What is Tax Accounting and its Importance?
Tax accounting is the process of assessing and calculating taxes, preparing and filing tax returns according to IRS regulations, replying to IRS notices and letters, conducting tax audits, and adhering to IRS guidelines.
In the USA, there are three kinds of tax systems, which are:
- Local and Municipal Taxes
- State Taxes, and
- Federal Taxes
Similarly, there are two broad categories of taxes:
- Direct taxes on income in the case of individuals and professionals, profits in the case of for-profit organizations like companies, S-Corp, C-Corp, LLC, etc.
- Indirect taxes in the form of duties, customs, excise, VAT, transaction tax, etc.
Small business owners must understand and be aware of tax rules and regulations to avoid penalties, fines, etc. Maintaining tax-related documents and an audit trail is important in case of an investigation or for filing for tax credits, exemptions, or supporting evidence for deductions.
A taxpayer could be an individual, business, corporation, or other entity. Tax accounting helps determine how much a taxpayer owes in taxes.
In the USA, the IRS (Internal Revenue Code) governs and implements taxation-related laws, which describe the rules and regulations followed by taxpayers.
Tax accounting helps businesses easily identify areas for revenue optimization, cost savings, and resource allocation. It also ensures that individuals or businesses accurately file their tax returns on time, report their tax liabilities, and adhere to the tax payment deadlines.
How does tax accounting work?
The tax accountant professionals help the business determine its total taxable income (the company’s annual income after expenses) and minimize tax liability while following the tax code. The procedure includes all the elements of tax accounting.
- Profit and loss:
It defines the company’s revenue, costs, and expenses over some time. It frequently displays the amount of money the business earned before taxes, which helps the tax accountant determine whether profits are subject to taxes and what obligations the business has.
- Liabilities:
Liabilities are of two types:
- Current-year liabilities include short-term obligations due within one year or within a current fiscal year. Some examples are payroll taxes, short-term notes payable, rental fees, interest payable, income taxes, accounts payable, utilities, payroll due, and other short-term debts.
- Future year liabilities: These include long-term financial commitments. Some of the examples are government or state employee pension.
- Accounting method:
Cash or accrual are the two techniques that organizations must employ according to IRS regulations. The business records revenue in the period that is received by using cash-based accounting.
Therefore, revenue would be recorded and reported in tax returns in the next year if it received an order for products it sells late in the year, but no money changed hands until after the first of the following year.
By using the accrual basis method, businesses can record revenues and expenses as they occur rather than when money is actually transferred.
Who has to pay taxes in the USA?
In the U.S. taxation system, all levels of government, from federal to state to municipality, have the authority to tax, legislate, and regulate. Understanding who has authority over a particular matter is very important.
The federal, state, and municipal governments in the United States impose various taxes. These include income, payroll, property, sales, capital gains, dividends, imports, estates, and gifts.
The United States levies taxes on the income of its citizens and residents globally. One of the unique aspects of the U.S. taxation system is its treatment of non-resident citizens. All the non-resident aliens are taxed on their income sourced in the U.S. and functionally related to a U.S. trade or activity.
Everyone has to pay taxes as per the U.S. taxation system:

- Individuals: They are the ones who pay their annual individual income taxes to the IRS and state revenue departments.
- Professionals: They are those who earn income from salary or anyone practicing a profession, such as a doctor, teacher, or lawyer.
- Corporates ( for-profit organizations): All the business entities that are registered under the law of the United States. In addition to their owners, corporations are required to pay taxes on their taxable income. Taxes are levied on dividends that shareholders receive from corporations.
S corporations, or corporations wholly owned by citizens or residents of the United States, have the option to choose to be treated like partnerships. Certain additional business entities, such as limited liability companies, have the option of being regarded as partnerships or corporations. Partnership do not pay income tax. The partners do include their portions of partnership items in their tax calculations.
