A credit card grace period is the days between the billing date and the due date. During this period, no interest is charged on purchases if you pay your balance in full.
The grace period is typically given to newly purchased products rather than to services such as cash advances and transfers. For any of these purchases, interest will be charged from the date of occurrence unless they qualify for a particular 0 percent APR tease.
What is a Credit Card Grace Period?
The Credit Card Grace Card refers to the period between the issuance of a credit card statement and the due date, during which the consumer bears no interest for any purchase made on the card.
The grace period is the time that elapses between the time a consumer makes purchases through his/her credit card in the previous billing cycle and the time he/she is required to pay interest on the outstanding balance made during the current billing cycle.
It is only applicable if the consumer cleared his or her last credit card balance in full and timely and did not roll over a balance for any part of the preceding billing cycle.
Note: It is advisable to read the terms and conditions of your credit card and find out if it has a grace period.
How Long is a Typical Grace Period for a Credit Card?
A grace period normally ranges from 21 days to 55 days. Remember that having a credit card grace period does not mean that you have more time until the due date.
When you make partial payments, fail to make the necessary minimum payment on your credit card, or pay your bill after the due date, your credit card company will start charging interest on your balance.
In addition, you will incur late penalties if you fail to make a payment or make it after the due date.
To prevent interest payments, you must pay off your credit card balance in full before the payment due date. At the absolute least, you must make the minimum payment, and you will then be charged interest on any balance carried over to the next month.
| Tip: To maintain your grace period, make sure to pay your bills in full and on time each month. If you pay in full for some months but not others, you may lose your grace period for the month in which you do not pay in full and the following month. |
If you pay off your credit card amount every month during this grace period, you will avoid incurring interest on your purchases. However, the grace period usually only applies to new purchases, not cash advances, balance transfers, or special promotional deals.
Example of Credit Card Grace Period
| Let’s understand this with an example: If your billing cycle ends on May 31, your credit card statement detailing the amount due is issued on the same day. Assuming a 30-day grace period, your payment due date would be June 30. By paying the full balance within this timeframe, you can avoid any interest charges. |
How Long is the Grace Period On Credit Card?
Credit card lenders or companies must send cardholders their bills at least 21-25 days before payment is due. Sometimes, some credit cards consider those 21 days, as well as the time between when you made your purchases inside the billing cycle, to be a grace period if you have paid your previous balance in full. This means grace periods might last nearly two months.
How Does the Credit Card Grace Period Work?
To fully enjoy a grace period, you must understand the credit card’s billing cycle, the expense of carrying a debt, and how the lender charges interest on your purchases.
These key concepts assist in clarifying how grace periods work:
- Billing Cycle
Your credit card company establishes a billing cycle, which is typically one month long. Finally, your purchases are totaled and presented in a statement.
- Statement Generation
Your credit card provider generates a statement of your purchases at the end of each billing cycle that summarises the transactions completed during that time.
- Grace Period
The grace period begins on the day your statement is generated and normally lasts 21-25 days, depending on the credit card provider.
- Interest Fee
If you pay off your credit card amount in full by the due date during the grace period, you will not be charged interest on your transactions.
- Interest on Unpaid Balances
If you fail to pay the entire balance by the due date, the remaining balance will start to accrue inte
How Can Credit Card Grace Periods Save you Money?

If you are keen on maintaining your credit card balance, it is very important to make the most out of the grace period. If done with some thought, one can manage their cash flow and make the right usage of the credit card.
Here’s how to get the most out of your grace period:
1. Pay Your Full Balance On Time
The simplest way to avoid interest charges is to always make full payments for the amount charged on your statement by the due date. If you are unable to contribute the total amount, ensure that you contribute at least the minimum.
The balance will then attract an interest rate, as will any other purchase made after this. If you transfer lesser balances, then the interest you will be charged will also be reduced.
Example:
If your statement balance is $500 and your due date is the 25th of the month, by the due date, you must pay $500. Thus, you avoid interest charges that could come along the way if you have a line of credit.
However, if you pay only $250, interest will be charged on that amount and all purchases made after the date of the statement.
2. Buy at the Right Time to Gain Most Benefits
To maximize your grace period further, make your purchases at the start of a billing cycle. However, if you want to take much more time, you will have a full cycle with interest and a grace period.
For bigger purchases, this strategy could allow you to go up to two months without accruing interest.
Example:
Your account’s billing cycle ends on the 10th of the following month. If you purchase $200 and have the records that it reflects in your statement, the purchase attracts an interest-free period of 25 days from the 5th to the 30th.
For example, if you make the same $200 purchase on the 20th, those will count in your next cycle, and you get a full month + the interest grace period.
3. Set a Budget
Having a budget will allow you to control your purse strings well, enabling you to manage your credit card balance correctly. It is best to think of your credit card as an interest-free loan.
If the grace period is understood correctly, complete payment should be made on the statement balance before the grace period expires.
