2011 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) for both Windows and Mac. It offers clear instructions for downloading…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2012 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
This page provides easy access to download QuickBooks Desktop 2012 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise, Mac) for both Windows and Mac. It offers step-by-step instructions on…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2014 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
This page provides users with direct access to download QuickBooks Desktop 2014 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) for both Windows and Mac. It offers clear, country-specific…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2015 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
Reinstalling the discontinued QuickBooks Desktop 2015 version carries significant risks, primarily data security and compliance exposure, as the software no longer receives security updates or…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2016 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
Accessing the discontinued QuickBooks Desktop 2016 software involves significant challenges, primarily due to high security risks associated with using unsupported software and downloading installers from…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2017 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
This article helps users download QuickBooks Desktop 2017 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) for both Windows and Mac. It addresses the need for obtaining the correct…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2018 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
This article guides users through the process of downloading QuickBooks Desktop 2018 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) for both Windows and Mac. It addresses the issue…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2019 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
This article provides step-by-step instructions to download QuickBooks Desktop 2019 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) for both Windows and Mac. It helps users easily access and…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2020 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
QuickBooks Desktop 2020 offers tailored solutions for businesses of all sizes, providing seamless accounting management. Whether you need Pro, Premier, Accountant, or Enterprise editions, it…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2021 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
QuickBooks Desktop 2021 provides efficient solutions for managing accounting tasks, available in Pro, Premier, Accountant, and Enterprise editions. With optimized features for both Windows and…
-
Download QuickBooks Desktop 2022 (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) – Windows & Mac
QuickBooks Desktop 2022 streamlines accounting tasks with enhanced automation and faster bill payments. It offers various editions (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise) for different business needs…
-
QuickBooks Desktop 2023 : Download (Pro, Premier, Accountant, Enterprise)
QuickBooks Desktop 2023 offers users an efficient way to manage their business finances, providing tools for inventory tracking, mileage monitoring, and easy cash flow visibility.…
-
QuickBooks Desktop Enterprise 2024 Download (Silver, Gold, Platinum | 1 Year Subscription | Up-to 5 Users)
QuickBooks Desktop Enterprise 2024 is a 64-bit software suite requiring robust hardware, including a minimum of 8 GB RAM for client workstations and up to…
-
QuickBooks Desktop Accountant 2024 (Download, Up-to 5 Users)
QuickBooks Desktop Accountant 2024 simplifies accounting tasks for accountants and bookkeepers with enhanced collaboration tools, secure data management, and efficient client workflows. It allows managing…
-
QuickBooks Desktop Premier 2024 (Download, Up-to 5 Users)
QuickBooks Desktop Premier 2024 introduces essential upgrades focused on security, compliance, and multi-user performance for business accounting professionals. The software features robust data protection via…
-
How to Fix Unable To Create Accountant’s Copy In QuickBooks Desktop Error
If you’re unable to create an Accountant’s Copy in QuickBooks, this guide helps resolve the issue efficiently. Common causes include outdated software, large file sizes,…
-
How to Fix “QuickBooks User Already Logged In Error”?
If you’re encountering the “QuickBooks User Already Logged In” error, it typically arises from issues like improper session termination, network conflicts, or corrupted company files.…
-
Troubleshooting QuickBooks Unable to Commit File Write Operation to Disk
The article addresses the issue of QuickBooks failing to write file operations to disk, commonly caused by corrupted company files, incorrect backup paths, or update-related…
-
How To Resolve QuickBooks TLS 1.2 Internet Security Levels Error?
This article details the necessary troubleshooting for the QuickBooks TLS 1.2 Internet Security Levels error, which prevents secure communication for vital connected services like payroll…
-
Fix QuickBooks Error: The Attempt to Log in With The Username Failed Issue
The QuickBooks Desktop login error, often manifesting as “User ID Admin is already logged in,” is a critical interruption frequently caused by phantom user sessions,…
-
Resolving The QuickBooks Startup Issues After Windows 11 Update
QuickBooks Desktop may fail to launch or experience errors following a major operating system update, like the transition to Windows 11, due to file corruption,…
-
How to Fix QuickBooks Server Busy Error (This Action Cannot be Completed)?
Experiencing the QuickBooks Server Busy Error? This issue typically arises when excessive background processes or resource limitations interfere with QuickBooks’ ability to connect to the…
-
How to Resolve QuickBooks Search Not Working Issue in Desktop?
If your QuickBooks Desktop search function is not working, it could be due to outdated software, corrupted files, or interference from other programs. This issue…
-
Fix QuickBooks Online Running So Slow?- Performance Issue
To fix QuickBooks Online’s slow performance, run internet speed test to ensure a fast internet, clear the browser cache and cookies, disable browser extensions, reload…
-
How to Fix QuickBooks is Not Showing Mapped Drives Issue?
If you’re unable to view mapped drives in QuickBooks, it may be due to network discovery issues, improper drive mapping, or DNS/IP configuration errors. This…
-
How to Fix QuickBooks Has Stopped Working or Not Responding Error?
