Highlights (Key Facts & Solutions)
- Tax Tracking is Critical: The payroll item’s Tax Tracking Type must be correctly set to Health Coverage Cost to ensure the employer-paid amount is properly reported in W-2 Box 12, Code DD.
- W-2 Code DD is Non-Taxable: The amount reported under W-2 Code DD represents the total cost of coverage (employer and employee portions) for informational purposes only; it is not taxable income.
- Payment Best Practice: Use the Enter Bills and Pay Bills features to record payments to the insurance vendor, which creates a robust audit trail and ensures accurate accrual accounting, avoiding the use of complex manual Journal Entries.
- Liability and Expense Must Match (Desktop): When setting up the ACA W-2 reporting payroll item, assign the same nominal account to both the payroll liability and expense fields to track the cost per employee without duplicating the actual expense on the P&L.
- Adjusting Errors: Prior-period payroll contribution errors must be corrected using the Adjust Payroll Liabilities tool, not by editing old paychecks, to maintain the integrity of filed tax reports.
- Zero Net Paycheck: The technical process of creating a zero net paycheck is used to record the employer’s non-cash contribution to an employee’s YTD wages for W-2 reporting without affecting their bank account.
- Refund Handling: If a vendor refund or overpayment is received, it must be deposited back to the original Health Insurance Expense Account to correctly reduce the total expense on the Profit and Loss statement.
Overview
To record employer-paid health insurance in QuickBooks, begin by creating a payroll item for the company contributions, then assign it to the employees and record the payments as expenses, either through journal entries or a bill.
Under the Affordable Care Act, also known as Obamacare, most Americans are required to maintain a basic level of health insurance referred to as minimum essential coverage defined by the Department of Health and Human Services.
“Employer-sponsored coverage” includes health insurance for current employees, their families, and retired employees. Federal law allows former employees to keep their employer’s health insurance, at their own cost, for a limited time after leaving the job.
If your company has an insurance benefit plan, you need to set up and manage payroll items for your insurance benefit plan in QuickBooks Online Payroll and QuickBooks Desktop Payroll to track and tax it appropriately.
In order to set up, add, edit, and track insurance benefits plans or employer health benefits, you must determine the type of health benefit plan or insurance benefit plan.
However, if you don’t have an insurance benefit plan, QuickBooks has partnered with Allstate Health Solutions to provide employee health benefit options for QuickBooks Online Payroll customers.
Prerequisites / Considerations To Take Before Recording Health Insurance in QuickBooks
Before recording Health Insurance in QuickBooks, make sure to address several key areas to avoid any technical problems in the future.
Tax Implications of Employer – Paid Health Insurance
- Determine Taxability: Verify that health insurance premiums paid for employees are assessed for taxability. Generally, employer-paid premiums are exempt from federal income and payroll taxes.
- W2 Form: Employee benefits are recorded in the W-2 Forms which are submitted to the IRS for reporting purposes. W-2 tax forms, also known as the Wage and Tax Statement, is a document an employer sends to each employee and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- W-2 Reporting: The Affordable Care Act requires employers to report the total cost of employer-sponsored health coverage on employees’ W-2 forms. This amount includes both employer and employee contributions but is not taxable. W-2 forms contain essential information about employees’ earnings and tax withholdings, and they are submitted to the IRS. Employees use this form to file federal and state taxes. A W-2 employee is one whose employer deducts taxes from their paycheck and reports it to the government.
Ensuring Compliance with ACA Requirements
- Identify Applicable Provisions: Identify the applicable ACA provisions based on your organization’s size. Employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees are subject to the Employer Shared Responsibility provisions.
- Offer Minimum Essential Coverage (MEC): Ensure that the health insurance plan provides MEC and is affordable, as defined by the ACA, to avoid potential penalties.
- Reporting Obligations: Understand ACA reporting requirements, including Forms 1094-C and 1095-C, which detail the health coverage provided to employees.
Differences Between Pre-Tax and Post-Tax Health Insurance Deductions
- Pre-Tax Deductions: These reduce an employee’s taxable income, leading to tax savings for both the employee and employer. Common pre-tax deductions include premiums for medical, dental, and vision insurance.
- Post-Tax Deductions: These do not reduce taxable income. There are still some deductions for certain benefits, like some life insurance policies, which may be post-tax.
- Setup in QuickBooks: When setting up payroll items in QuickBooks, specify whether each deduction is pre-tax or post-tax to ensure accurate tax calculations and reporting.
Reviewing Employee Agreements & Health Insurance Plan Details
- Examine Employee Contracts: Review agreements to understand the commitments regarding health insurance benefits, including employer contribution rates and eligibility criteria.
- Analyze Plan Documents: Understand the specifics of the health insurance plan, such as coverage options, premium amounts, and any employee cost-sharing responsibilities.
- Communicate with Employees: Clearly inform employees about their benefits, contribution amounts, and any actions required on their part.
For QuickBooks Desktop
How to record Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop?
Step by Step to record Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop
Step 1: Create a Payroll Items
- Go to the Lists menu and the Payroll Item List.
- Click Payroll Item and tap on “New”.
- Choose Custom Setup and click Next.
- Select Deduction or Company Contribution and click Next.
- Name the insurance type (e.g., Medical, Vision, Dental).
- Enter the following:
- Agency Name and Account Number: Select the agency name to which liability is paid (or add it) and the account number.
- Tax Tracking Type: Set the Tax Tracking Type to Premium Only/125 (for pre-tax) and None (for after-tax). Then, click Next three times.For the None tax tracking type, choose net pay in the Gross vs. net window, then hit the Next icon.