Example:
Let’s assume that you have $500 that you can spend as you please in a month. Thus, tracking your expenses allows you to use your credit card only for purchases within this limit and make a payment in full before the due date.
For instance, when you buy groceries worth $100 using your credit card, and you buy 200 worth of gas, you will be charged $300 in a statement, which can be paid by the due date to minimize interest charges.
4. Avoid Carrying a Balance
The key to making good use of the grace period is paying your bill in full every month. Even if you continue into the next month with a balance remaining, you may lose your grace period, and thus, interest will be added to any new purchases.
That only happens when you pay off your balance, which lets you retain the grace period you negotiated on your credit card.
Example:
Let’s say your statement balance is $300, but you manage to pay $100; the remaining balance is $200, which will be carried over to the next month. This balance will start incurring interest, and you will lose your grace period for new purchases.
On the other hand, paying up to $300 in full means that in the next cycle, you will not incur any additional interest on the balance or new products.
5. Effectively Manage your Credit Card for Expected Expenses
If you cannot control your urge to spend, it would be ideal to only use your credit card in situations where you already know you can pay up before the due date.
By sticking to the planned amount for each category, you will maximize your payments, ensuring they clear their balance, and you will not be charged any interest.
Example:
For instance, you might be considering a $400 plane ticket at the beginning of the month and are aware that you can afford to pay for it on the due date.
This enables its holder to charge any item that he or she wants on the credit card and make the full and timely repayment before the due date, hence avoiding any interest.
However, if you use the card to make random purchases, as you do not need to, your chances of repaying it in full may be strained.
6. Set Up Automatic Payments
To avoid being devoid of a grace period, it is prudent to make arrangements for auto payments of your statement balance.
This ensures that you pay your outstanding amount in full every month, even if you forget or are occupied.
Example:
If you know your statement balance is $400 and your due date is the 25th, automatic payment means that your card issuer will pay the stated balance before the due date.
This prevents you from forgetting to make a payment, so there is no need to incur extra interest charges.
How Can Grace Periods Maximize Your Credit Card Rewards?
The grace period comes between 21 to 25 days from the last date of your billing cycle and allows you to clear your balance before it starts to attract interest charges.
Here’s how you can use this feature to your advantage:
- Don’t Charge and Optimize Profit
Paying off your balance in full if you have the cash during the grace period helps prevent interest charges from devaluing your rewards.
For example, utilizing an incentive card like the Chase Sapphire Preferred® Card, which pays 3X points on Dining and 2X Points on Travel, earns you valuable points while keeping your spending interest-free if you pay off the balance before the due date.
- Time Big Purchases Wisely
Whenever you are planning a big purchase, try to time it until the billing cycle commences. This gives you the maximum time to pay it off within the grace period. This basically assists in giving the maximum time within the grace period to pay off what has been borrowed.
More easily, using credit cards like the Citi® Double Cash Card, which offers 2% cash back, 1% when you buy, and 1% when you pay, could double the rewards when using this strategy.
- Link Grace Periods with introductory APR Offers
Some cards, like the Wells Fargo Active Cash® Card, have no annual fees and include 0% APR introductory periods.
You also get 2% back on every purchase. By following the grace period curve to ensure the introductory APR has ended, you can always reap from those points without being charged interest.
- Optimize Category Rewards
Cards with bonus categories that change each quarter, such as the Discover it® Cash Back, enable their holders to charge up to 5% on certain items, such as groceries, gas, or even dining.
No value erodes for these rewards through interest charges when your balance is paid fully within the grace period.
- Redeem Points From Daily Purchases
Merchant purchases, such as food and electricity bills, can also contribute to the accrual of rewards, and charges apply if they settle before the grace period.
The Blue Cash Preferred® Card offers an enrollment bonus of $150 once you spend $1,000 in the first three months of opening the account. It also offers the following rewards: 6% cash back on up to $6,000 per year at US supermarkets.
This way, it becomes possible to protect all those bonuses, remain profitable, and pay the balance on time.
Who is Eligible for Credit Card Grace Periods?
