Cash management is critical to businesses for the simple reason that, through cash management, there is always liquidity to perform the corporation’s day-to-day financial activities and also optimal use of cash resources as available. Efficient cash management helps corporations keep running with smooth operations, avoiding crises and being well-prepared for growth.
Monitoring, analyzing, and controlling a company’s cash flow is important to maintaining liquidity, reducing borrowing costs, mitigating risks, and ensuring the company has enough money to operate. Strong cash management is essential to preserving a corporation’s financial health and success in today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment.
What is Cash Management?
Cash management is the process of optimizing cash flow to ensure a business has sufficient funds for daily operations while effectively investing surplus cash. The main objectives of cash management are meeting financial obligations, investing surplus cash, optimizing cash holdings, and planning for future cash needs.
Effective cash management contributes to a company’s financial stability and growth by providing visibility into cash positions, negotiating favorable payment terms, and establishing efficient collection methods.
Why is Cash Management Important for Your Business?
In many ways, cash management is very important for establishing and maintaining a company’s fiscal foundation. Being the most commonly used method of paying obligations, such as utilities and other bills, cash is the largest earning asset and hence should be managed as such. It alters the sum of future growth for the company. Another consideration that many firms deem very crucial is the ability to keep balances of cash while at the same time earning a return on such cash if it is idle.
Cash management can be linked to your company’s banking system and its associated applications that allow you and your business administrators to access funds all day long, every day of the week. If your company is directly connected with online banking, it provides better control of your cash flows and is more accessible. This flexibility is crucial since every business entity is unique and may require various cash management options and services.
Effective cash management during a recession is particularly important, as it helps businesses navigate financial challenges by optimizing liquidity and minimizing costs. Additionally, cash management is essential for students to manage limited funds which helps them to budget effectively and avoid unnecessary debt.
Cash Management at Various Stages of the Business
Depending on the stage of the firm, different cash management techniques are used. For instance, established businesses may concentrate on maximizing cash flow to support development and expansion, but startups may prioritize liquidity to meet initial operational costs. Businesses must carefully strike a balance between keeping enough working capital and investing in new prospects during a growth phase. Managing cash flow becomes even more important to ensuring survival during a recession or other economic crisis. Depending on the unique financial constraints and objectives of each phase, a customized strategy for cash management is required.
How Does Cash Management Work?
Cash management is the process which manages the company’s cash flows to make sure that there is sufficient liquidity to meet its financial obligations. This also includes tracking cash inflows and outflows, forecasting future cash requirements, and deciding how to invest surplus cash to generate returns.
Cash management includes various steps:
- Make a cash budget that will forecast cash inflows and outflows.
- Execute cash flow management strategies, such as giving discounts for early payments.
- Negotiate with your suppliers to enter into the best payment terms with them.
- Invest surplus cash in low-risk, short-term instruments such as money market funds or short-term government securities.
- Monitor cash balance regularly and also review your fund management plans.
What is the Importance of Cash Flow Statement in Cash Management
A cash flow statement is considered a very crucial aspect through which a cash flow management plan can be created.
The cash flow statement records all the cash flows of a business, including:
- Cash Flow from Operating Activities
- Cash Flow from Financing
- Cash Flow from Investing
At the bottom of the cash flow statement it is shown how much cash the business has. The statement can display negative also if there is more outflow that inflow.
A cash flow statement is a key tool which creates a cash flow management plan since it provides the business’s current cash flow performance as a baseline against which to improve.
What are the Different Types of Cash Management?

1. Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Cash management is the process of tracking, evaluating, and regulating an organization’s cash intake and outflow to ensure it has enough money to pay its debts and make the required investments. To put it briefly, it entails overseeing a company’s financial flow.
2. Free Cash Flow to Equity
The cash reserve that remains after capital is reinvested is known as the free cash flow to equity.
3. Free Cash Flow to the Company
The amount of cash generated from operations after depreciation, costs, and taxes are paid is known as free cash flow. This establishes a company’s profitability and is mostly used for financial appraisal.
4. Net Change in Cash
This displays the total cash flow change between accounting years.
What are the Functions of Cash Management?