- Contribution amount and limit: Leave the Default rate and limit fields blank. You can add the rate and limit when the item is added to the employee profile.
- Click OK to save.
Step 2: Assign to Employees
- Click on the “Employees” menu and then click on “Employee Center”.
- Click twice on the Employee’s name and go to the “Payroll Info”
- Under the section for Additions, Deductions, and Company Contributions, add the new payroll items.
- Enter the contribution amount per period and the limit.
- Press the OK button.
Step 3: Record the Payment
- Click on the “ Vendors” menu and click on the “ Enter Bills” option on the screen.
- Now, mention the insurance company, policy number and the payment amount.
- Assign the expense to the correct account.
- Use the “Pay Bills” tool to pay the bill.
How to Add / Modify and Remove Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop?
Step to add/modify and remove Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop
Case 1: Add Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop
- Click on the Employees menu, choose the Employee Center and click twice on the Employee’s name.
- Select the Payroll Info section.
- Under the section for Additions, Deductions, and Company Contributions, add the health benefit insurance items.
- Enter the contribution amount per period and the limit.
- Press the OK button.
Case 2: Modify Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop
- Navigate to the Lists menu, and then choose the Payroll Item List. Then, hit right-click on the item and select Edit Payroll Item.
- Change the info as needed on each window.
- Press the Finish icon.
Case 3: Remove Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop
- Click on Employees and select Employee Center. Then, select your Employee.
- Select the Payroll Info section.
- Under the section for Additions, Deductions, and Company Contributions, select the amount (if there’s any) and the item name, and then press Delete on your keyboard.
- Hit the OK tab.
How to Create Zero Net Paychecks for Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop?
Step to create zero net paychecks for Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop
Step 1: Set up a Dummy Addition Item
- Navigate to the Lists menu and then choose Payroll Item List.
- Right-click anywhere, then press New and select Custom Setup > Next.
- Opt for Addition and press Next.
- Enter the name of the item and click Next twice.
- Hit the None icon under the Tax Tracking type drop-down menu and click Next three times.
- Select Net Pay and hit Next.
- Press the Finish button.
Step 2: Create a company paid insurance Item
- Click on the Lists menu and then choose Payroll Item List.
- Click-right anywhere, then press New and select Custom Setup > Next.
- Select Deduction, then press Next.
- Enter the deduction name and double-click on Next.
- Choose None under the Tax tracking type drop-down menu. Then, hit Next three times.
- Press the net pay radio button.
- Click Next and then hit the Finish icon.
Step 3: Create the payroll check
- Click on the Employees menu and then select Pay Employees.
- Choose Unscheduled Payroll.
- Update the date and then click the employee name.
- Select the Open Paycheck Detail option.
- Remove all the items in the Earnings section.
- Go to the Other Payroll Items section and then remove any addition or deduction items.
- Add the dummy addition and deduction item you’ve just created.
- Enter a sample amount (like 100).
- Make sure the Check Amount is zeroed out.
Liability Health Insurance (company paid) adjustment for zero-year-end balance
Below is the Step by step guide to create zero net paychecks to include the company-paid insurance in QuickBooks Desktop.
- Hit the Employees tab at the top menu bar and then select Payroll Taxes and Liabilities.
- Choose Adjust Payroll Liabilities.
- Type in the Date and Effective Date.
- Click Company under Adjustment is for.
- Select the Health Insurance item and enter the Amount.
- Tickmark the Accounts Affected checkbox and then hit OK.
- Press the OK button.
How to report Employer Health Insurance on W2 Forms in QuickBooks Desktop Payroll?
To report employer health insurance on W-2 forms in QuickBooks Desktop, create a new payroll item under Payroll Item List, set up as a company contribution, and add it to employee paychecks before year-end.
Steps by step guide to report Employer Health Insurance on W-2 Forms in QuickBooks Desktop Payroll
- Click on List and then select Payroll Item List.
- Hit the New Payroll Item tab.
- Select Custom Setup, then press the Next button.
- Choose Company Contribution and then click Next.
- Give a name to the payroll item. For example, “Reportable Health Coverage Cost”. Later, hit the Next icon.
- Choose the Liability account drop-down menu, and press Add new.
- Select Other Expenses and create a new account name (like “Reportable Health Coverage“). Hit the Save & Close tab.
- Navigate to the Expense account drop-down menu and then select the account you’ve just created. Click Next.
Note: Making the liability and expense accounts the same allows you to track your healthcare costs without impacting your financial reports. Press Yes on the warning prompt. - Opt for the tax tracking type drop-down and then choose Health Coverage Cost.
- Press Next three times and then hit the Finish tab.
- You need to add the healthcare company contribution to your employees’ paychecks and run a payroll before the end of the year.
For QuickBooks Online
How to Record Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Online?
Step 1: Create a Payroll Item
- Navigate to Payroll Menu> Employees and then choose your employee.