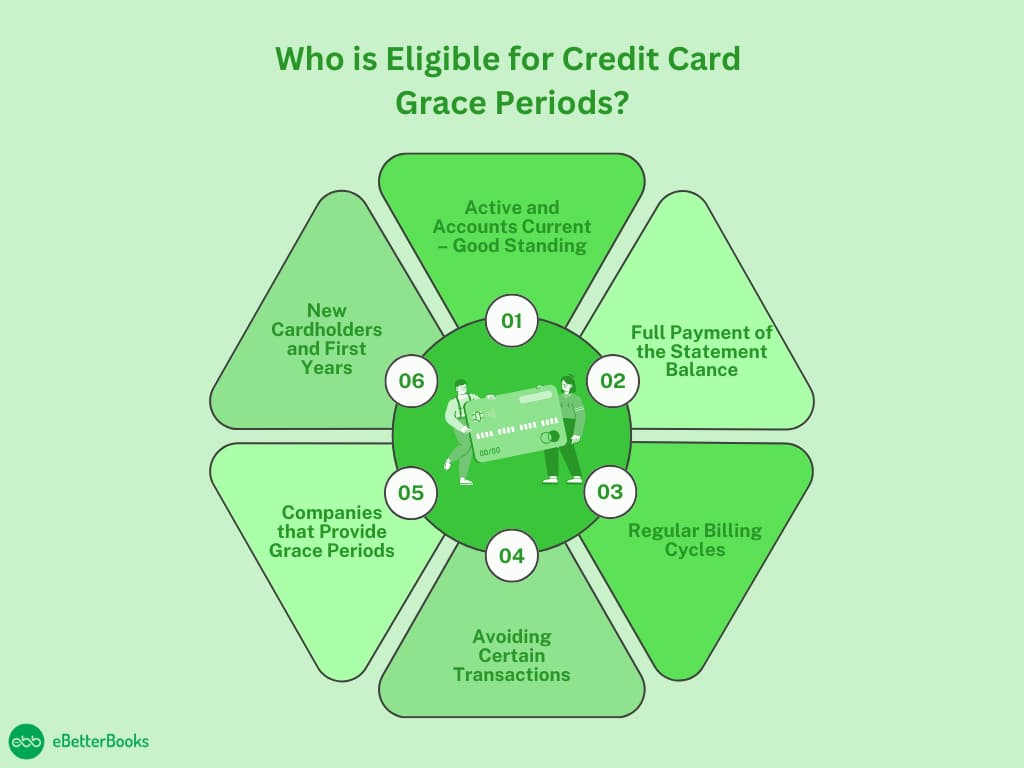
A credit card grace period is one of the privileges that enable users to make purchases without accruing interest on the purchases so long as they pay the amounts owed before the due date. However, only some people are entitled to this kind of benefit right away. Not all cards are issued with a grace period, and here are factors that will determine if you are a beneficiary or not:
1. Active and Accounts Current – Good Standing
The first qualification for eligibility is that the credit card account you are qualifying must be open and not in default. As a result, you have to maintain an active, unblocked credit card with no overdue payments or complications, including chargebacks or defaults.
In this case, if your card is suspended or closed, for instance, due to non-payment or other issues, you are eliminated from accessing the grace period. It is also very important that you don’t go overboard with spending over your credit limit.
2. Full Payment of the Statement Balance
To be eligible for the grace period, you need to make your minimum statement balance payment by the stated date. The grace period only kicks in if you start a billing cycle with a $0 balance on your account.
If you leave any balance unpaid, you forfeit your grace period right, and interest begins to be charged on new purchases as soon as they are made. The consequence of paying only the minimum amount or of keeping a balance over the month will be interest charges.
3. Regular Billing Cycles
Most credit card companies go for monthly statements, and where your specific card operates within these regular cycles, you are allowed the grace period.
An ideal billing cycle is between 28 and 31 days, and from the close of the cycle, you are afforded some grace period between 21 and 25 days, within which you should pay your bill before incurring interest.
This is a supremacy of most credit card companies mandated by federal statute, though it is only valid when one does not carry over a balance from the previous cycle.
4. Avoiding Certain Transactions
It’s important to remember that grace periods do not include balance transfers, cash advances, or any other special occasions. Many of these transactions begin charging interest immediately while you are still in the grace period on new cash advances.
If you transfer a balance or get a cash advance, interest will be charged from the date of the transaction or the date the card was issued. Any grace period you may have for new purchases will not apply to this.
5. Companies that Provide Grace Periods
It is important to note that some credit cards do not allow a grace period. This feature, however, is not universal: most major credit card issuers offer it; however, some specific types of cards, like high-risk or secure credit cards, do not.
So, it’s wise to go through the terms and conditions of any credit card that you wish to apply for some time and check to ascertain whether the Credit card offers a grace period.
If the card does not have this feature, interest starts to be charged on the purchase as soon as one is made.
6. New Cardholders and First Years
Most consumers are eligible for the grace period when they sign up for a new credit card, but they should review the disclosures of introductory periods. Certain card companies are likely to provide an initial 0% APR on purchases for a set amount of months, in which you would not be charged any interest.
Yet the rules change after the first month, and as with any other credit card, the standard grace period applies. During this period, one must make a complete payment of the balance to avoid interest.
Here are the types of transactions and the grace period eligibility criteria…
| Types of Transactions | Eligible for Grace Period | Notes |
| New Purchase | Yes | There is no interest if the full balance is paid on time. |
| Cash Advance | No | Interest starts immediately. |
| Balance Transfer | No | It often has its own interest rates. |
| Special Promotion | Card Specific | Check specific terms. |
What Can Cause You to Lose Your Grace Period?
There are several reasons you may lose eligibility for a grace period, including:
- Carrying a Balance: If you can’t clear the amount in full, the grace period is removed, and any new purchases will attract interest charges immediately.
- Late Payments: Failure to make the payment or paying an amount below the minimal required sum initiates the grace period and penalties, such as fees for lateness.