1. Inventory Management
Inventory management assures to bring out the blockage of any stock causing trapped sales, which contributes to the higher stock on hand. Since excess stock in inventory is an indication of low liquidity, through efficient fund management, firms should endeavor to sell the existing stock, which will translate into inflows.
2. Receivables Management
In the normal course of a credit sale, a sales account has an entry of sale, whereas a collections account remains pending most of the time. Cash management corresponds to meeting all the bill payables to ensure a sufficient amount of liquid cash in the business.
3. Payable Management
Payables are the company’s liability when purchasing any items on credit. Sometimes, organizations obtain loads from lending institutions or banks and are liable to repay within a stipulated time. Hence, effective fund management ensures that the repayment is made on time, avoiding any penalties or compensatory interest.
4. Short-Term Investment
The basic concept of cash management focuses on aspects such as cash deficits and bankruptcy. However, the same account may also be utilized to purchase short-term assets, such as government securities, to increase the value of money.
What are the Objectives of Cash Management?
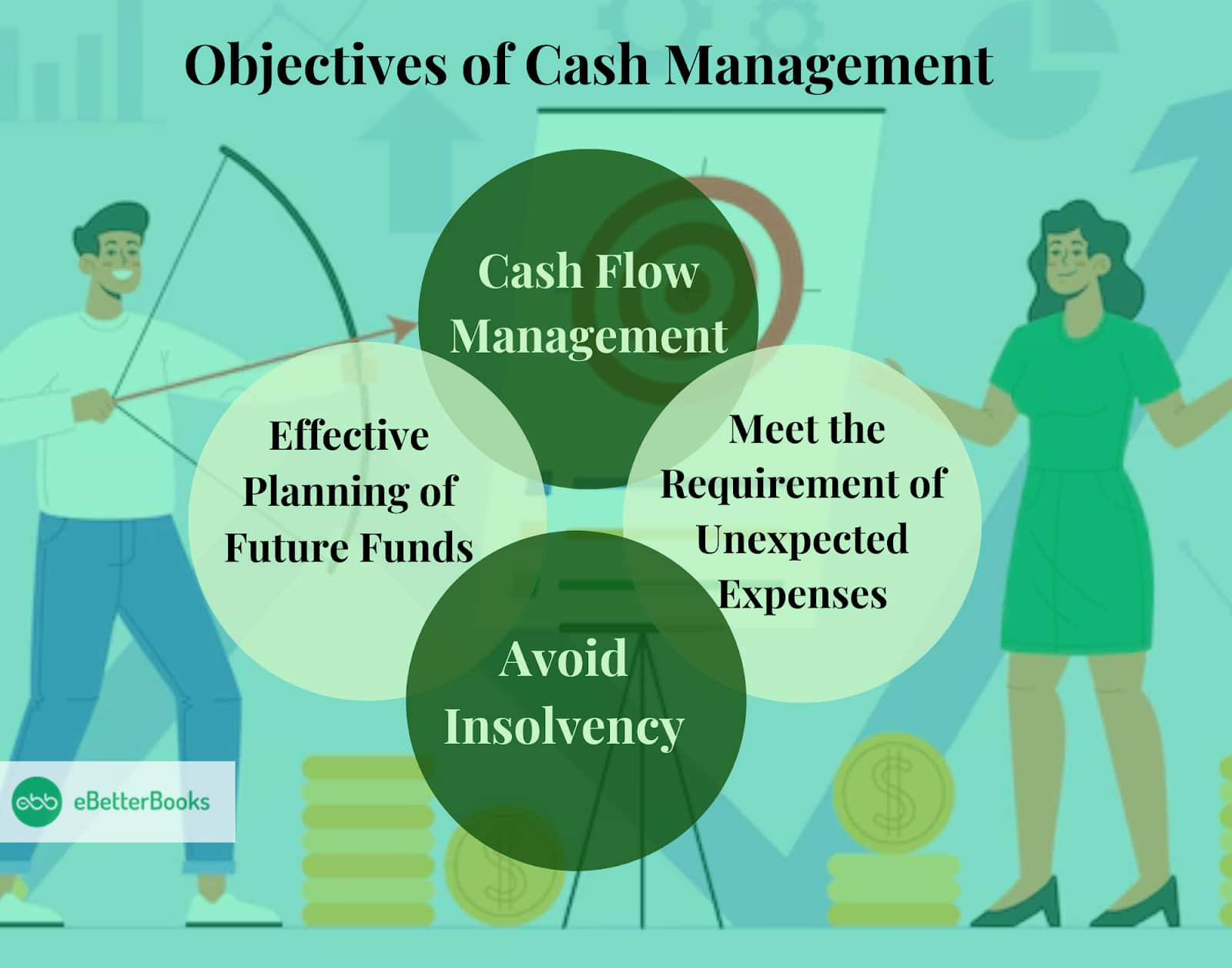
1. Cash Flow Management
The major goal of cash management is, therefore, the control of cash inflows and outflows. In particular, the approach minimizes fund loss and, at the same time, facilitates inflow, therefore warranting a firm’s optimistic financial position. It controls all areas of cash expenses and, consequently, achieves measures to limit their occurrence; it reduces operating costs.