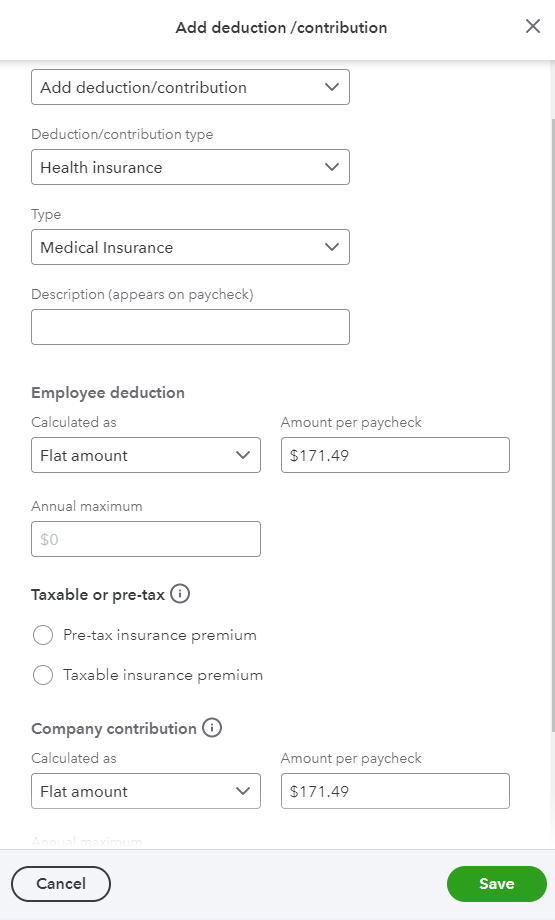
- Click on Start or Edit under the Deductions & contributions.
- Then, select + Add Deduction/contribution.
- Select the specific contribution item (Health Insurance benefit plans):
- Deduction/contribution: Add deduction/contribution
- Deduction/contribution type: Health insurance
- Type: Choose Medical insurance, Vision Insurance, or Dental Insurance. If you’re setting up a pre-tax item not listed like commuter benefit, AFLAC accident or cancer, etc, click on Vision Insurance.
- Under the Description (appears on a paycheck) field, enter the provider’s name and select how your deduction is calculated
- Then enter the amount or percent per paycheck.
- Choose Pre-tax insurance premium or Taxable insurance premium. If you contribute a matching contribution, add an amount or percent per paycheck for the company contribution.
- Once completed, press Save, then click Done.
Step 2: Record the Payment
- Click on “New” and then select “Journal Entry”.
- Enter the relevant accounts for health insurance payments (liability and expense accounts).
- Click “Save and Close”.
How to Edit / Remove an Insurance item in QuickBooks Online?
To edit or remove an insurance item in QuickBooks Online, go to Payroll > Employees, select the employee, modify or delete the contribution, and press Save and Done.
Steps to edit / remove an Insurance Item in QuickBooks Online
- Go to Payroll > Employees and then select your employee.
- From Deductions & contributions, choose Start or Edit.
- Then, click on Edit beside the contribution you want to modify or hit the Trash bin icon to remove the contribution.
- Press Save and then Done
How to Report Employer Health Insurance on W2 Forms in QuickBooks Online Payroll?
To report employer health insurance on W-2 forms in QuickBooks Online Payroll, go to Taxes > Payroll Taxes > Filings > Resources, edit Box 12/13, enter amounts in Box 12DD and Box 12FF, and click Submit.
Steps to report Employer Health Insurance on W-2 Forms in QuickBooks Online Payroll
- Go to Taxes, then select Payroll Taxes > Filings > Resources.
- Choose W-2s and then select Edit Box 12/13 on W-2 Copies B, C, & 2 (employee) from Employee W-2s.
- Enter the dollar amount for each employee:
- Use Box 12DD for the coverage you provide your employees.
- Use Box 12FF for reimbursements you give your employees.
- Click Submit.
How to Set up Health Insurance Reimbursement in QuickBooks Online?
To set up health insurance reimbursement for an employee in QuickBooks Online (QBO), follow these steps:
Steps to set up health insurance reimbursement in QuickBooks Online
- Go to Payroll > Employees.
- Select the employee.
- Under Pay types, choose Start or Edit.
- Scroll down to the Additional Pay Types section and select Reimbursement.
- If a reimbursement type is already listed, select it or choose + Another Reimbursement type to add a new one.
- Set a default amount or leave it blank to enter the amount during payroll.
- Optionally, rename the reimbursement type by selecting Edit next to it.
- Click Save when done.
- When running payroll, enter the reimbursement amount in the Reimbursement field.
How do I Categorize Employee Health Insurance in QuickBooks?
When managing or recording health insurance expenses in QuickBooks, ensure proper categorization to maintain accurate financial records. Here’s a streamlined approach to categorize health insurance expenses:
- Set up a specific expense account for health insurance. Categorize all health insurance-related payments here to separate them from other expenses.
- Avoid Duplicating Expenses
- For employee deductions and employer contributions, avoid duplicating expenses by properly assigning categories.
- In the “Employee Profile” under Deductions, set the “Company Contribution” field to 0.00 or None if you notice duplication.
- Allocate Expenses Correctly
- For employee deductions, ensure these accumulate in a liability account throughout the month.
- At the month’s end, reconcile by creating a journal entry. Adjust the liability account and allocate remaining amounts to the health insurance expense account.
- If health insurance is paid at the start of the month, categorize it in the banking tab as “Health Insurance Expense.” Adjust liabilities later during reconciliation.
- Fix Duplicated Entries
- Review transaction journals to find accounts affected by duplication.
- Reverse these transactions to correct overstated expenses.
How to Record Health Insurance Payments in QuickBooks?
You can record health insurance payments in QuickBooks using one of three ways: Payroll Item, Expense Transaction, or Journal Entry.
Method 1: Using a Payroll Item
- Go to Lists > Payroll Item List.
- Click Payroll Item > New.
- Choose Custom Setup > Next.
