Customer Prepayments are also known as Customer Deposits, where funds are received from customers in advance of the delivery of goods or services. These prepayments are accounted for as liabilities until the products or services are provided.
When a customer provides a prepayment, it affects the balance sheet by increasing the company’s liabilities and cash/assets.
By recording customer prepayments in QuickBooks, businesses can ensure that their financial records accurately reflect the amount of revenue already earned, providing a clear picture of their outstanding receivables. This practice also allows you to get more accurate cash flow forecasts and make better decisions related to budgeting and resource allocation.
Why do you need to Record Customer Prepayments in QuickBooks?
Recording customer prepayments in QuickBooks is crucial to accurately manage accounts receivable and maintain robust financial management practices within the business.
By recording customer prepayments in QuickBooks, businesses can ensure that their financial records accurately reflect the amount of revenue already earned, providing a clear picture of their outstanding receivables. This practice also allows you to get more accurate cash flow forecasts and make better decisions related to budgeting and resource allocation.
Integrating prepayments into the bookkeeping system offers streamlined tracking and reconciliation of customer balances, reducing the occurrence of errors or fraudulent activities, and ensuring complete transparency in financial reporting.
Recording Customer Prepayments in QuickBooks Online
Some customers may pay you in advance if you raise an invoice for the products or services provided. Customer prepayments are also known as Payments in Advance / Payments on Account.
For recording customer repayments, you need to:
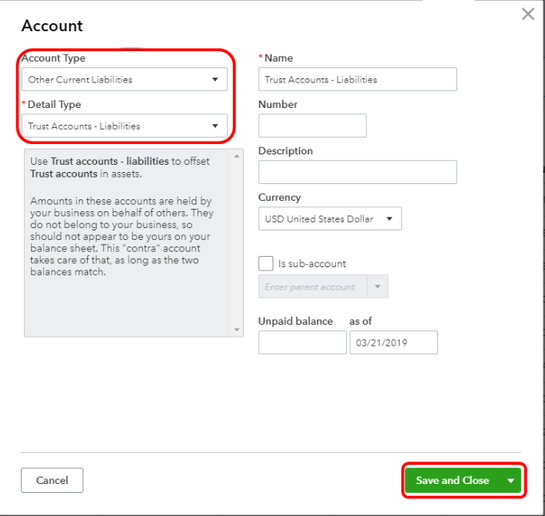
Step 1: Create a Current Liability account to track Prepayments
- Navigate to Transactions
This is typically found in the main menu of your accounting software. It allows you to manage various financial transactions.
- Choose Chart of Accounts
The Chart of Accounts is a listing of all accounts used in your business’s general ledger. This is where you will create the new liability account.
- Press the New Button
Look for a button labeled “New” or “Add” within the Chart of Accounts section. This action initiates the process of setting up a new account.
- Select Current Liabilities
In the Account Type drop-down list, choose “Current Liabilities.” This category includes obligations that are expected to be settled within one year, such as prepayments from customers.
- Detail Type Drop-down List
You’ll see another drop-down menu after selecting Current Liabilities for more specific classifications. Choose “Current Liabilities” again to ensure your account is correctly categorized.
- Enter Account Name
In the name field, type a descriptive name for your account, such as “Customer Prepayments.” This helps you and others understand the purpose of the account at a glance.
Tip: If a small number of Customers pay you in this way, you can create Sub-Accounts for each Customer as this will make it easier for you to track the amounts paid.
- Hit the OK Tab
Finally, confirm your entry by clicking on the “OK” or “Save” button. This action will create your new Current Liability account.