- Non-profit organizations: Non-profit organizations are legal entities formed and organized for charitable or socially beneficial purposes. Charitable organizations must pay business income taxes.
Understanding Corporate Taxation in the USA?
With the passage of U.S. tax reform legislation on December 22, 2017 (P.L. 115-97), the U.S. transitioned from a “worldwide” to a “territorial” tax system.
P.L. 115-97, among other things, permanently lowered resident corporations’ 35% CIT rate to a flat 21% rate for tax years starting after December 31, 2017.
For non-US persons, the U.S. taxation is determined by two key factors:
- The amount and duration of their presence in the U.S.
- The relationship of their income to the U.S.
These factors play a crucial role in deciding whether their income is subject to U.S. taxation or not.
- Tax Returns
Tax returns in the United States are reports submitted with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or a state or local tax collection body that contain information used to calculate income taxes or other taxes. Tax returns are prepared using forms provided by the IRS or another applicable taxing authority.
The U.S. tax system is built on the premise of self-assessment and voluntary reporting. A corporation taxpayer must file an annual tax return (usually Form 1120) by the 15th day of the fourth month following the end of the tax year.
A taxpayer may request an additional six-month extension of time to file their tax return. If you fail to file your return on time, you may face fines. Additional fines may apply for late returns on certain information returns that must be filed on time.
- Alternative minimum tax (AMT)
The Inflation Reduction Act, P.L. 117-169 (IRA), established a new corporate alternative minimum tax (also known as the CAMT) based on financial statement income. The CAMT is a 15% minimum tax applied on adjusted C corporation financial statement income (AFSI).
The CAMT increases the taxpayer’s tax when the base erosion and anti-abuse tax (BEAT) and regular tax surpass the preliminary minimum tax.
A minimum tax credit is created when a taxpayer pays CAMT because the tentative minimum tax exceeds regular tax plus BEAT. This credit can be claimed against regular tax in subsequent years to the extent that regular tax exceeds CAMT plus BEAT, and it can be carried forward.
- Base erosion and anti-abuse tax (BEAT)
A new U.S. federal tax known as the “base erosion and anti-abuse tax” (BEAT) was established by P.L. 115-97.
It has targeted the erosion of the U.S. tax base by imposing the following:
- Additional corporate tax liability on corporations (apart from S corporations, REITs, and regulated investment companies [RICs]) and their affiliates
- Average annual gross receipts for the three years ending with the previous tax year of at least USD 500 million
There are some exceptions, as certain banks and securities dealers made certain base-eroding payments to related foreign persons during the tax year of 3% (2% for certain banks and securities dealers) or more of all their deductible expenses.
The BEAT is applied to the amount after most tax credits have been deducted. The taxpayer’s regular tax liability is less than 10% (or 5% in 2018) of their “modified taxable income.”
- State and local income taxes
The CIT rates keep on from state to state, ranging from 1% to 12%.
- Sales taxes
It refers to the tax imposed on the finished goods and services. Value-added taxes and sales taxes are not allowed at the federal level. If your firm sells to clients in the United States, you must follow sales tax rules in the states where you meet registration requirements. These thresholds, tax rules, and the applicable rates vary by state and product, typically falling between 2.9% and 7.25%.
- Customs duties and import tariffs
All goods imported into the United States are subject to U.S. Customs entry regulations and are duty-free depending on their categorization under the applicable product in the United States Harmonized Tariff Schedule.
Liability for payment of duty and other customs fees is established when an entry is filed with U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). The person or legal entity on whose behalf the entry is made is responsible for paying the Importer of Record (IoR). However, the amount of duty payable may alter later if any of the information disclosed on entry is later shown to be inaccurate.
- Excise taxes
The federal and state governments levy excise taxes on various goods and activities, such as gasoline, kerosene, and diesel fuel, foreign insurance, ozone-depleting chemicals, and superfund taxes. Excise tax rates vary based on the goods and activities.