- Select Deduction or Company Contribution > Next.
- Name the item (e.g., Medical, Vision, Dental).
- Enter the agency, account number, tax tracking type, contribution amount, and limit.
- Click OK to save.
Method 2: Recording as an Expense Transaction
- In QuickBooks, go to Expenses.
- Click New Transaction > Expense.
- Enter details like date, payee, payment method, and amount.
- Categorize it under Health Insurance.
- Attach receipts or documentation if needed.
Method 3: Using a Journal Entry
- Click New (top left of QuickBooks Online).
- Select Journal Entry under the Other section.
- Enter the relevant accounts for health insurance payments.
- Click Save and Close.
How employer-paid health insurance affects payroll taxes in QuickBooks?
Managing employer-paid health insurance in QuickBooks is crucial for keeping your books accurate and ensuring compliance with tax regulations. Employer-paid health insurance significantly influences payroll taxes in QuickBooks. Understanding this impact is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process effectively.
Understanding Tax Implications of Employer-Paid Health Insurance :
- Federal Income Tax: Employer contributions to employee health insurance premiums are generally exempt from federal income tax.
- Social Security and Medicare Taxes (FICA): These contributions are typically not subject to FICA taxes.
- Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA): Employer-paid health insurance premiums are usually exempt from FUTA tax.
Troubleshooting & Common Issues in Recording Health Insurance
How to Fix employer-paid health insurance not appearing on W-2?
If your employer-paid health insurance isn’t appearing on your W-2 form, it’s essential to address this promptly to ensure accurate tax reporting.
Steps to fix employer-paid health insurance not appearing on W-2
- Review Your W-2 Form
- Box 12: This box should display the code “DD,” representing the total cost of employer-sponsored health coverage.
- Box 1: Confirm that your taxable wages don’t include the health insurance premiums, as these are typically pre-tax deductions.
- Consult Your Payroll or HR Department
- Immediate Contact: Reach out to your company’s payroll or human resources department to inform them of the omission.
- Provide Documentation: Have your health insurance enrollment forms or pay stubs showing premium deductions ready to support your claim.
- Request a Corrected W-2 (Form W-2c)
- Formal Request: Ask your employer to issue a Form W-2c, which corrects errors on the original W-2.
- Timeline: Ensure this is done promptly to avoid delays in your tax filing.
- Adjust Your Tax Return if Necessary:
- Amendment: If you’ve already filed your tax return using the incorrect W-2, you may need to file an amended return (Form 1040-X) once you receive the corrected W-2.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider consulting a tax professional to navigate the amendment process accurately.
Correcting payroll errors in QuickBooks related to health insurance involves identifying the discrepancies, adjusting payroll items, and ensuring accurate reporting. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
Step 1: Identify the Payroll Error
- Examine your payroll summaries and detailed reports to spot inconsistencies related to health insurance deductions or contributions.
- Ensure that each employee’s health insurance deductions are set up correctly in their profiles.
Step 2: Adjust Health Insurance Payroll Items
- Navigate to the “Lists” menu and select “Payroll Item List.”
- Locate the health insurance payroll item in question.
- Right-click on it and choose “Edit Payroll Item.”
- Verify the type (e.g., deduction, company contribution).
- Ensure the tax tracking type aligns with your health insurance plan.
- Confirm the correct liability and expense accounts are assigned.
Step 3: Correct Employee Payroll Information
- Go to the “Employees” menu and select “Employee Center.”
- Double-click on the employee’s name to open their profile.
- Navigate to the “Payroll Info” tab.
- In the “Additions, Deductions, and Company Contributions” section, verify that the health insurance item is listed with the correct amount.
- Make necessary adjustments and click “OK” to save changes.
Step 4: Update Past Payroll Transactions
- From the “Employees” menu, select “Edit/Void Paychecks.”
- Choose the paycheck containing the error and click “Edit.”
- In the paycheck window, adjust the health insurance deduction or contribution as needed.
- Ensure that the net pay reflects the correction.
- Click “Save & Close” to update the paycheck.
- Repeat this process for any other affected paychecks.
Employer Health Insurance Adjustments & Reconciliations
How to Adjust Prior Period Health Insurance Contributions in QuickBooks?
Adjusting prior period health insurance contributions in QuickBooks requires careful handling to ensure your financial records remain accurate. Here’s a step-by-step guide to assist you:
- Identify the Affected Period and Amount
- Determine the Specific Period: Ascertain the exact prior period(s) where the health insurance contributions need adjustment.
- Calculate the Adjustment Amount: Compute the total amount that needs correction for each affected period.
- Open QuickBooks: Launch your QuickBooks application.
- Navigate to Payroll Center: Click on ‘Employees’ in the top menu and select ‘Payroll Center’ from the dropdown.
- Go to ‘Payroll’ Tab: Within the Payroll Center, select the ‘Payroll’ tab.
- Choose ‘Adjust Payroll Liabilities’: Click on ‘Adjust Payroll Liabilities’ to initiate the adjustment process.
- Enter Adjustment Details
- Select the Affected Employee: In the ‘Employee’ field, choose the employee whose contributions need adjustment.
- Set the Date: Enter the date corresponding to the end of the affected payroll period.
- Specify the Adjustment Item: From the ‘Item Name’ dropdown, select the health insurance contribution item that requires adjustment.
- Input the Adjustment Amount: Enter the correction amount. Use a positive number to increase and a negative number to decrease the contribution.
- Add a Memo (Optional): For future reference, include a brief description or reason for the adjustment in the ‘Memo’ field.