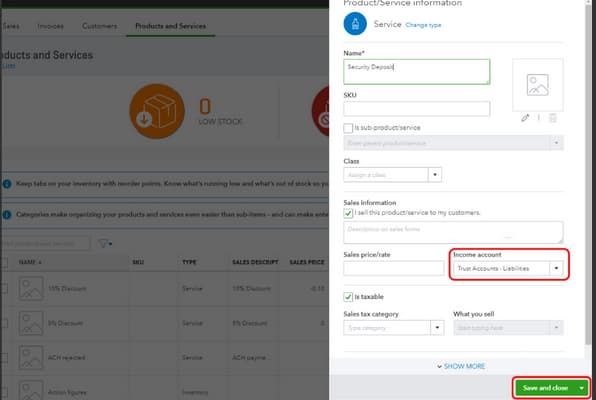
Step 2: Create a Product or Service Item that posts to the above Account
- Access Products and Services
Click on the Gear icon (⚙️) located in the upper right corner of your screen. From the dropdown menu, select Products and Services.
- Create a New Service
Click on the New button to initiate the creation of a new product or service. Choose Service from the options presented.
- Enter Service Details
In the Name field, enter a descriptive name for your service, such as Customer Prepayments.
- Select Income Account
Hover over the Income Account field. A drop-down menu will appear. Select the account you created in Step 1 from this drop-down list.
- Save Your Changes
After entering all necessary information, click on the Save and Close icons to finalize the creation of your service item.
Step 3: Enter Customer Prepayment
- Create a New Sales Receipt
Click on + New. Select Sales Receipt from the dropdown menu.
- Fill in Customer Details
Choose the Customer Name from the list. Set the Payment Date to reflect when the payment was received. Select the Bank Account where the money was deposited.
- Record the Prepayment
In the PRODUCT/SERVICE field, click on the Prepayments account that you created in Step 2. Enter the Amount Received in the Amount column.
- Save and Close
Press Save, and then close the window.
- Repeat for Additional Payments
For any subsequent payments made in advance of an invoice being raised, repeat steps 1 through 5 (3a-3e).
Step 4: Enter the Prepayment to the Invoice
- Create a New Invoice
Click on + New. Select Invoice from the dropdown menu.
- Fill in Customer Details
Enter the customer details as you normally would. List all services provided in the line items section to ensure that each service is detailed appropriately.
- Add Prepayment Item
On the last line of the invoice, select the customer prepayment item that you created in Step 2.
- Enter Prepayment Amount
Type the amount of prepayments as a negative value (e.g., -100.00).
- Review and Save
Double-check all entries for accuracy. Save/Send: Once confirmed, save or send the invoice as required.
IMPORTANT – The amount in Step 4d needs to be entered as a negative with a VAT code selected before, as this ensures VAT isn’t counted twice.
Step 5: Review & Pay the Invoice Balance – If there is a balance due after the prepayment is applied
- Find and Open the Invoice
Locate the invoice that requires payment. You can typically find this under the “Invoices” or “Accounts Receivable” section. Click on the invoice to open it.
- Press the Receive Payment Button
Look for the Receive Payment button, usually located at the top right-hand corner of the invoice page. Click on this button to initiate the payment process.
- Enter the Amount Being Paid
In the payment window that appears, locate the Amount box. Enter the amount you are paying towards the balance due on the invoice. Ensure that this amount reflects any prepayments already applied.
- Save and Close
After entering the payment amount, review all details to ensure accuracy. Click on the Save and Close tabs to finalize the transaction and update your records.
To identify the amount of prepayments made to a Supplier, you are recommended to run the following report:
- Navigate to Transactions and select Chart of Accounts.
- Locate the Customer Prepayments account.
- Under the Actions column to the right-hand side, choose the drop-down next to Account history and then click on Run Report.
- After this, hit the Report period drop-down menu and then select the required date range.
- If you have all Customer prepayments going to the same Account, click the Group by drop-down and press Name.
- Choose to Run Report at the end.
How to Set up, Record, and Manage Customer Prepayments in QuickBooks Desktop?
Customer prepayments, also known as customer deposits, are payments you receive from a customer before an invoice is created and the product or service is delivered.
Important: You can manage and use customer prepayments in QuickBooks Enterprise 24.0 or later.