- Stamp taxes
Stamp taxes are government-imposed taxes on legal documents related to the transfer of real estate or assets. Stamp taxes, often known as transfer taxes, are imposed by state and local governments when a real property transaction is formally recorded. The value of the real property being transferred often determines the tax.
- Payroll taxes
Payroll tax refers to the taxes that employees and employers pay on earnings, tips, and salaries. Employees have taxes taken from their paychecks and paid to the government by their employer. These taxes include income taxes at the federal, state, and local levels.
Employers are normally responsible for a 6% federal unemployment tax (FUTA) on the first USD 7,000 in salaries paid to employees who meet specified criteria, with state unemployment taxes potentially reducing this amount by up to 5.4%.
For 2024, social security tax is levied on the first USD 168,600 in salaries received by employees.
Employers are obligated to withhold an equivalent amount of FICA taxes from employee pay, federal income tax at graded rates, and a 0.9% additional Medicare tax on wages over USD 200,000.
Furthermore, states may levy state income tax, state unemployment tax, workers’ compensation insurance tax, and other state-level benefit requirements at variable rates based on state legislation and the type of employees’ activities.
For 2024 and 2023, the federal supplemental withholding rates are 22% on supplemental income less than USD 1 million in the aggregate and 37% on supplemental income more than USD 1 million.
- Property taxes
Local and state governments levy property taxes on real property, and most states charge a tax on company personal property.
- Tax Period
The tax period is between January 1 and April 15 of each year when taxpayers prepare to report their taxable income for the previous year. U.S. corporation taxpayers are taxed on an annual basis. Corporate taxpayers may select a tax year other than the calendar year. New corporations may choose a short tax year for their first tax period and for changing tax years.
What are Payroll taxes?
Payroll taxes are the taxes paid on employees’ salaries to finance social insurance programs. Both employees and employers pay a similar share of Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Payroll taxes are filed with the IRS (Internal Revenue Service) via forms like the W-2, W-3, and Form 940.
Examples of payroll taxes are:
- FUTA ( Federal Unemployment Tax Act )
- Withholding taxes
- FICA ( Federal Insurance Contributions Act, Social Security Tax)
- MEDFICA (Medicare Federal Insurance Contributions Act)
The different social insurance programs are:
- Social security
- Medicare
- Unemployment insurance

Taxes are deducted from employees’ paychecks and paid by the business to the government. Federal, state, and local income taxes are included.
In the U.S, the tax percentage is 15.3% as combined from employee and employer to fund various social programs such as Social security and medicare.
Payroll taxes are collected by federal and state governments. The government uses revenue from payroll taxes to fund programs such as healthcare, social security, and workers’ compensation.
Types of Payroll taxes

Federal Income Tax
The Internal Revenue Service imposes a tax on all earnings contributing to a taxpayer’s taxable income, which is known as federal tax. The federal government collects the federal income tax.
In order to file the federal income tax, you need to complete the Form W-4. Employers want their employees to use the Tax Withholding Estimator tool to estimate the federal income tax.
It refers to the tax collected by the U.S. government to fund the Social Security program and is formally entrusted with two security trust funds. The two security trust funds are the Federal Disability Insurance (DI) Trust Fund Federal Old-Age and the Survivors Insurance (OASI) Trust Fund.
Social Security is supported primarily through payroll taxes, which are called the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) or the Self-Employed Contributions Act (SECA).
The Social Security tax is separated into 6.2% that is visible to employees (as the “employee contribution”) and 6.2% that is visible only to employers (as the “employer’s contribution”).
Medicare Tax
It refers to the mandatory payroll tax, which funds medical, hospital, and hospice care to people after the age of 65, as well as for people with disabilities and certain illnesses.
The Medicare tax goes into two different funds: the Hospital Insurance Trust Fund and the Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Fund.