- Double-check all details to ensure accuracy.
- Save the Adjustment: Click ‘OK’ or ‘Save & Close’ to record the adjustment.
- Update Payroll Records
- Run Payroll Reports: Generate relevant payroll reports to confirm that the adjustment has been accurately applied.
- Inform Affected Employees: Communicate any changes to the employees involved, especially if the adjustment impacts their net pay or tax withholdings.
How to reconcile employer-paid health insurance at year-end?
Reconciling employer-paid health insurance at year-end in QuickBooks is essential for accurate financial records and tax reporting. Follow these detailed steps to ensure proper reconciliation:
Step 1: Verify Payroll Settings
- Ensure that the employer-paid health insurance is set up correctly in QuickBooks.
- Navigate to the Payroll Center.
- Click on “Payroll Setup” and review the “Deductions & Contributions” section.
- Confirm that the health insurance contribution is listed as a company-paid item.
Step 2: Review Payroll Reports
- Go to the “Reports” menu.
- Select “Employees & Payroll,” then choose “Payroll Summary.”
- Set the date range to cover the entire fiscal year.
- Locate the employer-paid health insurance amounts and note the total for the year.
Step 3: Cross-Check with General Ledger
- Access the “Chart of Accounts” from the “Lists” menu.
- Find the account associated with employer-paid health insurance expenses.
- Right-click on the account and select “QuickReport.”
- Set the date range to match your fiscal year.
- Compare the total in this report to the total from the Payroll Summary.
Step 4: Adjust Discrepancies
- If differences exist between the reports, investigate individual transactions.
- Ensure all health insurance payments are recorded correctly.
- Make necessary adjustments by creating journal entries:
- Go to the “Company” menu and select “Make General Journal Entries.”
- Enter the adjustment details, debiting or crediting the appropriate accounts.
Step 5: Update Employee W-2 Forms (U.S. Only)
- Employer-paid health insurance may need to be reported on employee W-2 forms.
- Navigate to the “Employees” menu and select “Payroll Tax Forms & W-2s.”
- Choose “Process W-2s” and review each form for accuracy.
- Ensure the health insurance amounts are correctly reflected in Box 12 with Code DD.
Step 6: Consult Tax Professionals:
- Tax regulations regarding employer-paid health insurance can vary.
- It’s advisable to consult with a tax professional to ensure compliance with current laws and accurate reporting.
Handling Overpaid or underpaid health insurance in QuickBooks
Handling overpaid or underpaid health insurance transactions in QuickBooks requires careful attention to ensure your financial records accurately reflect these discrepancies. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to assist you:
Step 1: Recording Health Insurance Payments
- Navigate to the ‘Expenses’ Section: Open QuickBooks and select ‘Expenses’ from the left-hand menu.
- Create a New Expense: Click on ‘New Transaction’ and choose ‘Expense’.
- Enter Payment Details: Input the payment date, payee (health insurance provider), and the amount paid.
- Assign the Appropriate Category: Select ‘Insurance’ or a similar category you’ve set up for health insurance expenses.
- Save the Transaction: After verifying all details, click ‘Save and Close’.
Step 2: Identifying Overpayments or Underpayments
- Review Statements: Regularly compare your QuickBooks records with statements from your health insurance provider to spot any discrepancies.
- Run Expense Reports: In QuickBooks, generate expense reports for your insurance payments to identify inconsistencies.
Step 3: Handling Overpayments
- Contact the Insurance Provider: Confirm the overpayment amount and discuss refund options or credit adjustments.
- Record the Refund in QuickBooks:
- Navigate to ‘Banking’: Go to the ‘Banking’ menu and select ‘Make Deposits’.
- Enter Deposit Details: In the ‘Received From’ field, enter the insurance provider’s name. For the ‘Account’ field, select ‘Insurance Expense’ to offset the overpayment. Input the refund amount.
- Save the Deposit: Click ‘Save and Close’ to record the refund.
- Adjust Future Payments (if credited):
- Modify Upcoming Expense Entries: Reduce the amount of your next payment by the credited overpayment amount.
- Document the Adjustment: In the memo or notes section of the transaction, note that this payment reflects an overpayment credit.
Step 4: Handling Underpayments
- Contact the Insurance Provider: Verify the underpayment amount and understand any potential penalties or interest.
- Record the Additional Payment in QuickBooks:
- Navigate to ‘Expenses’: Click on ‘New Transaction’ and select ‘Expense’.
- Enter Payment Details: Input the additional amount paid, ensuring the date and payee are correct.
- Assign the Appropriate Category: Select ‘Insurance’ or your designated health insurance expense category.
- Save the Transaction: After verifying all details, click ‘Save and Close’.
Step 5: At the end of each month, reconcile your QuickBooks accounts to ensure all health insurance payments and adjustments match your bank statements.
How to Add Health Insurance to a W-2 in QuickBooks
If you need to report health insurance on an employee’s W-2 in QuickBooks, you can do it in two ways:
Option 1: Add Health Insurance to Box 12DD or 12FF
- Go to Taxes > Payroll Taxes > Filings
- Select Resources > W-2s
- Click Edit Box 12/13 on W-2 Copies B, C, & 2 (Employee)
- Enter the health insurance amount for each employee
- Click Submit
Option 2: Set Up a Payroll Item for Health Insurance
- Go to Lists > Payroll Item List
- Click New Payroll Item
- Select Custom Setup > Company Contribution
- Name the payroll item (e.g., “Health Insurance”)
- Under Liability Account, select Add New, create a name, then Save & Close
- Under Expense Account, select the new account
- Choose Health Coverage Cost from the Tax Tracking Type drop-down
- Click Finish
Best Practices for Recording Employer-Paid Health Insurance
Accurate recording of employer-paid health insurance is essential for compliance, tax purposes, and efficient payroll management. Below is a detailed guide to help you maintain precise records, automate payroll processes, and ensure smooth year-end reporting of employer-paid benefits.