2. Effective Planning of Future Funds
It also manages cash by making more of the future cash to meet the near-future cash demands. This also helps to decide efficient capital expenditures and calculate the financial ratio analysis for debt and equity. In other words, after conducting proper planning, the company must also maintain adequate stocks of liquid cash that can be used for any unexpected necessities.
3. Meet the Requirement of Unexpected Expenses
When practicing cash management in an organization, the main goal is to ensure adequate liquid cash to handle any unexpected expenditure. This may include machinery failure or other unforeseen incidents. By maintaining a reserve of petty cash, the company can address minor, immediate expenses without dipping into surplus cash, ensuring smooth operations even in the face of unexpected costs.
4. Avoid Insolvency
Inadequate cash management will lead to a cash shortage, which will lead to failure in bill payments. This can lead to insolvency and erase the organization’s goodwill, which can pose a considerable threat to the organization.
Reasons for Poor Cash Management
Here are few reasons that result in poor cash management:
- Poor Understanding of the Cash Flow Cycle: A lack of knowledge about how cash moves in and out of a business can lead to mismanagement. A company can run out of money because it over-purchases inventory yet does not receive payment for it.
- Unpredictable Cash Flow: When a business has irregular or unpredictable income, it becomes challenging to manage cash effectively. Unexpected expenses or delays in receiving payments can quickly deplete cash reserves, leading to cash flow problems.
- Lack of Understanding of Profit Versus Cash: Many business owners confuse profitability with cash flow. Just because a business is profitable on paper doesn’t mean it has sufficient cash on hand to cover expenses. Understanding the difference between profit and cash is essential for proper cash management.
- Low Profits: If a business operates with low-profit margins, it may struggle to generate enough cash to cover expenses and invest in growth. Low profits can be caused by factors such as high costs, intense competition, or a lack of pricing power.
- Late Payments: When customers pay their invoices late, it can create cash flow problems for the business. Late payments disrupt the cash flow cycle and make it difficult to predict when cash will be available to cover expenses.
- Low Prices: Offering low prices to attract customers can be a double-edged sword. While it may increase sales volume, it can also lead to low-profit margins and insufficient cash flow to sustain the business.
- High Overhead Expenses: Excessive overhead expenses, such as rent, utilities, or administrative costs, can quickly consume a business’s cash reserves. Keeping overhead expenses under control is crucial for maintaining healthy cash flow.
- Poor Financial Planning: A lack of financial planning can lead to poor cash management. Without a clear understanding of financial goals, budgets, and forecasts, it becomes difficult to make informed decisions about cash allocation and investment.
- Poor Inventory Management: Holding too much inventory can tie up cash that could be used for other purposes, such as paying expenses or investing in growth. On the other hand, running out of inventory can lead to lost sales and dissatisfied customers.
Ways to Improve Cash Management
- Shorten the credit period by controlling the receivables through the enhancement of the billing and collection cycle.
- Increase the cash inflows by entering into lucrative negotiations with the suppliers.
- Minimize traditional payment practices and integrate variable online payment systems.
- For effectiveness, conduct a review and update of the cash management procedures and policies from time to time.
- The control should perform routine audits of cash management to determine areas requiring more attention and to observe all the relevant compliances.
- Find and track non-essential expenditures that lead to a decrease in cash expenses.
- Improve the cash management strategies to ensure that the company’s cash balances and cash transactions are more apparent.