The Medicare tax is a fair and equitable system, with both the employer and employee contributing 1.45%, totaling 2.9%. For individuals who earn over $200,000, an additional 0.9% is charged.
Federal Unemployment Tax
It refers to the tax that is imposed on employers to fund employment. This tax is only implemented for employers. A company becomes subject to FUTA (Federal Unemployment Tax Act) if it meets the following conditions:
- If a company pays employees wages of more than $1,500 in any calendar quarter during the year.
- One or more employees worked part of a day in twenty or more weeks during the year.
State Unemployment Tax
When an eligible worker is fired unwillingly (for any reason other than gross misconduct or leave), the state is required to provide unemployment compensation.
States charge employers an unemployment tax to help pay for this burden. Employers’ rates are determined by their experience with filing claims, just like in the case of insurance.
The tax rate on these employers rises in proportion to the number of claims filed by former workers. The state notifies an employer each year of its tax rate, which is always subject to a minimum amount.
Payroll Tax Forms
| Payroll Tax Forms as Mandated by IRS | ||
| S.No. | Form Name | Description |
| 1 | W-2 | The W-2, Wage, and Tax Statement is an IRS form that employers must send to an employee and the IRS every year. |
| 2 | Form 941 | Form 941, Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return, is used to report social security tax, income tax, or Medicare tax. |
| 3 | W-4P | W-4P, a Withholding Certificate for Periodic Pension or Annuity Payments, is a form where the payer can withhold the correct amount of federal income tax. |
| 4 | Form 8959 | Form 8959, Additional Medicare Tax, is used to determine the amount of additional Medicare tax you owe and the amount withheld by your employer ( if any ). |
| 5 | Form 1042-T | Form 1042-T, Annual Summary and Transmittal of Forms 1042-S is used to transmit paper Form 1042-S. |
| 6 | Form 944 | Form 944, Employer’s Annual Federal Tax Return, is for the smallest employers who will file and pay taxes annually instead of quarterly. |
Federal Payroll Tax rate
- Social Security tax rate: 6.2% for the employee + 6.2% for the employer
- Medicare tax rate: 1.45% for the employee + 1.45% for the employer
- Additional Medicare: 0.9% for the employee when wages exceed $200,000 in a year
- FUTA tax rate: 6% for the employer on the first $7,000 paid to the employee
Types of Tax Identification Numbers (TIN)

For filing taxes, the IRS allows different identification numbers to different taxpayers.
- Social Security number (SSN):
It is a 9-digit unique number assigned by the Social Security Administration to U.S. citizens, permanent residents, and temporary working residents. These numbers are commonly written as three fields separated by hyphens: XXX-XXX-XXXX. The three parts are:
- The first part is the Area number.
- The second part is the Group number.
- The third part is the Serial number.
The SSN is needed to secure legal employment in the U.S., receive social security benefits, and access certain government services.
- Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN):
It is a 9-digit number assigned by the Internal Revenue Service to non-residents and resident aliens, their spouses, and dependents who cannot get a Social Security Number. These numbers are written as 9XX-XXX-XXX (always start with the number “9”) and have a range of numbers from 50 to 65, 70 to 88, 90 to 92, and 94 to 99 for the fourth and fifth digits.
To apply for an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number, the applicant must fill out the W-7 form, along with another application form. This process ensures that the ITIN is issued to those who meet the eligibility requirements.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN):
It is a 9-digit number issued by the Internal Revenue Service to the business entity. It is also known as a Federal Tax Identification Number. These numbers are written as XX-XXXXXXX.
Eligible applicants should fill out Form SS-4 (available on the IRS website) and should use it to report their capital gains and income for taxation purposes. The IRS offers it for free, and business entities must apply for an EIN by phone, fax, online, or mail before they begin operating.
EIN stands for Employer Identification Number. It is a nine digit unique number which is assigned to the business entity. The EIN is also known as a Federal Tax Identification Number.
EIN is formatted as XX-XXXXXXX.