Keeping Accurate Records for Compliance & Tax Purposes
- Classify Health Insurance Premiums: Determine which health insurance premiums are employer-paid and which are employee-paid. This distinction is crucial for tax reporting and compliance.
- Document Plan Details: Maintain comprehensive records of each health insurance plan offered, including coverage specifics, eligibility criteria, and premium amounts.
- Track Employer Contributions: Record the exact amounts the employer contributes toward each employee’s health insurance premiums. This information is vital for tax reporting and financial analysis.
- Monitor Legislative Changes: Stay informed about changes in tax laws and regulations related to employer-paid health insurance to ensure ongoing compliance.
Automating Payroll Processes to Reduce Errors
- Implement Payroll Software: Adopt a reliable payroll system that supports the integration of benefits administration. This software should handle calculations, deductions, and contributions related to health insurance premiums.
- Integrate Benefits Data: Ensure that your payroll system is integrated with your benefits administration platform. This integration allows for automatic updates of employee benefit selections and corresponding premium amounts.
- Set Up Automated Deductions: Configure the payroll system to automatically deduct employee-paid premiums from their wages and account for employer-paid portions accurately.
- Regularly Audit Payroll Entries: Conduct periodic audits of payroll entries to identify and correct discrepancies related to health insurance premiums promptly.
Ensuring Smooth Year-End Reporting of Employer-Paid Benefits
- Prepare Annual Statements: Generate detailed reports summarizing the total employer-paid health insurance premiums for each employee over the fiscal year.
- Complete Required Tax Forms: Accurately fill out necessary tax forms, such as Form 16 in India, ensuring that employer-paid health insurance benefits are reported correctly.
- Distribute Employee Statements: Provide employees with statements detailing the total health insurance premiums paid on their behalf, which they may need for personal tax filings.
- Retain Records for Compliance: Store all related documents securely for the period required by law, typically several years, to comply with regulatory requirements and facilitate potential audits.
By following these steps, you can maintain accurate records of employer-paid health insurance, minimize errors through automation, and ensure compliance during year-end reporting.
Key Considerations for Accurate Employer-Paid Health Insurance Payroll in QuickBooks
Accurate recording of employer-paid health insurance is essential for tax compliance and financial clarity. Common errors—including payroll item misclassification, improper tax tracking, and duplicate expenses—can result in penalties and inaccurate reports. Customizing payroll items for various insurance plans, integrating contributions correctly with payroll taxes, and leveraging QuickBooks reporting tools help prevent these issues. A systematic troubleshooting process ensures ongoing accuracy, reducing audit risks and enhancing payroll efficiency.
Common Errors to Avoid When Recording Employer-Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks
Recording employer-paid health insurance often has 3 common errors: misclassifying payroll items, incorrect tax tracking, and duplicating expenses. Misclassification leads to inaccurate tax filings and penalties, affecting 1 in 4 businesses annually. Incorrect tax tracking causes wrong payroll tax calculations, risking fines up to 5% of payroll. Duplication inflates expenses, distorting financial reports and cash flow. To avoid these, verify payroll item setup, confirm tax tracking type matches insurance plan, and regularly audit employee deductions. Correcting errors early saves time, money, and IRS scrutiny, helping maintain compliance and clear financial records.
Integrating Health Insurance Contributions QuickBooks with Payroll Tax Calculations
Integrating health insurance contributions with payroll tax calculations is critical for accuracy, compliance, and cost control. Employer-paid premiums are generally exempt from federal income tax and FICA, affecting over 90% of U.S. employers. Misintegration can lead to incorrect tax withholdings, triggering IRS audits and penalties up to 10% of payroll. QuickBooks allows setting tax tracking types to Premium Only or None, ensuring correct calculations. Proper integration reduces manual errors, saves up to 15 hours monthly in payroll processing, and maintains employee trust by preventing paycheck discrepancies.
Customizing Payroll Items in QuickBooks for Different Types of Insurance Plans
Customizing payroll items for diverse insurance plans ensures precise tracking, reporting, and tax treatment. QuickBooks supports Medical, Vision, and Dental plans, each requiring distinct payroll items to avoid errors seen in 30% of small businesses. Tailoring payroll items by plan type simplifies employee eligibility management and contribution limits. It also ensures compliance with ACA and IRS rules, reducing audit risks by 25%. Proper customization enhances financial clarity, enabling businesses to allocate over 20% more accurately on benefit costs, ultimately improving budgeting and employee satisfaction.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide for Health Insurance QuickBooks Payroll Issues
Troubleshooting health insurance payroll issues requires a clear 4-step approach: identify, analyze, correct, and verify. First, identify discrepancies by reviewing payroll reports and employee deductions. Next, analyze payroll item setups and tax tracking for errors, which cause 40% of common issues. Then, correct mistakes by editing payroll items or adjusting entries. Finally, verify corrections through test payroll runs and reconciliations. Following this process reduces payroll errors by up to 35%, avoids IRS penalties, and ensures employee trust through accurate paycheck calculations. Consistent troubleshooting saves time and boosts compliance confidence.
