A corrupt Windows Registry can make it impossible for the user to bring the computer back to life, even to restart, shut down, or boot up.
The operating system provides a Windows Registry, which is an important component that stores configuration details about the operating system, its internal applications, and drivers. Broken registry items are the main causes of system errors and disruptions of normal system operation.
Windows system components and programs require these registry entries to function correctly. However, the registry collects more data with time and can become cluttered with broken or corrupted entries. The leftovers of its registry entries may remain even after uninstalling a program.
You can find a multitude of keys, values, and data entries within each hive. These components are very important because they configure the operating system and manage the installed software in your system. Due to these broken or corrupted registry entries, users will encounter system errors and disrupt the normal functioning of the system.
Contents
Registry errors will occur most frequently when the system closes down, and the possible causes of Windows Registry errors include:
If there’s a problem with the Windows Registry, you might see a System hive error or an error like one of the following:
You can find a multitude of keys, values, and data entries within each hive. These components are very important because they configure the operating system and manage the installed software in your system. Due to these broken or corrupted registry entries, users will encounter system errors and disrupt the normal functioning of the system.
These registry entries can lead to many problems within your Windows system if they are not repaired or fixed. Some common indicators of registry issues include:
Before you start fixing any registry errors, ensure that you understand the process and always begin by creating a backup of the registry. This way, if anything goes wrong, you can restore the previous version.
Method 1: Run the Disk Cleanup Tool:
The broken or corrupted registry entries can be there in the system due to accumulated junk files, temporary files, and the system. You can run the Disk Cleanup Tool to clean your system and free up some space, and resolve issues related to broken or corrupted registry entries.
Step 1: Open the search bar in Windows from your taskbar or use the Windows + S keyboard shortcut.
Step 2: Type Disk Cleanup.
Step 3: Select the C: drive from the drop-down menu.
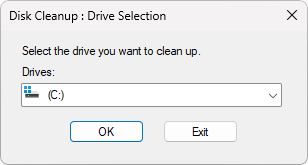
Step 4: Enter OK.
Step 5: Click on the Clean up system files button.
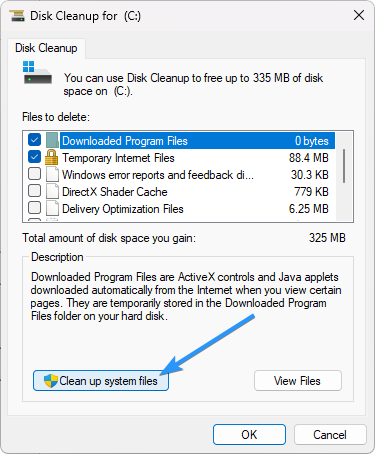
Note: To open the Clean up System files, you need an administrator account for this.
Step 6: Keep the drive selection as C:.
Step 7: Click OK to reopen the Disk Cleanup tool.
Step 8: Wait for the software to scan your system thoroughly.
Step 9: Click OK again.
Step 10: Click the Delete files to remove unnecessary files from your system. This action will also address any unwanted items that have been accumulated in the registry.
Method 2: Use the Automatic Repair Tool
The Automatic Repair Tool is a free tool that Microsoft introduced. This tool can be used to fix system boot issues and system registry files
Step 1: Press Win + L to sign out of Windows.
Step 2: Click on the power icon in the bottom-right corner.
Step 3: Then, press and hold the Shift key and click on the Restart option.
Step 4: Windows will restart and boot to the Windows Recovery options page.
Step 5: Go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options.