This number is assigned to the company by the Internal Revenue Service and it includes information about the state in which the company is registered.
Partnership firms, LLC and corporations must get their EIN to file their business income tax return. The different types of organizational structures that require EIN’s are:
- Real estate mortgage investment conduits.
- Businesses with a Keogh plan.
- Farmers’ cooperatives.
- Nonprofit organizations.
- Estates.
- Plan administrators.
- Businesses that pay excise, alcohol, tobacco or firearm taxes.
- Certain types of trusts.
Note: In case of sole proprietors or single member LLC with no employees, they have the option to use the Social Security number instead of EIN, while filing business tax.
EIN Format
EIN is written in the form of XX-XXXXXXX. There are EIN Decoders on the web that help in determining in which state the company registered the EIN.
| Location/ Campus | Valid EIN prefixes |
|---|---|
| Andover | 10, 12 |
| Atlanta | 60, 67 |
| Austin | 50, 53 |
| Brookhaven | 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 11, 13, 14, 16, 21, 22, 23, 25, 34, 51, 52, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 65 |
| Cincinnati | 30, 32, 35, 36, 37, 38, 61 |
| Fresno | 15, 24 |
| Kansas City | 40, 44 |
| Memphis | 94, 95 |
| Ogden | 80, 90 |
| Philadelphia | 33, 39, 41, 42, 43, 48, 62, 63, 64, 66, 68, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 91, 92, 93, 98, 99 |
| Internet | 20, 26, 27, 45, 46, 47, 81 |
| Small Business Administration (SBA) | 3 |
- Adoption Tax Identification Number:
It is a 9-digit number issued by the Internal Revenue Service to individuals who are legally adopting a child but cannot obtain an SSN to complete their tax return. It is a temporary number that expires after every two years, with certain exceptions.
The need for ATIN occurs when the child’s SSN is unknown or the child has never had an SSN. To apply for ATIN, use the W-7A tax form and provide below-mentioned information:
- Child’s name
- Birth information
- Name of the placement agency
While applying, make sure that the individual is a U.S. citizen or resident child and that the adoption procedure is pending.
- Preparer Tax Identification Number:
It is an 8-digit unique number issued by the Internal Revenue Service to paid tax return preparers. It was created to protect the privacy of tax preparers. All the enrolled agents ( the ones who assist or prepare the federal taxes for compensation ) must have a valid PTIN. You can get your PTIN by following the below-mentioned steps:
- Create your account.
- Apply for your PTIN.
- Pay your fee.
Once the fee payment is done, you will get the PTIN.
What are the different types of tax accounting?
- Tax Accounting for Individuals – Individuals’ main focus in tax accounting is factors such as income, investment outcomes, deductions, and other aspects impacting tax obligations. General accounting incorporates all financial funds ( inflows and outflows ), including personal expenses that do not have tax implications.
- Tax accounting for Businesses – Tax accounting involves a more detailed analysis for businesses than for individuals. In addition to tracking the company’s earnings, businesses must also account for outgoing funds related to business obligations. This includes specific business expenses and distributions to shareholders.
- Tax Accounting for Tax-Exempt Organizations – Even tax-exempt organizations require tax accounting. These organizations must file annual returns detailing incoming funds, such as grants or donations, and how these funds are used in their operations. This ensures compliance with laws and regulations governing tax-exempt entities.
Tax Accounting professionals
Hiring a professional tax accountant is optional, but if you have a tax accounting professional handling all your accounts, then handling the record is much easier. Tax accountants easily deal with confidential and complex data that is regulated by law.
There are different types of tax accountants based on the work industry or the client industry. Some of them are mentioned below:
- Management Tax Accountants: They are responsible for managing financial and tax matters for businesses or organizations.
- Small Business Tax Accountants: They are responsible for managing the finances of smaller and privately owned businesses.