Using QuickBooks Reports to Monitor Employer Health Insurance Expenses
QuickBooks reports help track employer health insurance expenses with precision, enabling better budgeting, auditing, and compliance. Key reports include Payroll Summary, Expense by Vendor, and Liability reports. Using these, businesses identify expense trends, detect discrepancies, and reconcile payments efficiently. Regular review reduces accounting errors by 30% and improves cash flow forecasting by 20%. Reports also simplify ACA and tax reporting, ensuring all health insurance contributions are accurately documented. Setting monthly report schedules enhances financial transparency and supports informed decision-making for employer benefits management.
Streamlining Health Insurance Management in QuickBooks
Automating health insurance recording in QuickBooks saves time, reduces errors, and ensures compliance with tax laws. It cuts payroll processing time by up to 40% and improves data accuracy, reducing mistakes by 25%. Since health insurance reporting rules vary by state and country, businesses must adapt QuickBooks settings to local regulations to avoid fines. Proper training of payroll staff on recording employer-paid insurance helps maintain accuracy and compliance, reducing errors by 30%. Transparent employee benefits statements improve understanding and trust, while year-end reconciliation ensures financial accuracy and audit readiness. Following these best practices enhances payroll efficiency and supports business growth.
Benefits of Automating Health Insurance Recording in QuickBooks
Automating health insurance recording in QuickBooks saves time, reduces errors, and ensures compliance. It eliminates manual entry, cutting payroll processing time by up to 40%. Automation improves data accuracy, decreasing misclassifications and tax errors by 25%. It streamlines employee contribution tracking, ensuring correct deductions every pay period. Automated systems generate timely reports, aiding in year-end reconciliation and tax filings. Businesses also benefit from improved audit readiness and reduced risk of penalties. Overall, automation enhances financial transparency and boosts payroll efficiency, allowing companies to focus more on strategic growth than on administrative tasks.
How Health Insurance Reporting Differs Across States (or Countries)
Health insurance reporting varies significantly across states and countries, impacting compliance and payroll processing. In the U.S., states like California and New York have additional reporting requirements beyond federal ACA rules, affecting 30% of employers. Some countries mandate detailed employee benefit disclosures that differ from U.S. standards. These variations influence payroll item setups, tax tracking, and W-2 reporting. Failure to adapt to local laws can result in fines up to $5,000 per violation. Understanding regional requirements helps businesses customize QuickBooks settings, avoid penalties, and maintain accurate records tailored to each jurisdiction’s regulations.
Tips for Training Payroll Staff on Employer-Paid Health Insurance QuickBooks Procedures
Effective payroll staff training on employer-paid health insurance ensures accuracy, compliance, and efficiency. Focus on clear instruction about setting up payroll items, tax tracking types, and recording contributions in QuickBooks. Use real-world examples and hands-on exercises to reinforce learning. Regular updates on tax law changes reduce errors by 30%. Encourage staff to double-check entries and run reports to catch discrepancies early. Providing reference guides and quick-checklists saves time and improves confidence. Well-trained staff minimize costly mistakes, improve employee trust, and ensure timely, error-free payroll processing for health insurance benefits.
Understanding the Impact of Employer-Paid Insurance on Employee Benefits Statements in QuickBooks
Employer-paid insurance significantly affects employee benefits statements by enhancing total compensation visibility, improving job satisfaction, and ensuring tax transparency. Including accurate health insurance costs in statements helps employees understand their true benefit value, which can be 20-30% of total compensation. Clear statements reduce confusion about payroll deductions and tax implications. Accurate reporting supports compliance with IRS and ACA regulations, minimizing audit risks. Transparent benefits statements also aid employee retention and recruitment by highlighting comprehensive health coverage. Businesses benefit from fewer disputes, smoother payroll reconciliation, and stronger employer-employee trust.
Best Practices for Year-End Health Insurance Data Reconciliation in QuickBooks
Year-end reconciliation of health insurance data ensures accurate financial records, tax compliance, and smooth audit processes. Begin by comparing payroll reports with insurance invoices to identify discrepancies. Reconcile employer contributions recorded in QuickBooks against actual payments made. Adjust any differences through journal entries before closing the fiscal year. Review employee W-2 forms to confirm proper reporting of health insurance amounts, especially in Box 12 with Code DD. Document all reconciliations and maintain records securely for audit readiness. Following these best practices reduces errors by 30%, prevents IRS penalties, and provides clear insights for future budgeting and benefits planning.
Conclusion!
Accurately recording employer-paid health insurance in QuickBooks, whether Desktop or Online, is vital for maintaining financial records and ensuring tax compliance. By setting up payroll items, allocating costs to the right accounts, and regularly reviewing entries, you can effectively track these expenses and improve reporting credibility while promoting transparency with employees.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is setting up the correct “Tax Tracking Type” crucial for employer-paid health insurance?
The Tax Tracking Type dictates how QuickBooks treats the employer’s contribution for tax reporting, which directly affects the employee’s W-2 form and tax liability.
- Non-Taxable Setup: For standard pre-tax medical, dental, and vision premiums, the employee deduction item’s Tax Tracking Type must be set to Premium Only/Section 125 or None (for after-tax), ensuring the amount is correctly excluded from federal and payroll taxes (Social Security/Medicare).
- ACA Reporting: If the employer must report the cost of coverage under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), the company contribution item’s Tax Tracking Type must be set to Health Coverage Cost.