Requirements to use Prepayments
Prepayments
- It can only be used with sales orders and estimates
- It can be used with Progress and Non-Progress estimates
- Can’t be edited once they’re applied to invoices
- Can’t be used with multi-currency turned on
Note: If you use Prepayments and then turn multi-currency on, Prepayments will be turned off.
Step 1. Turn on Prepayments
- Hover over the Edit menu, and then select Preferences.
- Choose Payments and then Company Preferences.
- Move to Prepayments and then click on Prepayment Settings.
- Press Turn On Prepayments.
- Moving towards the Current Liability account, then select an esxGo to Current Liability Account and opt for a current liability account or click to create a new one.
- Once done, press OK and then hit the OK tab once again in preferences.
Step 2. Receive Prepayments on a Sales Order or Estimate
It is important to create and save a new sales order or open any existing sales order.
Note: If you don’t have sales orders turned on in your company file, you’ll have to enable it first.
- Create a new existing sales order or estimate or open an existing one.
- Now, click on Receive Payments.
- Choose Prepayment on Sales Order or Prepayment on Estimate.
- Also, open Receive Payments from the home page or the Customer Center.
- Select Prepayment on Sales Order or Prepayment on Estimate, then the sales order(s)/estimate(s) to receive the prepayments.
- Enter the amount and other details for the prepayment, and then hit the Save and Close icons.
- Then, you’ll see the amount entered for PREPAYMENT APPLIED.
Step 3. Print a Sales Order or Estimate that shows a Prepayment Received
- Open the sales order or estimate, then click Formatting.
- Choose Customize Data Layout and then Footer.
- Now, select Prepayments and Balance Due.
Note: You can opt for Layout Designer to adjust the position of these fields under the print template.
- Press OK and click Print.
Step 4. Apply a Prepayment Credit to an Invoice
- Go to the sales order or estimate and then choose Create Invoice.
- Press Save this invoice, and then Yes to apply for prepayment credits.
Note: you can also click Apply for credits on an invoice to apply for prepayment credits.
- Select the prepayment credit and enter or edit the credit amount to apply to this Invoice. Then hit the Done tab.
Run Reports to see Open Prepayments on Sales Orders or Estimates
There are two reports you can run to see open prepayments and open prepayment balances: the Open Prepayments by Customer and the Open Sales Order by Customer reports. Here’s how to run and customize them.
Open Prepayments by Customer Report
This report allows you to access all open prepayments you’ve received that you haven’t applied to an invoice.
- Move to Reports.
- Click on Customers & Receivables.
- Then, select Open Prepayments by Customer.
You can customize this report to include prepayments that have been fully applied to invoices.
- Choose Customize Report, then Filters.
- After this, select Prepayment Balance, then Either, and press OK.
Open Sales Order by Customer Report
- Head to Reports and then Sales.
- Choose Open Sales Order by Customer Report.
The Prepayment Open Balance has been added to this report. You can customize this report to show open estimates and sales orders.
- Click on Customize Report, then Filters.
- Select Transaction Type, then Multiple Transaction Types.
- After this, choose Estimate and Sales Order, then press OK.
- Hit the OK tab again.
The report will update to display both open sales orders and estimates with their open prepayment balances.
Edit a Prepayment
You can edit a Prepayment if it hasn’t been applied to an invoice. But once it’s been applied to an invoice, you’ll have to delete the prepayment (this will also delete the two linked general journal entries) and then create a new Prepayment.
Refund a Prepayment
Prepayments, like other customer payments, can be refunded. If the payment hasn’t been deposited to your bank, you can delete the prepayment and the sales entries it’s applied to (sales order, estimate, and invoice). However, if the prepayment has been deposited to your back, you can either create a credit memo and apply it to another invoice or write a check to the customer.
Record Upfront Customer Deposits in QuickBooks!