The “QuickBooks Has Stopped Working or Not Responding” error commonly arises from software environment issues, including corrupted program files, conflicts with third-party applications, or damaged…
-
How to Resolve QuickBooks Error 80029c4a Can’t Load Dynamic Link Library?
QuickBooks Error Code 80029c4a typically arises when DLL files are corrupted or missing, preventing the software from opening or causing system crashes. This issue can…
-
Fix QuickBooks Web Connector Error QBWC1085?
If you’re facing QuickBooks error QBWC1085, it’s likely caused by a corrupt or inaccessible QWCLOG.TXT file, preventing the Web Connector from functioning. This article provides…
-
How to Fix QuickBooks has Stopped Working or not Responding Error?
The “QuickBooks has stopped working” or “Not Responding” error is a common software malfunction often caused by factors such as a corrupt QBWUSER.INI file, damaged…
-
How to Resolve QuickBooks Event ID Log Error 4?
The QuickBooks Event ID 4 error, often caused by a corrupted .NET Framework, damaged company files, or conflicts with third-party software, disrupts QuickBooks operations, potentially…
-
How to Fix QuickBooks Error C=51 When Attempting to Delete a Transaction List?
QuickBooks Error Code C=51 occurs when users can’t find the TxList, often due to damaged company files, corrupted databases, or lost transactions. This article provides…
-
How to Resolve QuickBooks Error 1014 (OL and OLSU Bank Feeds Error)?
QuickBooks Error 1014 arises due to cache issues, causing delayed software response, company file hangs in multi-user mode, or system freezes. This disrupts workflow and…
-
A Comprehensive Guide for Dealing With QBDBMgrN Stopped Error
The QBDBMgrN not running error is a critical service failure in the QuickBooks Database Server Manager that prevents concurrent multi-user access to company files. This…
-
How To Fix “QuickBooks Desktop Freezing Up Error” Problem?
Fixing the QuickBooks Desktop Freezing Up Error requires a multi-faceted approach, as the issue can stem from corrupted configuration files, system resource depletion, or installation…
-
How to Fix QuickBooks Desktop Display Issues in Windows 11, 10, 8 or 7?
If you’re experiencing QuickBooks Desktop display issues, such as fuzzy fonts, black screens, or strange sizing, it could be due to high-resolution DPI settings, incompatible…
-
How to Fix QuickBooks Compatibility Issue with Windows 10?
If you’re facing compatibility issues between QuickBooks and Windows 10, it could be due to mismatched software versions. This article provides a clear guide to…
-
QuickBooks Cannot Complete The Current Action Due To A Missing PDF Component – Resolved
The QuickBooks Missing PDF Component Error is a system malfunction that prevents QuickBooks Desktop from generating, printing, or emailing PDF documents. This issue arises when…
-
How to Fix QBDBMgrN Not Running on this Computer Server Problem?
The article addresses the “QBDBMgrN Not Running on This Computer” error in QuickBooks, caused by firewall settings or installation issues blocking the QuickBooks Database Server…
-
How to Fix QBCFMonitorService Not Running On This Computer? – (Not Starting or Crashing)
If you’re facing the “QBCFMonitorService not running” error in QuickBooks, this article offers essential troubleshooting steps to resolve the issue. The problem, often caused by…
-
Resolve Intuit Data Protect Not Working Issue in QuickBooks
Resolving Intuit Data Protect (IDP) backup failures is crucial for maintaining QuickBooks data security against corruption or loss. The “IDP Not Working” error, often signaled…
-
Most Common QuickBooks Crashing or Not Responding Errors/Problems
This guide helps QuickBooks users troubleshoot and resolve common errors, ranging from login issues and data handling problems to performance lags and system incompatibilities. By…
-
How to Resolve QuickBooks Online Sync Errors Messages? -Authentication Error
QuickBooks Online sync errors can disrupt business operations, often caused by issues like incorrect sync settings, client mismatches, or invoicing problems. This guide offers practical…
-
How to Fix QuickBooks Online Advance Search is Not Working?
If the QuickBooks Online search function stops working, it can disrupt your business operations. Common causes include outdated software, corrupted search index files, browser issues,…
-
How to Resolve QuickBooks Online Payroll Not Working Error?
The “QuickBooks Online Payroll Not Working” error typically occurs due to connectivity issues, outdated tax tables, incorrect system time, or multi-user mode conflicts. To resolve…
-
How To Fix QuickBooks Online Login Problems On Google Chrome?
If you’re encountering login issues with QuickBooks Online on Google Chrome, this article provides effective solutions. Common causes include firewall settings, incorrect sign-outs, outdated cache,…
-
Become An Expert With QuickBooks Training & Certification
QuickBooks training equips you with the essential skills to manage your business finances, even without prior accounting knowledge. By learning how to use QuickBooks’ features…
-
Fix QuickBooks Unable to Connect to Remote Server Issue
Facing the QuickBooks Unable to Connect to Remote Server issue? This guide helps you identify the causes and resolve them effectively. Whether it’s adjusting firewall…