- Certain Transactions: It is important to note that balance transfers, cash advances, and similar operations do not usually qualify for this grace period, and they attract interest from the day the transfer is made.
The Impact of Grace Periods on Other Debt
Grace periods are useful for many types of debt because they imply that the debtor has a certain period during which he/she does not need to make payments.
These periods allow borrowers more time to make the payments without attracting penalties or having their credit rating affected. However, they may be different, as they depend on the kind of debt one has and the policies of the credit company.
Student Loans
Grace Period: 6 months (for federal loans usually)
Details: Federal student loans allow, for example, a grace period of six months after graduation. Indeed, during this period, borrowers do not have to pay back any loans. This time provides an opportunity for graduates to get a job or make other preparations before starting to pay back the loans. Nevertheless, interest may continue to be charged on certain loans (such as unsubsidized federal loans).
Mortgages
Grace Period: 10-15 days
Details: Most mortgage creditors offer a brief period of forbearance, which ranges between 10 and 15 days after the due date. This means that if a mortgage payment is made during this period, no penalty charge is added. Nonetheless, the borrower should be cautious that even during the grace period, interest continues to build up, and payments in default after the grace period are deemed past due.
Auto Loans
Grace Period: 10-15 days
Details: Like mortgages, auto loans are normally accompanied by a brief grace period. Borrowers can be offered a grace period of 10 to 15 days before they are charged for late payment. Although this may help, it slows, and interest keeps piling up. Once the grace period is over, the loan is deemed past due.
Personal Loans
Grace Period: 15-30 days
Details: A personal loan may also include a grace period, usually 15 – 30 days, depending on the nature of the loan. If a payment is made during this period, no penalty fee is incurred. However, interest does not cease to grow, and the grace period is aimed only at sparing borrowers from immediate consequences.
Payday Loans
Grace Period: Varies (may offer extensions)
Details: Some payday lenders allow the borrower to roll over the loan or give extra time to pay it. However, such extensions always attract other costs in addition to having a relatively high interest rate. Payday loans are often short-term, and if the amount borrowed is not repaid at the agreed-upon time, then the lender will roll it over, but this will be at a higher interest rate.
Situations Where Your Credit Card Grace Period Pays You Off!
| Situations | Example | How the Grace Period Works |
Buying Smart for Large Purchases | If you buy a $1200 laptop during the start of the billing bicycle, you have a 25-day grace period to pay off your bill. | The grace period here helps you pay off your laptop bill in 2 months so that you can avoid interest and allow extra time to gather funds. |
Managing a Tight Month | The bills for the month are higher than expected, and you need to wait until the next month’s paycheck. | The 25-day grace period allows you to cover immediate needs now and pay next month, avoiding interest and maintaining flexibility for urgent expenses. |
Covering Emergency Expenses | Your car was hit by an accident, and you need an emergency fund of $700 for replacement purposes. | The grace period lets you cover the repair now and pay off the balance by the due date, avoiding stress and interest on an unexpected expense. |
Maximizing Cash Flow | You booked a $1000 vacation during the billing cycle, and then you have 25 days of grace period. | This allows you to pay off the vacation cost after you return, giving you nearly two months to enjoy your trip and budget without immediate out-of-pocket costs. |
The Bottom Line
It is important to be aware of how grace periods and credit card rewards are useful so that you can take advantage of some key benefits. Paying your balance in full within that grace period means that you can avoid interest charges while getting reward points for charges.
This strategy not only adds more value to the rewards you offer but also plays an important role in improving your creditworthiness.
The golden rule when using the card is to avoid hasty payments and take full advantage of the grace period to understand your debts on the credit card.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if you don’t pay your entire balance?
If you are unable to make the whole payment by the due date, you must make at least the minimum payment—or more, if possible. If you lose the grace period, you have to pay interest, but you won’t pay a late fee.
How long is the grace period for your credit card?
The grace period for a credit card typically lasts from 21 days to 25 days. You can ask for your grace period by checking your cardholder agreement. The grace period duration comes with the fee and annual percentage rate (APR). Apart from checking your agreement, you can also call your lender’s helpline and ask about the grace period directly.
Does a grace period work with credit card cash advances?
The credit card grace period is only applicable with purchases. Cash advances do not qualify for the grace period. Cash advances can incur with the interest immediately when in use.
Which credit card does have a grace period?
Whether it is the major credit card issuer or the smaller one, it gives you a grace period at the time of paying your statement balance in full by the due date. This is mandatory to provide a grace period to the cardholder.
-
Absorption Costing: Meaning, Components, Formula, and Limitations?
Absorption costing provides a comprehensive method for determining product costs by including both fixed and variable manufacturing expenses. This approach is crucial for businesses to…
-
Credit Card – Know Everything About Credit Cards!
Credit cards are products used by consumers to make purchases through credit meant to be paid later. They are easy to access, offer numerous bonuses…
-
Capital Lease: Definition, Example, Advantages & Disadvantages?