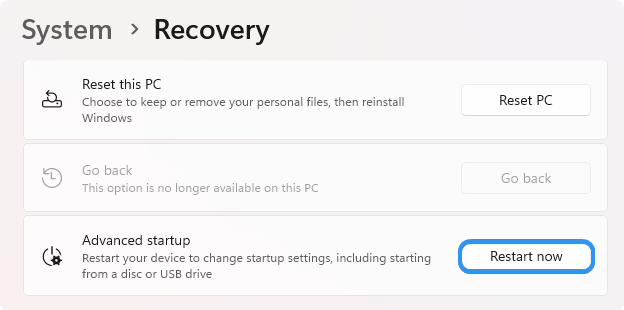
Step 6: Select the Startup Repair option on the Advanced Options page.
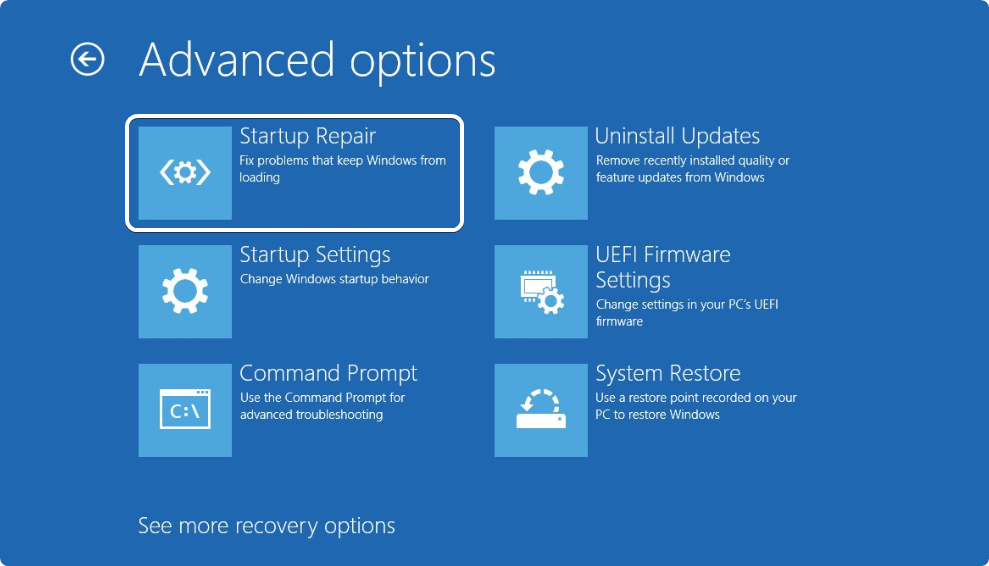
Step 7: The utility will begin diagnosing your system and attempt repairs.
Step 8: Restart the system after the repair process is complete.
Method 3: Run SFC Scan
SFC or the System File Checker is a tool introduced by Windows that can be used to scan the system for corrupted or missing system files.
Step 1: Press Win + R to open the Run command box.
Step 2: Type cmd in the text input box and then press Ctrl + Shift + Enter simultaneously.
Step 3: A command prompt window will open with administrator privileges.
Step 4: Type sfc /scannow and press Enter to perform the command.
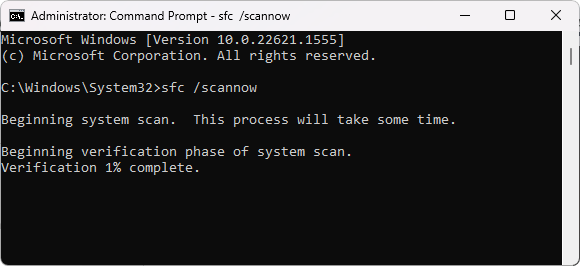
Step 5: The utility will scan your system for corrupt or missing files and replace them with fresh copies.
Step 6: Allow the utility to complete the scan and file replacement process.
Step 7: Close the command prompt window and restart your computer.
Method 4: Run DISM Scan
DISM, which stands for Deployment Image Servicing and Management, is also one of the in-built Windows tools that repair system files that are related to registry entries.
Step 1: Press the Windows + S shortcut keys to open the Search Bar.
Step 2: Type Command Prompt and choose Run as Administrator.