You’re recommended to set up and use an item which has a liability account on it to hold customer deposits. Yes, it’s also a liability since you received the prepayment before providing the services. This way, although your business is holding the deposits, no sales income is posted until it’s applied.
Once you open the liability account you’ve created, do you only see A/R? With this, let’s make sure you’ve set them up correctly, as well as the Receive payment.
So, let’s record the upfront deposits you received from your customer. Follow the steps below to record upfront customer deposits in QuickBooks:
Select Enter Sales Receipts
Navigate to the Customers menu and choose Enter Sales Receipts.
Choose Customer or Job
From the Customer: Job drop-down list, select the appropriate customer or job.
Deposit Account Selection
If the Deposit To field appears, select the account where you want to deposit the funds. If this field does not appear, the funds will be recorded as Undeposited Funds, which can be deposited later.
Select Payment Method
Choose the payment method used for the deposit.
Enter Relevant Information
Fill in the necessary details, such as Date and Sale No., in their respective fields.
Detail Section
In the Detail section, choose the Upfront Deposit item you created from the Item drop-down list.
Input Deposit Amount
Enter the amount of the deposit or retainer in the Amount field.
Save Transaction
Click on Save and Close to complete the entry.
To record the Payment as a Deposit, here’s how:
- Click +(plus) icon.
- Select Bank Deposit.
- Once done, choose Accounts Receivable under Account to enter Bank Deposit.
- Hit the Save and Close tabs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Recording Customer Prepayments
Recording customer prepayments accurately is crucial for maintaining financial integrity and ensuring proper cash flow management.
Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Misclassifying Prepayments as Revenue
One of the most significant errors is treating prepayments as revenue before the corresponding goods or services have been delivered.
Prepayments should be recorded as liabilities, specifically under accounts such as Unearned Revenue or Customer Deposits.
Recognizing these amounts as revenue prematurely can lead you to overstate income statements and misleading financial reports which can affect business decisions and investor perceptions.
Failing to Link Prepayments to Customer Accounts
Another common mistake is not linking prepayments to the respective customer accounts. This negligence can result in balance mismatches and complicate the reconciliation process.
When prepayments are not tagged to specific customers it becomes challenging to track outstanding liabilities and apply payments accurately against future invoices which leads to confusion during audits or financial reviews.
Delaying Application of Prepayments to Invoices
Refrain from forgetting or delaying the application of prepayments to invoices can create discrepancies in accounting records. It is important to apply prepayments promptly once the related service or product is delivered.
It ensures that the liability is reduced accordingly and that the revenue is recognized accurately in financial statements. Delays can lead to complications in cash flow management and may result in customer dissatisfaction if their payments are not reflected correctly.
Advanced Strategies for Managing Customer Prepayments in QuickBooks
Effectively managing customer prepayments is vital for accurate accounting and healthy cash flow. This guide covers advanced QuickBooks techniques, from handling partial payments to automating workflows. Each strategy is designed to help you streamline operations, improve financial clarity, and maintain strong customer relationships. Whether you’re managing multiple projects or adapting to industry-specific needs, these insights will empower you to optimize your prepayment processes with precision and confidence.
How to Handle Partial Prepayments and Split Payments in QuickBooks
Partial prepayments and split payments in QuickBooks are useful for improving cash flow management and offering flexibility to customers. To implement them correctly, follow these structured steps:
- Use Partial Prepayments to Improve Cash Flow: Partial prepayments allow you to collect a portion of the total payment before delivery. This approach helps reduce financial risk and secures commitment from the customer.
- Apply Split Payments for Flexible Transactions: QuickBooks enables you to split payments across multiple methods (e.g., cash, credit card, bank transfer). You can also break down large invoices into smaller, manageable payments while tracking each one separately.
- Create Separate Sales Receipts or Invoices for Each Installment: For every partial or split payment, generate a distinct sales receipt or invoice. Be sure to assign the correct liability account and link it to the respective customer record to maintain accuracy.