A capital lease allows businesses to use assets without upfront purchase costs, with the option to own the asset at the end of the lease…
-
Cash Advance – Definition, Types and How Does it Work?
A cash advance offers quick access to funds in emergencies, but comes with high fees and immediate interest charges. It’s ideal for urgent, short-term financial…
-
Overhead Cost: Meaning, Types, Formula, and Ways to Reduce?
Overhead costs are essential business expenses that are not directly tied to production but are crucial for daily operations. These costs, which include rent, salaries,…
-
Debt Collection Software: What It Is and Why Your Business Needs It?
Debt collection software is an essential tool for businesses seeking to streamline their debt recovery process, improve efficiency, and enhance financial control. It automates manual…
-
How to Write and Print Checks for Bills Already Entered in QuickBooks Desktop?
Mastering check writing and printing in QuickBooks Desktop requires understanding the two distinct payment workflows: Write Checks (for immediate, non-liability payments) and Enter Bills/Pay Bills…
-
How to Switch To Multi User Mode From Single-User Mode in QuickBooks?
Switching to Multi-User Mode in QuickBooks allows multiple users to access and update company files simultaneously, essential for businesses with multiple departments or users. The…
-
QuickBooks Payroll Subscription: Types, Activation, & Cancellation
Managing QuickBooks Desktop Payroll subscriptions involves understanding the distinct features of the Basic, Enhanced, and Assisted tiers, the specific activation procedures, and the financial consequences…
-
How to Link a Bank Account to QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Linking a bank account to QuickBooks Desktop or Online streamlines financial management by automating transaction downloads and eliminating manual data entry. This process significantly simplifies…
-
How to Change the Primary Admin User in QuickBooks Online?
If you need to transfer the primary admin role in QuickBooks Online, this guide outlines the steps to ensure the right person manages your company’s…
-
How to Setup QuickBooks Desktop – A Step-by-Step Guide
Setting up QuickBooks Desktop streamlines your financial management by guiding you through installation, activation, and customization. This step-by-step guide helps you create a new company…
-
How to Set up Vehicles and Mileage Tracking in QuickBooks Online?
This guide helps you efficiently set up and track vehicles and mileage in QuickBooks Online. It walks you through adding vehicles, enabling auto-tracking, managing trips,…
-
How to Rename .ND and .TLG Files in QuickBooks
Renaming corrupted .ND and .TLG files in QuickBooks can resolve network and data issues, especially when the company file fails to open or encounters errors.…
-
QuickBooks Time Review 2025 – Details, Pricing, & Features
QuickBooks Time is a cloud-based time tracking solution designed to streamline workforce management for businesses of varying sizes, automating payroll, invoicing, and job costing. It…
-
QuickBooks Online 2025 – Uses, Versions and More
QuickBooks Online is a cloud-based accounting software designed to streamline financial management for small businesses. It simplifies invoicing, expense tracking, and tax compliance with real-time…
-
Invoicing in QuickBooks – Make and Send Invoices, Process Payments, and More
QuickBooks Invoicing simplifies the billing process for small business owners by automating invoice creation, payment tracking, and reminders. It helps save time, reduce errors, and…
-
How to Reconcile Bank Accounts in QuickBooks?
This guide helps you reconcile your bank accounts in QuickBooks, ensuring your financial records match your bank statements. By identifying discrepancies, errors, or fraudulent activity,…
-
How to Export a Chart of Accounts in QuickBooks?
This overview details the essential procedures and financial rationale for exporting a Chart of Accounts (COA) from Intuit’s QuickBooks software, a crucial task for businesses…
-
Create and Send Invoices in QuickBooks: A Complete Guide
Managing invoices effectively in QuickBooks requires understanding the platform’s specific conversion methods and internal settings. The content provides critical clarity on the difference between creating…
-
What are Non Cash Expenses? Meaning Examples, and Importance?
Non-cash expenses, like depreciation, amortization, and stock-based compensation, impact a company’s financial statements without involving cash outflows. Understanding these charges is essential for accurate reporting,…
-
Borrowed Capital: Definition, Types and Example?
Borrowed capital refers to funds obtained through debt instruments like loans, bonds, and lines of credit, empowering businesses to finance growth, operations, or assets without…
-
Operating Cash Flow (OCF): Definition, Importance & Methods?
Operating Cash Flow (OCF) measures the cash a company generates from its core operations, providing insights into its ability to sustain and grow without external…
-
Cash vs Accrual Accounting: What’s the Difference?
Choosing between cash and accrual accounting depends on your business’s size and complexity. Cash accounting is simpler and works well for small businesses, tracking cash…
-
What is Amortization and Depreciation with an Example?
This article clarifies the differences between depreciation and amortization, two essential accounting methods for managing asset costs. Depreciation applies to tangible assets, while amortization applies…
-
Is Depreciation an Operating Expense?