What are the Cast Management Strategies?
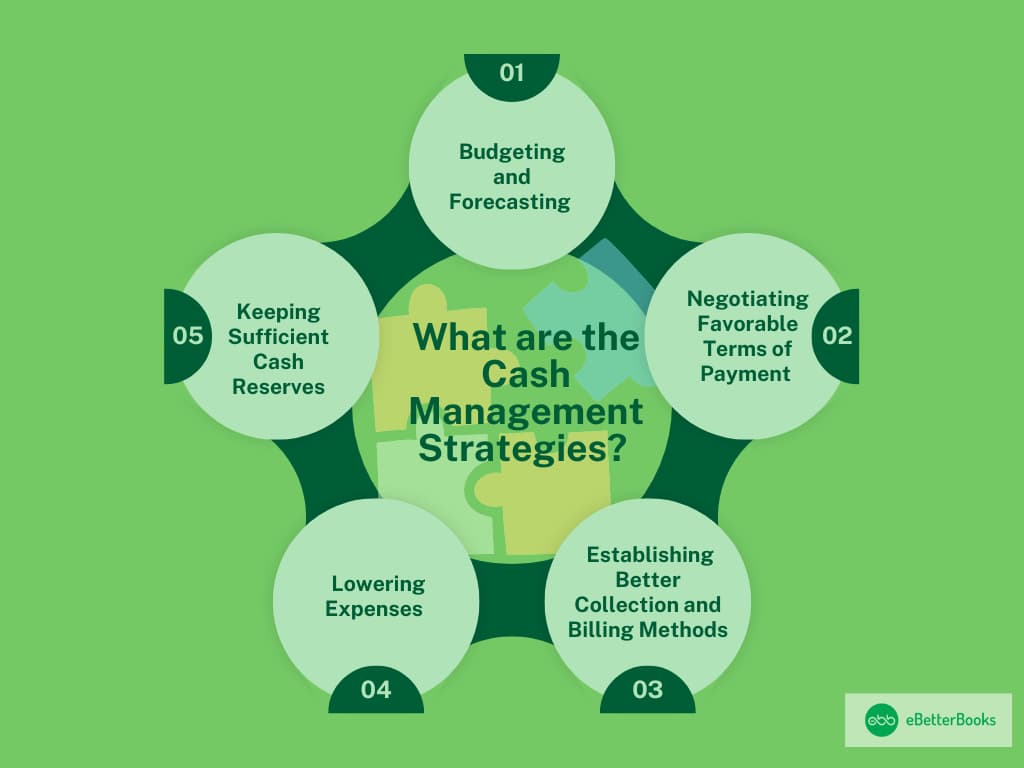
1. Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting are cash management techniques that involve planning for an organization’s various sources of cash inflow potential. Based on this forecasting, the accounting department develops a budget for managing operations in case of any shortfalls in meeting the forecasted amounts.
2. Negotiating Favorable Terms of Payment
When forming a contract to enter business, payment conditions must be agreed upon to ensure efficient cash inflow management. Appropriate practice standards, such as offering certain percentages off if customers pay before the agreed time, must also be developed.
3. Establishing Better Collection and Billing Methods
This is an optimistic way of cash management; thus, it is wiser to incorporate the best collection and billing method in a company. In some aspects, less complicated and time-consuming processes, such as online payment gateways, shall be applied so that there can be ease in paying the credit.
4. Lowering Expenses
As one basic approach to managing cash, organizations have to find avoidable expenses and eliminate them to preserve cash. Thus, for instance, different cost-saving measures and better contract terms with clients can regulate expenses to some extent.
5. Keeping Sufficient Cash Reserves
It helps to keep a second reserve of adequate cash for rainy days and emergencies. Such cash reserves can be used to compensate for any undesirable incidents.
Important Terms in Cash Management
Below mentioned is the list of important terms in Cash Management:
- Cash Flow: The Flow of money in and out of a business.
- Cash Flow Statement: This is an essential financial document that shows cash-related operating, investing, and financing activities.
- Accounts Receivable (AR): This is the amount of money that clients owe a business for the goods or services provided to them under credit terms.
- Accounts Payable (AP): The money that is owed to suppliers for goods or services that are purchased on credit.