- CPA Tax Accountants: They provide services related to tax filing, replying to IRS notices, and are eligible to testify tax statements and declarations.
- Personal Tax Accountants: They are responsible for managing individuals’ taxes.
- Forensic Tax Accountants: They are responsible for investigating businesses and individuals in anticipation of legal proceedings.
- Government Tax Accountants: They are the ones who work with state, federal, and local government agencies.
What are the services offered by a Tax Accountant?
- Maintaining annual tax-related plans for clients.
- Managing tax audits with authorities ( if needed).
- Making sure clients meet the tax deadlines quarterly or annually.
- Maintaining federal and state tax returns.
- Providing tax planning advice.
- Informing clients about tax laws and liabilities
- Ensuring that the client pays less.
Outsource your tax accounting for a Stressfree tax season – eBetterBooks
If you are someone who needs tax services for a small business, it’s time for you to try out eBetterBooks for tax assistance.
eBetterBooks offer the most affordable plans and the best domain specialists to help you with all tax services, like generating accurate documents, adhering to IRS tax guidelines, classifying income and expenses, tracking tax credits, etc.
From tax planning to tax preparation, their dedicated professionals will provide you with tax consultation, online tax filing support, and VAT return submission.
eBetterBooks, the tax service provider will also assist you in detecting possible deductions or exemptions, conducting audits, developing future tax strategies, and presenting tax projections.
Using tax accountant software
In order to handle your tax finances, there are different software available in the market. One of the well-known software is QuickBooks by Intuit. They offer both desktop and cloud-based accounting setups to the business. While handling the financial data, you may encounter some errors. The reasons behind this are:
- There could be a damaged program file in the system.
- Your company name may be too long.
- The software installation is not done correctly.
- Your windows may not be updated.
- Your program files may be damaged.
- The software is not updated.
- The data files are not synced with the software.
eBetterBooks will assist you in resolving these errors and help you get a better understanding of your financial record.
EIN vs SSN
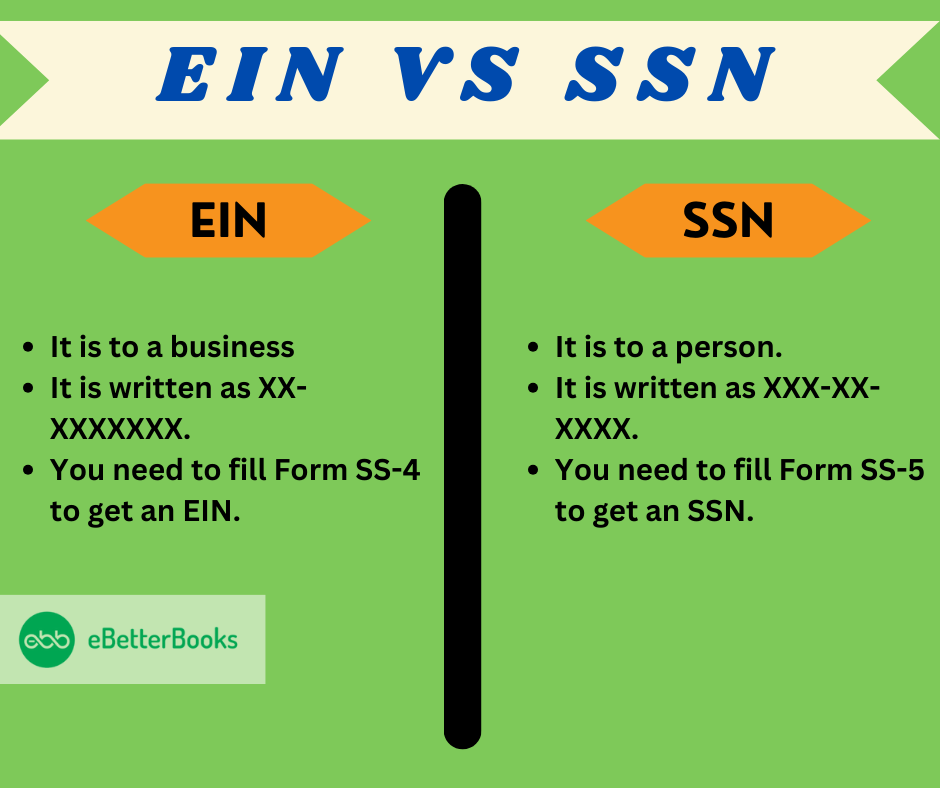
| Employer Identification Number (EIN) | Social Security Number (SSN) |
| It is to a business | It is to a person. |
| It identifies a business in the US. | It identifies US citizens and permanent residents. |
| It is written as XX-XXXXXXX. | It is written as XXX-XX-XXXX. |
| The IRS uses EIN to keep track of the business filings. | The IRS uses EIN to keep track of personal tax filings. |
| You need to fill Form SS-4 to get an EIN. | You need to fill Form SS-5 to get an SSN. |
What Exactly Is A Tax Deduction?