This article helps businesses understand the role of depreciation in managing fixed assets. It explains when depreciation is categorized as an operating or non-operating expense,…
-
Debt Servicing: Meaning, Calculations and Ratio
This article explains the concept of debt servicing, detailing how individuals, businesses, and governments manage debt payments, including interest and principal. It explores key concepts…
-
What is Capital Gains – Tax, Example, Types and Calculation?
Capital gains refer to the profit earned from the sale of assets like stocks, bonds, or real estate. This article explains how capital gains are…
-
What Property Can Be Depreciated?
This article clarifies how businesses and individuals can depreciate property, helping them lower taxable income by spreading asset costs over time. It explains which assets…
-
Cash Basis Accounting – Definition, Example and Uses?
Cash basis accounting simplifies financial tracking by recording transactions only when cash is received or paid. Ideal for small businesses or service-based companies, it offers…
-
Petty Cash: Definition, Types, Process, and Recommendations
Petty cash management is essential for businesses to efficiently handle minor, everyday expenses like office supplies, lunches, and reimbursements. By setting up a structured petty…
-
Cost and Pricing: Relationship, Impact, Strategies, and Common Mistakes
Effective pricing requires a deep understanding of various costs, including fixed, variable, direct, indirect, and overhead expenses. Accurately factoring in these costs ensures businesses cover…
-
Debt Collection Cycle: Meaning, Collection Method, and Regulations?
Debt collection services help businesses recover overdue payments, offering solutions for customers facing financial challenges. By utilizing modern techniques and technology, debt collectors ensure effective…
-
Fixed Cost vs. Variable Cost – Difference, Relationship, and Importance?
Understanding the distinction between fixed and variable costs is key for managing business expenses effectively. Fixed costs, like rent and salaries, remain constant, while variable…
-
12 Types of Costs in Cost Accounting?
Cost accounting helps businesses track and manage both direct and indirect costs to optimize operations, enhance profitability, and control expenses. By distinguishing between cost types…
-
Process Costing: Definition, Formula, Format, Example, and Methods?
Process costing is a method used in industries with continuous production of similar products, such as chemicals, textiles, and food. It helps businesses allocate production…
-
Capital Expenditure (CapEx) Definition, Formula, and Examples?
This article explains Capital Expenditure (CapEx), the funds invested by a business to acquire, maintain, or improve long-term assets like property, machinery, and technology. It…
-
Depreciable Cost: Formula, Example, Merits and Demerit?
The Depreciable Cost method helps businesses determine the value of an asset that can be depreciated over its useful life, excluding its salvage value. By…
-
What Property Cannot Be Depreciated?
This article helps business owners identify which assets can and cannot be depreciated for tax purposes. It clarifies that property like land, personal items, inventory,…
-
Working Capital Management: Definition, Components & Types?
Working capital management is essential for businesses to efficiently manage cash flow, meet short-term obligations, and support long-term growth. By optimizing the use of current…
-
Inventory Valuation: Meaning, Importance, Types, and Challenges
Inventory valuation helps businesses determine the financial value of goods for sale or production, impacting profitability, cash flow, and tax liabilities. By selecting the right…
-
Salvage Value – Formula, Example, Merits and Demerit?
This article explains the concept of salvage value, which is essential for accurate depreciation calculations and asset disposal planning. By correctly estimating an asset’s salvage…
-
What is Bad Debt Expense: Formula and Preventive Measures?
Bad debt expense impacts businesses by reflecting the amount owed by customers that is unlikely to be recovered. It helps provide a realistic financial picture,…
-
Liquidity and Liquidity Ratios: Definition, Types & Example
Liquidity ratios are essential tools to assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations, helping investors, creditors, and analysts evaluate financial health. They provide…
-
Declining Balance Depreciation – Formula, Example, Merits and Demerit
The Declining Balance Depreciation Method helps businesses manage the depreciation of assets by applying a higher depreciation rate in the early years of an asset’s…
-
Depreciation: A Comprehensive Guide
This article explains depreciation and its role in allocating the cost of tangible assets over their useful life for tax and accounting purposes. It details…
-
Cost of Living: Meaning, Index, Influencing Factors, and Ways to Reduce?
The article explains the concept of the cost of living and its impact on lifestyle choices. It helps users understand how to evaluate living expenses…
-
What is Capital – Types, Uses and Examples of Capital?
The article addresses the concept of capital, its forms, and its crucial role in business growth and economic productivity. Capital, encompassing assets like cash, machinery,…
-
Cash Flow Statement: Definition, Uses & Examples?
A cash flow statement is crucial for businesses to track cash inflows and outflows, ensuring liquidity and financial stability. It helps businesses manage cash, forecast…
-
Why is Cash Management for Businesses Important?
