The number of hours in a non-leap year ( standard year ) is 8,760. A standard year has 365 days, and each day has 24 hours. The number of hours in a year varies depending on the type of year.
It is crucial to know the number of hours in a year for businesses as it helps them calculate employee salaries, plan work schedules, and evaluate their productivity. It is also useful for individuals to manage time effectively and maintain a healthy work-life balance.
By understanding the number of hours in a year, we can make the most of our time and prioritize what truly matters in our lives.
Contents
| Type | Definition | Calculation | Total Number of Hours |
| Standard Year | A standard year has 365 days. | 365 days * 24 hours | = 8,760 hours |
| Leap Year | A leap year occurs every four years, totaling 366 days. | 366 days * 24 hours | = 8,784 hours |
| Mean Year | A mean year is the average length of a year, accounting for both standard and leap years, and is approximately 365.25 days. | 1 mean year = (365+1/4-1/100+1/400) days = (365.2425 days) 365.2425 days * 24 hours | = 8,765.82 hours |
| Julian Year | A Julian year is exactly 365.25 days. | 365.25 days * 24 hours | = 8,766 hours |
Work hours refer to the time an employee is required to be on duty, as defined by their employer.
Work hours, often referred to as “work day,” encompass the time spent on tasks and duties necessary to fulfill a specific job.
However, depending on the job, work hours may also include:
Some situations require employees to be compensated for hours spent on non-work tasks, also known as hours of service.
These may include:
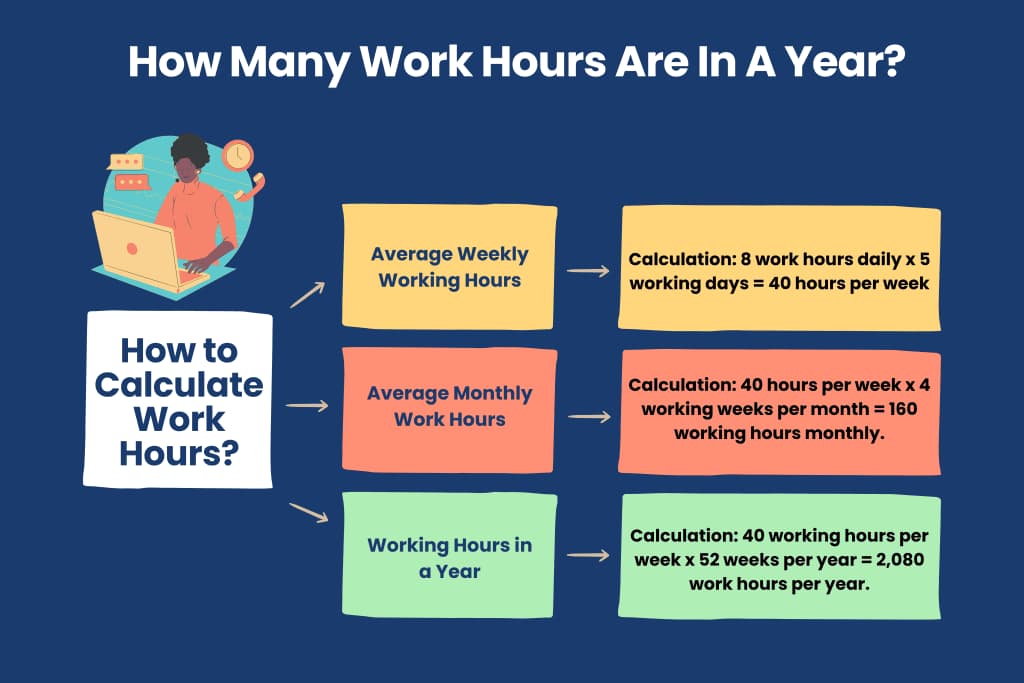
To calculate the annual working hours, let’s start with the standard workweek and then multiply it by the number of weeks in a year. Take a common approach of 5-day workweek, which results in 52 weeks per year. The standard workday is typically 8 hours, which gives us a standard 40-hour workweek.
Let’s break down the calculation with an example:
Now, Apply the Formula:
Working Hours = Weeks × Days × Hours
Working Hours = 52 weeks × 5 days/week × 8 hours/day
Working Hours = 2080 hours
By doing this calculation, we get a result of 2,080 hours, which represents the standard annual working hours assuming a 5-day workweek. It’s important to note that only some follow the 5-day, 8-hour standard. In some cases, a few industries may have different structures that follow a 4-day workweek with longer daily hours.
Most of the businesses will accommodate for time off, including employee sick days, paid holidays, paid time off, and other work absences throughout the year.
For instance, if we assume 8 paid holidays and 10 days of paid time off, that takes 18 workdays throughout the year. This means that the average employee will work 1,936 annual hours without taking any other unpaid days off.
Paid holidays are the days off that employees receive for almost all federally observed holidays (national, state, or religious). The company usually pays wages to the employees for taking these days off. In fact, these holidays are typically included as part of an employee benefits package.
The most typical paid holidays in the US include:
The number of paid holidays and the percentage of workers who get them are different for each industry. Some companies add more holidays to their paid holiday schedule, which can depend on where they are located and what their employees think over time.
Paid time off, or PTO is a benefit provided by organizations that compensate employees during their absence from work. Employees use PTO for multiple reasons, for example, when they fall sick when they want to go on vacation, or for personal reasons.
Companies often use PTO as an alternative to offer specific vacation time, sick time, or personal days. There are many different policies companies may have related to their PTO works, and one of the more common methods businesses use is accruing hours within a bank.
Here are the types of PTO that companies might offer to pay employees when they’re not working:
| Work Hours | Non-Work Hours |
| It refers to the designated period during which an individual is expected to be actively engaged in their job or profession. | It refers to the time when an individual is not officially engaged in their job or professional duties. |
| It involves tasks, responsibilities, and commitments related to employment. | It includes breaks, evenings, weekends, holidays, and any other time outside the regular working schedule. |
| Example- 9 AM to 5 PM (Monday to Friday for office jobs) | Example- After 5 PM on weekdays, weekends, and holidays |
| It includes breaks, evenings, weekends, holidays, and any other time outside the regular working schedule. | During this time, employees have the freedom to relax, engage in hobbies, and enjoy leisure activities away from the demands of the workplace. |
These factors influencing work hours can vary across industries, job types, and individual preferences:
Understanding the technical aspects of annual working hours is important for every business and employee. Calculations based on work hours form the basis for labor contracts, payroll management, and regulatory compliance.
Individuals and companies can gain insights into time management and make informed decisions about work schedules and productivity by just making use of simple and direct calculations.
Understanding the total annual work hours is essential for fair employee compensation under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). The FLSA requires employees to earn at least the minimum wage, not exceed 40 hours per week, and receive overtime pay for hours worked beyond that.
Working beyond the usual 40-hour week can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases and strokes. Prolonged hours may lead to chronic stress, adversely affecting the body over time.
In a traditional five-day workweek, there are 260 working days in a year. This means you spend about 71% of your year working, not including any time off. To find out how many working days you have this year, subtract the number of federal holidays your company allows, as well as any vacation time you plan to take.