A tax deduction is an expense that is deducted from your taxable income. In other words, it refers to an item or expense that can reduce the taxes a person owes in an accounting year.
Tax deduction is also known as “tax write-off”.
Tax deductions are beneficial for small businesses as they lower the tax bill, and the business pays a comparatively lower amount.
Tax deductions are of two types:
Standard deductions
Standard deductions refer to the amount that tax filers can subtract from their adjusted gross income to lower the amount of income that is subject to tax.
The Internal Revenue Service adjusts the standard deduction each year for inflation. The standard deduction amount is based on age, filing status and other criteria.
Itemized deductions
Itemized deductions refer to specific expenses that can be subtracted from each component of the gross income to reduce the tax bill.
The list of expenses which can be itemized includes charitable contributions, medical expenses, or state and local taxes. The items covered in the itemized deduction are listed on Schedule A of IRS Form 1040.
Taxpayers have the flexibility to choose the type of deduction that best suits their financial situation – standard deductions or itemized deductions. It’s important to keep all the necessary documents in hand in case the IRS requests them.
In case you are not well versed with the nuances of tax accounting laws and codes by the IRS, it is advisable to outsource your tax preparation and tax filing to a tax service provider.
List of Business Tax deductions

1. Standard Mileage Rates
A standard mileage tax deduction is the default cost per mile for taxpayers who deduct the expense of using their vehicle for charitable, business, or medical purposes. It is set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
The tax rates differ annually, and they are the same for all types of vehicles, whether electric or gas-powered. The current Standard mileage rate is 67 cents per mile.
2. Work Opportunity Tax Credit
The Work Opportunity Tax Credit is a federal tax credit for businesses. It is a powerful incentive for employers, offering tax credits for hiring individuals from certain targeted groups who have faced barriers to employment.
Employers must first get certification from a State Workforce Agency (SWA) stating that the new hire satisfies the requirements of one of the target groups before they may submit a claim for a Work Opportunity Tax Credit. IRS Form 8850 and one of two Department of Labor forms are used for this.
3. Opportunity Zones
Opportunity Zones are tax incentives to encourage investment and growth in distressed areas of the United States.
These economic development tools are used for commercial and industrial real estate, infrastructure, and housing.
4. Employee Retention Credit
Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is a refundable payroll tax credit designed to encourage employers to retain their employees during the COVID-19 pandemic tax years 2020 and 2021.
It is also known as the Employee Retention Tax. Companies who file an adjusted Form 941 X – Quarterly Federal Payroll Tax Return for the quarters in which they were an Eligible Employer are still able to apply for the ERC.
5. Clean vehicle credits
The clean vehicle credit is a nonrefundable credit meant to lower the cost of qualifying plug-in electric or another clean vehicle.
Clean vehicles include battery electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid vehicles, and fuel-cell electric vehicles. Always determine if your vehicle qualifies for the tax credit criteria or not.