- Working Capital: An indicator of a business’s short-term operational liquidity, defined as the difference between current assets and current liabilities.
- Current Ratio: The current ratio is one of the liquidity ratios used to determine a company’s capacity to meet the immediate payment of its stock through current assets.
- Quick Ratio: A short-term working capital indicator calculated based on a firm’s current capacity to transform its most easily realizable assets into liability payments.
- Collection Process: It refers to the process of recovering an amount due to the business from customers about bills issued.
- Cash Disbursement: The payment of cash for consumptions or other commitments or other necessities or arising from other obligations.
- Cash Forecasting: The activities that look into the future to determine the amount of cash that is expected to flow in and out of an organization.
Understanding Cash and Cash Equivalents in Cash Management
Cash includes physical currency, such as coins and banknotes, along with funds in checking accounts that can be accessed immediately. Cash equivalents, on the other hand, are short-term investments that are highly liquid and can be converted into cash within three months or less.
Common examples of cash equivalents include:
- Treasury bills
- Commercial paper
- Money market funds
- Bank certificates of deposit (CDs)
These assets are characterized by their low risk of value fluctuation and ease of conversion into cash, making them essential for liquidity management.
Its Importance in Cash Management
- Liquidity Management: CCE plays an important role in a company’s liquidity management strategy. It provides the necessary funds to cover immediate operational expenses, such as paying suppliers, covering payroll, and managing other short-term liabilities. A robust CCE balance indicates a company’s ability to meet its financial commitments without delay.
- Financial Stability: Organizations can navigate unexpected financial challenges, such as economic downturns or sudden rise in operational costs by maintaining an adequate level of cash and cash equivalents. This stability allows companies to avoid potential liquidity crises that could jeopardize their operations.
- Investment Opportunities: Companies often invest excess cash in cash equivalents to earn a return while maintaining liquidity. This strategy allows businesses to capitalize on short-term investment opportunities without sacrificing their ability to access funds quickly when needed.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Many lenders require businesses to maintain certain levels of CCE as part of loan agreements. This requirement serves to protect lenders’ interests while encouraging companies to manage their liquidity effectively.
Liquidity Ratio to Measure Cash Efficiency
A Liquidity ratio is a financial ratio used to determine whether a company is able to pay its short-term obligations. This metric helps a company determine whether it can use current or liquid assets to cover its current liabilities.
There are three types of liquid ratios mentioned below:
- Current Ratio: The current liquidity ratio is the easiest one to calculate and interpret. To find it, divide current assets by current liabilities.
- Quick Ratio: The quick liquidity ratio, also known as the Acid test ratio, is used to identify whether a company has enough liquid assets that can be instantly converted into cash to meet short-term dues.
- Cash Ratio: The cash liquidity ratio only considers a company’s most liquid assets—cash and marketable securities. These are considered the most readily available assets for a company to pay its short-term obligations.
What is ACH?
ACH, known as Automated Clearing House, is a method of making payments electronically in the U.S. It is managed by the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA). ACH debit and credit transactions initiated through consumer electronics will be cleared on the same day. Organizations that create these transactions are referred to as ACH Originators.
ACH transactions are electronic payments made when the customer authorizes an ACH-originating institution to make direct debit or credit from or to the customer’s checking or savings account. An example of applying utilitarianism is an employer providing the option of payroll Direct Deposit.
Tools to Manage a Business Cash Flow
Various tools, such as automation, APIs, and treasury management software, can assist in this process.
1. Automation
Automation helps businesses to simplify cash flow management by reducing manual tasks and minimizing errors.
Key benefits include:
- Efficiency: Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks such as invoicing, payment processing, and cash flow forecasting, allowing finance teams to focus on strategic activities.
- Real-time Data: Automation provides real-time visibility into cash positions, enabling businesses to make informed decisions quickly.
- Reduced Costs: Automation can significantly lower operational costs associated with cash management processes by minimizing manual effort.
2. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
APIs facilitate the integration of various financial systems and applications by enhancing cash flow management capabilities.
Key benefits include:
- Data Integration: APIs allow businesses to connect their treasury management systems with banking platforms, accounting software, and other financial tools, ensuring seamless data flow.