Step 3: Click on Yes to permit the app to open with administrator rights.
Step 4: Type DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth command.
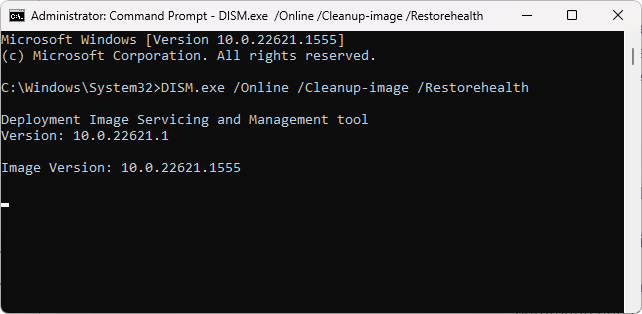
Step 5: Press Enter.
Step 6: The tool will take some time to scan and repair the issues related to the system image.
Step 7: Once the issue is solved, close the command prompt and restart the system.
Method 5: Import Registry Backup
Creating registry backups could resolve the broken or corrupted registry entries issue with the system. This option will only work if you have a recent registry backup.
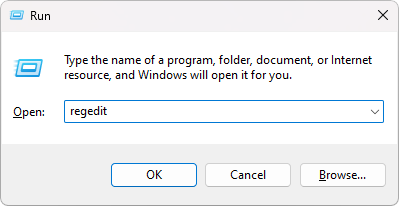
Step 1: Press Windows + R to open Run.
Step 2: Type regedit to open Registry Editor and press OK.
Step 3: Go to the Registry Editor toolbar and click on File> Import.
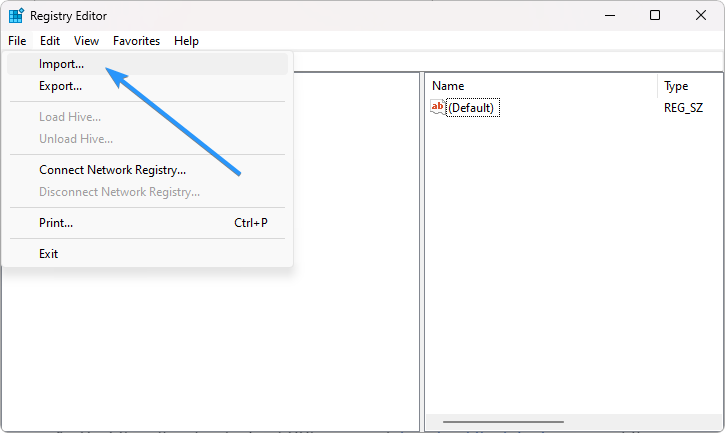
Step 4: Go to the Registry Backup File location.
Step 5: Choose the registry file.
Step 6: Click on Open.
Method 6: Scan System for Malware
If the system is attacked by Malware, it can break or corrupt the existing registry entries. You can run a full system scan with the help of the Windows Defender tool to scan any malware infections that are causing registry issues.
Method 7: Use System Restore Point
This option is only recommended if you have a recent restore point saved. Restore your system to the point when it was last working efficiently. If you have a system restore point saved from a time when your system was working correctly, then restoring your system to that point can fix any issues you may be experiencing with your registry.
Repairing registry entries associated with errors requires a systematic approach to ensure accuracy and avoid further system issues. Start by knowing which particular error has been detected, then proceed to back up the registry in case the worst thing happens. Try with the help of Windows Registry Editor or third-party utilities for Windows to define and remove corrupt entries.
Ans: These registry entries can lead to many problems within your Windows system if they are not repaired or fixed. Some common indicators of registry issues include:
Ans: Editing the registry can be risky if you lack experience. A single mistake can make your system unusable. Always back up the registry before making changes.
Ans: If the error continues and other solutions do not work, reinstalling Windows is an effective method to fix registry problems. Be sure to back up your data first.