- Record All Payment Details Clearly: Always log the date, amount, and payment method for each transaction. This practice ensures transparency and maintains a clear audit trail for future reference.
- Ensure Books Stay Reconciled in Real Time: A structured approach to handling partial and split payments increases financial accuracy, simplifies follow-up on dues, and helps keep your accounting records updated and balanced.
Managing Customer Prepayments Across Multiple Projects or Jobs
Customer prepayments for multiple projects can lead to confusion and misallocations if not managed properly. To handle them effectively in QuickBooks, follow these best practices:
- When customers prepay for multiple jobs, you must separate each amount, assign it to a specific project, and avoid mixing balances.
- In QuickBooks, use sub-customers or job tracking to tag each payment accurately, maintain control, and prevent allocation errors.
- Always create individual sales receipts or deposits for each project to reflect true liability and streamline billing later.
- This method improves reporting clarity, shows project-level cash flow, and helps identify under- or over-utilized funds.
- Proper project tagging avoids confusion, ensures customer trust, and keeps your project timelines financially aligned.
Tracking Prepayments in Industry-Specific Scenarios (e.g., Construction, Events, SaaS)
Prepayments are handled differently across industries, and understanding their application is key to accurate financial management.
Here’s how prepayments function in key sectors and how QuickBooks supports these workflows:
- Construction: Prepayments are typically used to cover upfront material costs, secure scheduling, and reduce financial risk for contractors before the work begins.
- Events: Deposits help confirm bookings, reserve key resources (such as venues or equipment), and ensure customer commitment prior to event delivery.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Advance payments lock in user subscriptions, improve revenue forecasting, and support automated recurring billing structures.
- QuickBooks Functionality: QuickBooks enables businesses to assign prepayments to specific projects, classes, or service items, ensuring that revenue recognition remains accurate and aligned with the work performed.
- Best Practice: Adapting prepayment workflows according to the specific industry prevents misallocation, improves compliance with accounting standards, and ensures that clients receive fair and transparent billing.
How to Adjust Prepayments When Invoices Are Modified or Cancelled
Adjusting prepayments correctly is crucial to ensure your financial records remain accurate and compliant.
Follow these key steps to handle prepayments when invoices are changed or cancelled:
- Update Prepayment for Modified Invoices: If an invoice is modified (e.g., amount changed), adjust the linked prepayment to match the new total. This prevents overbilling and keeps your liability records accurate.
- Handle Cancellations Properly: When an invoice is cancelled, you must either delete the prepayment entry, reassign it to another invoice, or issue a refund—based on what the customer prefers.
- Use the Right Accounting Tools: Use tools like credit memos, journal entries, or re-applied payments in accounting software (such as QuickBooks) to adjust the books correctly.
- Maintain Full Audit Trail: Document all changes with clear notes, including the customer name and original transaction references. This supports audit readiness and transparency.
- Ensure Accuracy and Compliance: These practices help you avoid reporting errors, maintain customer trust, and stay compliant during financial audits or reviews.
Automating Prepayment Workflows Using QuickBooks Integrations and Add-Ons
Automating prepayment processes in QuickBooks helps reduce manual effort, eliminate common errors, and improve overall cash flow tracking.
To streamline this, follow these steps and use recommended tools:
- Set Up Prepayment Automation: Use QuickBooks features or add-ons to schedule and apply customer prepayments automatically. This saves time and ensures accurate application of advance payments.
- Integrate with Workflow Tools: Connect QuickBooks with platforms like Zapier, TSheets, or InvoiceSherpa to automate reminders, payment confirmations, and data syncing between systems.
- Use Smart Add-Ons: Implement add-ons that support split payments, real-time customer balance updates, and automatic matching of payments to invoices.
- Enhance Reporting and Reconciliation: Automated systems improve reporting accuracy and accelerate bank reconciliation by reducing human errors and duplications.