- Customization: Organizations can customize their cash management solutions to meet specific needs by leveraging APIs to integrate functionalities that are most relevant to their operations.
- Real-time Transactions: With APIs, businesses can execute transactions in real-time, improving liquidity management and reducing the risk of cash shortfalls.
3. Treasury Management Software (TMS)
Treasury management software is a comprehensive solution designed to automate and enhance financial operations within a business.
Key features include:
- Cash Management: TMS provides tools for tracking incoming and outgoing payments, ensuring that funds are available when needed.
- Liquidity Management: It enables businesses to monitor their liquidity positions and forecast future cash flows effectively.
- Risk Management: TMS helps identify and manage financial risks such as foreign exchange and interest rate risks.
- Reporting and Analytics: Advanced reporting features allow users to create customizable reports that provide insights into cash flow trends and financial performance.
Is there a difference between cash management and treasury management?
In banking, both Cash Management and Treasury Management are technical names for some services related to cash shuffling. The latter of these two terms is CT; however, it is much more comprehensive and encompasses Treasury Management apart from funding and investments.
The services that can be grouped under cash management when finance professionals are speaking about it are such services as wire transfers, sweep accounts, merchant services, and business credit options.
Managing Cash Through Internal Controls
The following are some of the internal controls applied in a business organization towards the management of efficient business cash flows. It is worth noting that internal controls are many and may include features through which the companies can account for their compliance with the set regulations. Some of these tools, resources, and procedures enhance operations to minimize fraud.
Some of a company’s top cash flow considerations include the following:
- The average length of AR
- Collection processes
- Write-offs for uncollected receivables
- Liquidity and rates of return (RoR) on cash equivalent investments
- Credit Line management
- Available operating cash flow
Cash Management of Working Capital
Working capital is a major component of operating activity cash flows and is influenced by changes in AR and AP. Investing and financing cash flows are typically considered exceptional financial events requiring unique funding techniques.
The difference between a company’s current assets and current liabilities is its working capital. In cash flow management, working capital balances are crucial because they indicate how many current assets a business has available to pay for its current liabilities.
The following are typically included in working capital:
- Current Assets: Cash, inventory, and accounts receivable due in less than a year.
- Current Liabilities: All short-term debt payments due in a year, as well as all accounts payable due in a year.
Example Why Cash Management is Necessary?
In September 2008, the multinational financial services company Lehman Brothers filed for bankruptcy. Inadequate cash management procedures were a major contributing factor in this disaster.
This is how their demise was influenced by poor cash management:
- High Leverage and Illiquid Assets: Lehman Brothers owed a lot of money compared to its equity, which was indicated by its high leverage ratio. They invested a large portion of their money in long-term, illiquid products such as mortgage-backed securities. They were unable to rapidly sell these assets to raise money when their value fell.
- Short-Term Funding: Lehman Brothers’ operations were primarily financed by short-term funding. As market confidence declined, lenders’ reluctance to offer short-term loans resulted in a liquidity crisis.
- Cash Flow Mismatches: Lehman’s cash inflows and outflows were noticeably out of balance. Despite having sizable long-term investments, they were unable to meet their urgent financial needs because those investments could not be sold for a profit fast enough.
- Failure to Maintain Sufficient Cash Reserves: The company did not have enough cash on hand to protect itself from market changes. Even with the option of a cash advance, the severe market conditions and the extent of Lehman’s financial needs made it impossible to stay afloat.
Cash management involves effectively managing cash inflows and outflows. Both consumers and corporations should be aware of this procedure. Effective cash management allows an organization to pay off debt, save for future growth, and maintain cash reserves.
Tips on Managing Cash during Recession
Opt for Zero Base Budgeting
Businesses opting for zero-based budgeting during a recession can be an effective strategy for managing their finances, controlling costs, and ensuring resources are allocated efficiently. Zero-based budgeting requires businesses to build their budget from scratch, justifying every expense as it helps businesses cut unnecessary expenses and prioritize essential spending during economic downturns.
Zero-based budgeting forces businesses to review all expenses and justify their necessity, making it easier to identify and eliminate unnecessary or non-essential costs.
Zero-based budgeting gives businesses greater control over cash flow because it requires a detailed evaluation of every expense as it enables better allocation of funds to high-priority areas while ensuring that cash flow is maintained.