6. Credit for builders of energy-efficient homes
Eligible contractors who build or reconstruct qualified energy-efficient homes can significantly boost their finances by claiming tax credits of up to $5,000 per home. This serves as a strong incentive for them to engage in energy-efficient construction.
7. Advanced energy project credit
The Advanced energy project credit is a lucrative opportunity for manufacturers and other entities. By investing in qualifying advanced energy projects, they can benefit from this credit, available through the Department of Energy, which is designed to encourage and support such investments.
8. Employer-provided child care credit
The Employer-provided childcare credit is designed to help employers cover some childcare facilities for their employees. Companies that provide childcare for their employees become eligible for the tax credit.
Under the Employer-Provided Childcare Credit, employers can receive a tax credit of up to $150,000 annually to offset 25% of qualified childcare facility expenses and 10% of qualified child care resource and referral expenses.
9. Research credit
For those interested in the Research credit, the IRS provides comprehensive guidelines and audit technique guides to assist in the examination of research credit cases, ensuring a clear and most importantly, a fair process.
10. Deducting business expenses
It’s crucial to understand the different types of business expenses, and the general rules for deducting expenses. This knowledge will help you navigate the tax system effectively and ensure you’re not missing out on potential deductions.
11. Energy-efficient commercial buildings deduction
Energy-efficient commercial buildings tax deduction is a federal incentive designed to promote energy efficiency in commercial buildings. It is also known as Section 179D.
Building owners stand to benefit significantly by increasing energy efficiency in certain building systems by at least 25%, as they may be able to claim a tax deduction. This not only reduces their tax burden but also contributes to a more sustainable environment.
12. Abusive tax shelters and transactions
The IRS has a comprehensive strategy to combat abusive tax shelters and transactions, which includes guidance on abusive transactions, regulations governing tax shelters, and a hotline for taxpayers to report abusive technical transactions.
Conclusion
Tax accounting is a useful accounting tool that helps companies understand their tax liability and avoid penalties. It helps both businesses and individuals declare their correct income and pay appropriate taxes while following GAAP regulations.
FAQs
Q 1. Who issues EIN?
Ans. Employer Identification Number ( EIN ) is issued by the Internal Revenue Service.
Q 2. In how many days, EIN is issued?
Ans. The time duration to get the EIN depends upon the medium through which you have applied for.
If you have:
- Apply by Mail: You will get the EIN number in four weeks.
- Apply online: You will get the EIN immediately.
- Apply by Fax: You will get the EIN in about one week, but if you have not included the fax number, then it might take up to two weeks.
Q 3. Does EIN have an expiration date?
Ans. No, EIN doesn’t have an expiration date. Once the EIN has been created and assigned to an entity , it will never expire, even if the entity disappears.
Q 4. Is EIN for individuals or businesses?
Ans. EIN is for the business entity in the United States. You need to have EIN in order to run your business.
Q 5. Does getting an EIN cost money?
Ans. No, EIN is a free service provided by the Internal Revenue Service.
Difference Between Business Expenses and Personal Expenses
This article helps small business owners, self-employed individuals, and gig workers understand the crucial distinction between business and personal expenses. It explains how accurately categorizing…
Selecting Tax Service Provider
This article emphasizes the importance of hiring a qualified tax professional to navigate the complexities of tax filing. It highlights how experts, such as CPAs,…
General Business Credit
General Business Credit (GBC) helps businesses reduce their tax liabilities by offering tax credits that directly lower the amount owed. This credit supports businesses of…
C-Corp Taxes in USA
A C Corporation offers liability protection and unlimited growth potential through stock sales, making it an attractive option for businesses seeking to raise capital. While…
Partnership Firm Taxes
This article helps partnership firms and LLC owners understand the key aspects of their tax obligations in the U.S. It explains pass-through taxation, self-employment taxes,…