- Choose Tools Based on Your Business Needs: Select integrations and add-ons based on your business size, industry, and workflow complexity to optimize efficiency and avoid unnecessary overhead.
Essential Supplementary Insights for Effective Customer Prepayment Management
Understanding the nuances of customer prepayments is key to maintaining accurate financial records and improving cash flow management. This section explores crucial supplementary topics, including the difference between prepayments and retainers, accounting impacts, and best internal control practices. You’ll also learn how to reconcile accounts efficiently and use custom reports to gain actionable insights. These insights will help you avoid errors, optimize workflows, and make smarter financial decisions with QuickBooks.
Key Differences Between Prepayments and Retainers in QuickBooks
Prepayments and retainers both involve upfront customer payments but serve different purposes. Prepayments are advances for specific goods or services, recorded as liabilities until delivery. Retainers are deposits for ongoing or future services, often used by consultants or agencies, and may be drawn down over time. In QuickBooks, prepayments link directly to invoices, while retainers require careful tracking to apply against multiple bills. Understanding these differences helps maintain accurate records, avoid revenue misstatements, and manage customer expectations clearly. Proper classification ensures compliance and improves financial reporting accuracy.
How Prepayments Affect Cash vs. Accrual Accounting Methods
Prepayments impact cash and accrual accounting differently, affecting when revenue and expenses are recognized. In cash accounting, prepayments are recorded as income only when received, improving immediate cash flow visibility. In accrual accounting, prepayments are treated as liabilities until the product or service is delivered, ensuring revenue matches earned periods. QuickBooks supports both methods, allowing businesses to track prepayments accurately and comply with accounting standards. Understanding these distinctions helps you maintain clear financial records, avoid misstated income, and make informed budgeting decisions based on your accounting approach.
Best Practices for Internal Controls on Customer Prepayments
Strong internal controls on customer prepayments protect your business from errors, fraud, and mismanagement. Start by segregating duties—ensure different employees handle receipt recording, bank deposits, and reconciliation. Use approval workflows for large prepayments, and maintain detailed documentation linking payments to customers and invoices. Regularly reconcile prepayment liability accounts in QuickBooks to catch discrepancies early. Implement audit trails and restrict access to sensitive financial data. These practices improve accuracy, safeguard cash flow, and enhance stakeholder confidence in your financial reporting.
Reconciling Prepayment Accounts During Month-End and Year-End Closures
Reconciling prepayment accounts regularly is crucial for accurate financial reporting. At month-end and year-end, review all customer prepayments recorded in QuickBooks. Match prepayment balances against invoices issued to ensure proper application. Identify any unapplied or misclassified amounts and correct them promptly. Reconciliation helps detect errors, prevents revenue misstatements, and ensures your liability accounts reflect true obligations. Consistent closing processes improve audit readiness and provide management with reliable cash flow and profitability insights.
Using Custom Reports to Monitor Prepayment Trends and Customer Behavior
Custom reports in QuickBooks help you analyze prepayment trends and understand customer payment behaviors. By filtering data by date, customer, or job, you can identify which clients frequently make prepayments and their typical amounts. Monitoring these patterns aids in forecasting cash flow, tailoring payment terms, and improving customer relationship management. Custom reports also highlight delayed applications or unapplied prepayments, allowing timely corrective actions. Leveraging these insights strengthens financial planning, reduces risks, and supports strategic decision-making.
Bottom Line!
Thus, Customer Prepayments (Customer Deposits) are used when you receive a payment from a customer, but there is no invoice that the payment can be settled against. These types of payments help you to manage accurate financial records and ensure that your company’s cash flow is effectively monitored.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can incorrect classification of prepayments impact financial audits and tax reporting?
Incorrectly classifying prepayments as revenue rather than liabilities can lead to overstated income figures, resulting in misleading financial statements and potential audit failures. This misclassification may cause discrepancies in tax reporting, increasing the risk of penalties and interest charges by tax authorities, as reported by 42% of businesses facing tax compliance issues. Furthermore, inaccurate classification complicates cash flow analysis and budget planning, potentially leading to poor business decisions and financial instability.