Efficient cash management is essential for businesses to maintain liquidity, reduce borrowing costs, and support growth. It involves optimizing cash flow to ensure sufficient funds…
-
FIFO vs. LIFO: Inventory Valuation (Differences, Examples, Alternatives, and How to Calculate)
This article compares FIFO (First In, First Out) and LIFO (Last In, First Out) inventory valuation methods. FIFO prioritizes older inventory for sales, which can…
-
Cost of Sales: Definition, Importance & Examples
The Cost of Sales (COS) is a crucial metric for businesses, reflecting the direct expenses tied to producing goods or services. By understanding COS, businesses…
-
Bad Debt: Write-offs and Provision Method
This article addresses the issue of bad debt, which occurs when loans or credit extended to customers cannot be recovered, impacting a company’s profitability, cash…
-
Inventory Holding Cost: Meaning, Example and Ways to Reduce?
Inventory holding costs, including storage, insurance, depreciation, and opportunity costs, significantly impact a business’s profitability. Effectively managing these costs by optimizing inventory levels, improving demand…
-
How to Record Reimbursement in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
This article provides a step-by-step guide to effectively track and manage employee, owner, and client reimbursements in QuickBooks. By recording and reimbursing business expenses paid…
-
Standard Cost Accounting – Meaning, Purpose, and Variance
Standard costing helps businesses manage and control production costs by setting benchmarks for materials, labor, and overheads. It enables efficient budgeting, price setting, and performance…
-
What is it and What is its Importance Cost of Goods Sold?
The article explains the concept of Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), detailing its role in determining a business’s gross profit by calculating production-related expenses. It…
-
Cost Sheet: Meaning, Importance, Format, Components and Preparation?
A cost sheet helps businesses control expenses, fix selling prices, and make informed decisions. It breaks down various costs like direct material, labor, and overheads…
-
Cost Accounting: Meaning, Importance, Types and Methods
Cost accounting helps businesses control costs, improve efficiency, and optimize pricing strategies. By analyzing direct, indirect, fixed, and variable costs, it aids decision-making, budgeting, and…
-
Account Receivable: A Debt or an Asset?
This article explains accounts receivable (AR), which represents money owed to a business by customers. It details the AR process, from credit extension to payment…
-
What is Debt? Work, Types, and Examples
This article addresses how debt functions, types of debt, and strategies to manage it effectively. It explains consumer, secured, and unsecured debt, highlighting the differences…
-
How do I Record a Non Cash Donation in QuickBooks Online and Desktop?
Recording non-cash contributions in QuickBooks is crucial for nonprofit organizations to maintain compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and IRS regulations. This process requires…
-
How to Record PPP Loan Forgiveness in QuickBooks Desktop & Online?
Recording PPP loan forgiveness in QuickBooks is essential for small businesses to ensure compliance and accurate financial reporting. By properly documenting the loan forgiveness, businesses…
-
How to Record COGS in QuickBooks Desktop / Online?
This article explains the importance of accurately calculating and tracking the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for businesses. It helps companies assess profitability, optimize inventory…
-
How to Record Loan Payable in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Accurately recording loans in QuickBooks Desktop and Online requires specific setup and transaction splitting to comply with accounting standards and tax rules. The most critical…
-
How To Record A Grant In QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
This guide offers a step-by-step approach to effectively record and manage grants using QuickBooks, ensuring financial transparency and compliance. It covers essential practices for nonprofits…
-
How to Record Interest Income in QuickBooks Desktop/Online?
Efficiently recording interest income in QuickBooks ensures accurate financial records, compliance with tax regulations, and informed decision-making. By categorizing interest from various sources like bank…
-
How to Record a Rebate in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Rebates are a valuable financial incentive, offering partial refunds to customers after a purchase. This article explains how to accurately record rebates in QuickBooks, both…
-
How to Record Personal Money put into Business QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Recording personal money in QuickBooks ensures accurate financial tracking by properly categorizing owner contributions and investments. By setting up equity accounts and recording transactions like…
-
How to Record A Returned Wire Transfer in QuickBooks Desktop & Online?
This article addresses how businesses can efficiently handle and record returned wire transfers in QuickBooks, ensuring accurate financial tracking. It guides users through the step-by-step…
-
How to Record a Line of Credit in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Learn how to effectively manage your business’s line of credit using QuickBooks. This article guides you through setting up and recording a line of credit,…
-
How to Record a Negative Deposit in QuickBooks Online & Desktop?
If you’re dealing with negative deposits in QuickBooks due to refunds, reversals, or corrections, this guide shows you how to resolve the issue. Whether you’re…
-
How to Record a Partial Payment in QuickBooks Desktop/Online?
Recording partial payments in QuickBooks Desktop and Online is a vital practice for managing cash flow and maintaining accurate financial records. The guide provides specific,…
-
Refund and Returns Policy
Our return and refund policy ensures a smooth process within 30 days of purchase. Items must be unused, in original packaging, and accompanied by proof…
-
How to Record Advance Payment from Customers in QuickBooks Online & Desktop?
Recording customer prepayments in QuickBooks ensures accurate financial management by tracking advance payments as liabilities until services or goods are delivered. This process enhances cash…
-
How to Record A Promissory Note in QuickBooks Online and Desktop?