- Compliance Risk: Using the wrong tracking type will result in incorrect payroll tax calculations and possible penalties from the IRS for misreporting wages.
2. How does the W-2 Code “DD” relate to employer-paid health insurance, and is it a taxable amount?
W-2 Box 12 Code DD is an Affordable Care Act (ACA) reporting requirement for informational purposes only; it is not taxable income to the employee.
- Reporting Requirement: Code DD represents the total cost of the employer-sponsored health coverage (including both employer and employee contributions). This requirement applies to employers who file 250 or more W-2s for the year (though state laws, like Vermont’s, may require it for all employers).
- Non-Taxable Status: The amount reported under Code DD is for the employee’s information only. The value of the employer contribution remains excludable from the employee’s gross income and is not taxable (not included in Box 1, 3, or 5).
- IRS Compliance: Reporting Code DD correctly demonstrates the employer’s compliance with ACA transparency requirements regarding the cost of health coverage.
3. What is the accounting purpose of creating a “zero net paycheck” in QuickBooks Desktop for employer contributions?
A zero net paycheck is a specific, non-cash transaction created to record a company-paid liability or contribution without generating any taxable income or cash payment for the employee.
- Tracking and Reporting: It ensures the employer’s portion of the insurance contribution is properly recorded against the specific employee’s file and included in the annual reporting totals (like the W-2 Code DD amount).
- No Cash Impact: The paycheck’s earnings and deduction/contribution items (often using dummy Addition and Deduction items) are balanced to result in a net zero amount. This ensures the payroll transaction records the contribution without affecting the employee’s bank account.
- Procedure: This specialized process is used when the employer pays the cost directly to the vendor, but the cost must still be linked to the employee’s year-to-date (YTD) figures.
4. When recording the payment to the insurance vendor, why is it best practice to use the “Enter Bills” feature instead of a Journal Entry?
While a Journal Entry (JE) can record the expense, the “Enter Bills” and “Pay Bills” features provide a superior audit trail and ensure proper accounting for cash flow under the accrual method.
- Accounts Payable Tracking: Using Bills documents the original invoice amount, the vendor, the date due, and creates a liability (Accounts Payable). This is essential for tracking vendor balances and managing cash flow.
- Accrual Basis Accuracy: Recording the Bill when the invoice is received captures the expense in the correct accounting period, even if payment is deferred (accrual method). A JE bypasses the Accounts Payable process.
- System Integrity: Using the Pay Bills function to clear the liability ensures the vendor balance decreases appropriately, preventing the bill from showing up as unpaid on reports.
5. Why must the payroll liability and expense accounts for ACA W-2 reporting be the same in QuickBooks Desktop?
This specific setup is a technical workaround within QuickBooks to track the cost of coverage per employee for W-2 reporting without creating a double expense on the financial statements.
- Tracking without Financial Impact: By assigning the same account (e.g., “Reportable Health Coverage”) as both the Payroll Liability and the Payroll Expense account for the W-2 item, the amount automatically zeros out on the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement and Balance Sheet.
- Zero Net Effect: When the payroll item is used, the system records:
- A Credit to the “Liability” side of the account.
- A Debit to the “Expense” side of the same account.
- Purpose: This satisfies the IRS requirement to track the reportable cost on a per-employee basis while avoiding duplication of the actual insurance premium payment already recorded via the “Enter Bill” function.
6. What is the process for adjusting a prior period health insurance contribution if a payroll error is discovered?
Adjusting prior period contributions requires using the dedicated Adjust Payroll Liabilities feature, as manually editing paychecks can disrupt tax reports.
- Dedicated Tool: The Adjust Payroll Liabilities tool is the correct method for correcting year-to-date (YTD) wage bases, tax amounts, and contribution items (including health insurance) without affecting the net pay already issued.
- Procedure Steps (QuickBooks Desktop):
- Go to Employees $>$ Payroll Taxes and Liabilities $>$ Adjust Payroll Liabilities.
- Set the Effective Date to the last paycheck date of the affected quarter or month.
- Select the Employee Adjustment option and the employee name.
- Under the Item Name column, select the health insurance item.
- Enter the adjustment Amount (positive to increase, negative to decrease).
- Select Accounts Affected to control whether the adjustment impacts the G/L balances (it often should not for W-2 adjustments).
- Tax Integrity: This method is necessary to ensure payroll reports (including W-2s) reflect the correct YTD figures for compliance.
7. How should a business handle an overpayment or underpayment discovered after a health insurance payment has been recorded?
Any refund or credit for a recorded payment (overpayment) must be tied back to the original expense account to correct the total cost reported on the Profit and Loss statement.
- Overpayment (Refund): If the vendor sends a refund check for a paid bill, the refund must be recorded as a deposit.
- In the Make Deposits screen, the Received from is the vendor, and the Account field should be categorized as the Health Insurance Expense Account.
- Goal: This reduces the total recorded expense for the year, ensuring the final expense figure is accurate.
- Underpayment (Additional Expense): If an additional payment is required, it is recorded as a new Expense or a new Bill. The payment is categorized to the Health Insurance Expense Account, increasing the total expense for the period.
- Accuracy: This ensures the final balance in the Health Insurance Expense account matches the actual net cost to the business.
Disclaimer: The information outlined above for “How to Record Employer Paid Health Insurance in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?” is applicable to all supported versions, including QuickBooks Desktop Pro, Premier, Accountant, and Enterprise. It is designed to work with operating systems such as Windows 7, 10, and 11, as well as macOS.