What are the risks of not reconciling customer prepayment accounts monthly in QuickBooks?
Failing to reconcile prepayment accounts monthly increases the chance of unnoticed errors, such as duplicated payments or misapplied credits, which can skew financial reports and customer balances. According to a survey, 38% of small businesses reported cash flow issues directly linked to reconciliation lapses. Additionally, lack of regular reconciliation undermines internal controls, raising the risk of fraud and making audits more time-consuming and costly.
How do customer prepayments influence a company’s working capital and liquidity ratios?
Customer prepayments boost a company’s current liabilities, which can reduce working capital if not managed properly, potentially signaling liquidity constraints to investors. This affects liquidity ratios like the current ratio, which, if skewed by large prepayments, may misrepresent a company’s ability to cover short-term obligations. Studies show that 45% of companies with significant prepayments face challenges in presenting clear liquidity metrics, impacting creditworthiness and financing options.
Implementing segregation of duties ensures that the person recording prepayments is different from the one reconciling accounts, reducing fraud risks. Using automated alerts for unusual prepayment amounts or frequencies helps detect potential fraudulent activities early, supported by data showing a 30% decrease in fraud cases with such controls. Regular audits combined with employee training on prepayment policies also reinforce accountability and improve financial transparency across the organization.
How does Sales Tax (or VAT) interact with customer prepayments in QuickBooks?
Sales Tax or VAT should not be calculated or posted when you receive the prepayment. The prepayment is a liability (Unearned Revenue), not yet a sale. Tax is only due and recognized when the prepayment is applied to a final invoice and the service or goods are delivered (when the revenue is legally earned). This is why you must enter the prepayment as a negative line item on the invoice to ensure the tax is calculated correctly on the full amount of the sale, but only once.
What is the fundamental difference between the Unearned Revenue and the Accounts Receivable accounts?
Unearned Revenue (Customer Prepayments) is a Liability account, representing money you owe back to the customer (either in service or cash) because you have received the funds but haven’t earned them yet. Accounts Receivable (A/R) is an Asset account, representing money the customer owes to you for services or goods that have already been delivered. The act of applying a prepayment to an invoice moves the amount from the Liability (Unearned Revenue) side to the Asset (A/R) side, simultaneously booking the income.
In what ways can multi-currency settings complicate the recording of prepayments in QuickBooks?
Multi-currency settings introduce exchange rate fluctuations that affect the valuation of prepayments, potentially causing discrepancies in liability and revenue accounts. QuickBooks disables prepayments when multi-currency is turned on, limiting businesses’ ability to track advance payments accurately across currencies. According to financial software users, 28% report challenges reconciling prepayments due to currency conversions, complicating financial reporting and cash flow management in global operations.
How do I handle a prepayment when the customer later cancels the order and requests a full refund?
If the customer cancels and you issue a refund, you must first ensure the prepayment has not been applied to an invoice. You would then issue a refund check or create a Credit Memo (if the funds were originally recorded as Undeposited Funds or the process needs a proper audit trail). The refund transaction should reduce the Cash account and also reduce the Customer Prepayments (Liability) account, bringing the liability balance down to zero for that customer.
Why does my balance sheet show a large balance in the “Customer Prepayments” account?
A large balance in the Customer Prepayments (Unearned Revenue) account means your business has a significant obligation to perform services or deliver goods in the future. While this looks good for cash flow, it is a liability. It signals that you need to focus on fulfilling those pending orders to convert the unearned liability into earned revenue on your Profit & Loss Statement.
What are the operational challenges in applying prepayments to multiple invoices across fiscal periods?