Recording a promissory note in QuickBooks ensures accurate tracking of loans and repayments. It helps businesses maintain correct financial records by properly managing both receivables…
-
How to Record 401k Employer Contributions in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Accurate recording of 401k employer matching contributions in QuickBooks Desktop and Online is essential for compliance, tax advantages, and financial reporting. The process requires establishing…
-
How to Record Bank Charges in QuickBooks Desktop & Online?
Recording bank charges accurately in QuickBooks Desktop and Online is crucial for precise financial reconciliation and tax preparation. The fundamental procedure involves creating a dedicated…
-
How to Record an Opening Balance in QuickBooks Online and Desktop?
This article guides you on how to accurately record and manage your opening balance in QuickBooks, ensuring your financial records match your actual bank or…
-
How to Record an Invoice in QuickBooks Desktop & Online?
Recording payments for invoices in QuickBooks ensures your financial records are accurate and up-to-date, preventing errors during bank reconciliation and report generation. Whether you’re dealing…
-
How to Record Vehicle Loan in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Recording vehicle loans in QuickBooks helps businesses manage liabilities and track vehicle-related expenses like interest. By setting up the right accounts, entering loan and interest…
-
How to Record a Security Deposit in QuickBooks Desktop or Online?
Managing security deposits in QuickBooks is a critical compliance task requiring the funds to be strictly classified as a Liability because they are legally owed…
-
How to Record Certificate of Deposit in QuickBooks Online & Desktop?
This article explains how to properly record a Certificate of Deposit (CD) in QuickBooks to ensure accurate financial records and cash-flow management. By following step-by-step…
-
How to Record Credit Card Cash Back Rewards in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Correctly recording credit card cash back rewards in QuickBooks is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and optimizing business savings. The standard accounting best practice…
-
How to Record a Stop Payment in QuickBooks Desktop & Online?
QuickBooks offers an essential “Stop Payment” feature, allowing businesses to cancel erroneous or fraudulent payments, preventing financial losses and maintaining accurate records. By properly recording…
-
How to Record Insurance Claim Payment in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?
Recording insurance claim payments in QuickBooks ensures accurate financial records, streamlines transaction tracking, and improves financial management. By properly categorizing incoming claims and associated expenses,…
-
Adagio To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Transitioning from Adagio to QuickBooks Online simplifies accounting through seamless cloud-based data conversion. eBetterBooks ensures precise migration of historical data with 14-day data protection, resolving…
-
Acumatica To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Seamlessly migrate from Acumatica to QuickBooks Online with eBetterBooks’ expert conversion services. Our solution guarantees secure, accurate data migration, ensuring a smooth transition with minimal…
-
Accountedge To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Migrate seamlessly from AccountEdge to QuickBooks Online with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. Our solution ensures accurate, efficient, and secure transfer of your financial data,…
-
Xero To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Seamlessly switch from Xero to QuickBooks Online with eBetterBooks’ trusted data conversion services. This solution ensures accurate, secure, and uninterrupted financial data migration while enhancing…
-
Simply Accounting to QuickBooks Data Conversion
Looking to switch from Simply Accounting to QuickBooks? Our expert conversion services ensure a smooth and secure transition, providing you with advanced reporting, customizable invoices,…
-
Sage 100 To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Make the transition from Sage 100 to QuickBooks Online effortlessly with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. Seamlessly migrate your financial data, ensuring accuracy and security,…
-
Oracle To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Transition seamlessly from Oracle to QuickBooks Online with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. Our specialists ensure accurate, fast, and secure migration of your financial data,…
-
MYOB To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Easily transition from MYOB to QuickBooks Online with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. Our tailored solutions ensure accurate migration of your financial data, streamlining your…
-
Microsoft Access To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Transition seamlessly from Microsoft Access to QuickBooks Online with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. Gain the advantages of cloud-based accounting, including multi-user access, robust security,…
-
Maxwell to QuickBooks Data Conversion
Effortlessly Transition from Maxwell to QuickBooks with Expert Data Conversion Services Seamlessly migrate your financial data—including transactions, accounts, and employee details—from Maxwell to QuickBooks Pro,…
-
Master Builder to QuickBooks Data Conversion
Optimize your financial management by migrating from Master Builder to QuickBooks Pro, Premier, or Enterprise. This seamless transition ensures accurate data transfer, including customer/vendor lists,…
-
MAS Dynamics To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Migrate seamlessly from MAS Dynamics to QuickBooks Online with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. Enjoy cloud-based access, real-time updates, multi-user collaboration, and automated backups, all…
-
MAS 90 To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Effortlessly transition from MAS 90 to QuickBooks Online with expert-guided data conversion services. Overcome MAS 90’s limitations like complexity and high costs by leveraging QuickBooks…
-
MAS 500 To QuickBooks Online Data Conversion
Simplify your accounting by migrating from MAS 500 to QuickBooks Online with eBetterBooks’ expert data conversion services. This solution resolves the complexities of transitioning financial…