Applying prepayments to multiple invoices across different fiscal periods complicates revenue recognition and may cause timing mismatches in financial statements, impacting compliance with accounting standards. This often requires meticulous tracking to ensure prepayments are correctly allocated without double counting or omission, which, according to studies, causes reconciliation errors in over 35% of companies. Additionally, managing these allocations manually increases administrative burden and the risk of miscommunication between accounting and sales teams.
How do prepayments affect cash flow forecasting accuracy in seasonal businesses?
Prepayments provide upfront cash that can smooth out cash flow fluctuations typical in seasonal businesses, improving liquidity management and operational planning. However, if not properly tracked or applied, they can create misleading cash flow projections, causing 33% of seasonal businesses to overestimate available funds. Accurate recording of prepayments helps predict resource needs and avoid cash shortages during off-peak periods, supporting more reliable budgeting and growth strategies.
What is the impact of delayed prepayment application on revenue recognition and compliance standards?
Delaying the application of prepayments to invoices postpones revenue recognition, which can distort financial statements and mislead stakeholders about a company’s performance. This delay may cause non-compliance with accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP, exposing the business to regulatory risks and potential penalties. Studies indicate that 29% of companies face audit adjustments due to improper timing in revenue reporting linked to prepayment delays, highlighting the importance of timely application.
How can businesses utilize QuickBooks reports to identify trends in customer prepayment behavior?
QuickBooks reports like “Open Prepayments by Customer” help businesses analyze which customers frequently pay in advance, aiding cash flow forecasting and credit management. Tracking these trends can reveal seasonal or project-based payment patterns, allowing tailored sales strategies and improved customer relationships. According to industry surveys, companies using such reporting tools see a 25% improvement in predicting payment cycles and reducing overdue accounts.
What steps can companies take to educate their accounting teams on proper prepayment management?
Companies should conduct regular training sessions focused on recording, applying, and reconciling prepayments in QuickBooks to minimize errors and ensure compliance. Providing clear, documented procedures and real-world examples enhances understanding, which 60% of firms report improves accuracy in financial entries. Additionally, encouraging cross-department communication between sales and finance teams fosters accountability and streamlines the prepayment workflow.
How do prepayments interact with progress billing in industries like construction and services?
Prepayments in progress billing serve as upfront funds that secure project financing and reduce credit risk, helping contractors manage cash flow effectively. They must be carefully tracked to ensure they’re correctly applied against incremental invoices, which aids in compliance with revenue recognition standards specific to long-term contracts. Studies show that 40% of construction firms report improved project financial management when integrating prepayments with progress billing in QuickBooks.
Common errors include failing to match prepayments to the correct invoices, double counting prepayments, and neglecting to update liability accounts, all of which distort financial statements and cash flow reports. Avoiding these requires consistent monthly reconciliation, clear documentation, and use of QuickBooks reports to track open prepayments, reducing errors by up to 35%. Additionally, training accounting staff on proper procedures ensures accuracy and streamlines audit processes.
What type of internal control should I implement to prevent the accidental recognition of unearned revenue?
The best internal control is segregation of duties. Specifically, ensure that the person who records the initial sales receipt (posting the payment to the liability account) is not the same person who creates the final invoice and applies the prepayment (recognizing the revenue). This two-step process adds a verification layer, drastically reducing the risk of prematurely recording the cash received as earned revenue.
How can automating prepayment workflows improve accuracy and reduce manual errors in QuickBooks?
Automating prepayment workflows in QuickBooks minimizes human errors by standardizing data entry, ensures timely application of prepayments to invoices, and enhances real-time tracking of customer deposits. Automation reduces processing time by up to 50%, according to industry benchmarks, and improves financial visibility by integrating with payment gateways and reporting tools. This leads to better cash flow management, fewer reconciliation issues, and strengthened compliance with accounting standards.
Disclaimer: The information outlined above for “How to Record Customer Prepayments in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?” is applicable to all supported versions, including QuickBooks Desktop Pro, Premier, Accountant, and Enterprise. It is designed to work with operating systems such as Windows 7, 10, and 11, as well as macOS.