Cash is King, Don’t Sell on Credit
Selling on credit during economic downturns can be risky, as businesses face a higher likelihood of delayed payments or defaults. So, in order to tighten credit terms or eliminate them, customers must pay upfront or on delivery.
Businesses should provide lower pricing or special offers to customers who pay upfront in cash, as this encourages immediate payments and ensures liquidity. The faster you invoice, the sooner you can expect payment, so businesses should automate the invoicing process to ensure there are no delays in sending out bills.
Reassess your Expenses and Increase your Savings
Businesses should start by reviewing their profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow to identify areas of unnecessary spending and eliminate or reduce spending on non-core activities such as office perks, non-critical travel, and luxury upgrades. If you have employees working remotely or extra space, consider downsizing or subleasing parts of your office to reduce rent costs.
Businesses can offer part-time, freelance, or remote work options to reduce payroll expenses. During the recession, every business should prioritize marketing efforts that bring the best return on investment (ROI), such as targeted digital advertising, email marketing, or referral programs.
Short Working Capital Cycle
Businesses need to shorten their working capital cycle during a recession, and this can be achieved by focusing on efficient inventory management, effective accounts receivable and payable processes, and improved cash flow forecasting. These strategies can help enhance liquidity, reduce financial stress, and maintain operational stability even in challenging economic conditions.
A short working capital cycle is crucial for businesses during a recession because it ensures that cash flows quickly through the business, reducing the risk of liquidity issues. To achieve this, inventory turnover rates should be analyzed, and excess stock should be reduced to free up cash. Businesses should implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices to minimize holding costs and avoid overstocking. Using electronic invoicing can speed up the process and reduce administrative time. Regularly update cash flow forecasts to anticipate cash needs and manage working capital effectively.
Optimize Debt Collection
Optimizing debt collection during a recession is crucial for maintaining cash flow and ensuring business stability. There are times when customers may delay or default on payments due to financial strain, so businesses should identify customers with the largest outstanding balances and focus collection efforts there. Recovering significant amounts from large accounts can have a bigger impact on cash flow.
Businesses should reach out to customers before their payment due dates with friendly reminders, reinforcing the importance of timely payments. Businesses should allow customers to pay in smaller, manageable installments rather than requiring full payment upfront. Flexible payment plans can make it easier for customers to pay off their debts gradually, increasing the chance of recovery.
Invoice Factoring
During a recession, invoice factoring can be a useful strategy for businesses to maintain liquidity, improve cash flow, and avoid taking on debt. Businesses should carefully evaluate the costs, customer credit risk, and the terms of factoring agreements to ensure it’s the right solution for their specific financial situation.
It provides immediate cash for operational needs without the burden of traditional loans, helping businesses survive economic downturns while still meeting financial obligations. Businesses can use the immediate cash from invoice factoring to cover operational expenses such as rent, utilities, inventory purchases, and employee salaries. This liquidity is especially crucial during a recession when maintaining regular cash flow is more difficult.
During a recession, customers may delay payments due to their financial difficulties, extending payment terms from 30 or 60 days to 90 days or longer, but invoice factoring allows businesses to receive most of the invoice amount immediately, preventing cash flow issues caused by slow-paying clients.
Don’t Take Loans/Debt During Recession
Businesses should avoid taking any loans or debt during the recession in order to protect themselves from economic instability. By avoiding debts, businesses can maintain financial flexibility, minimize risk, and concentrate on sustaining cash flow and operational efficiency.
Economic downturns often persist longer than anticipated, and if a company incurs debt in the hopes of quickly recovering, it may find it difficult to make payments on time. It is preferable to exercise caution and avoid taking on obligations that can impede long-term rehabilitation.
Opt for Performance Marketing Rather than Physical Marketing
During a recession, businesses can benefit from performance marketing by maximizing their return on investment, targeting the right audience with precision, and adapting quickly to changing market conditions, all while minimizing costs and risks associated with traditional physical marketing.
Performance marketing enables businesses to retarget visitors who have interacted with their website or content but haven’t converted, providing another opportunity to close the sale and make marketing more effective. Performance marketing allows businesses to quickly adapt to changing market conditions, economic trends, or consumer behavior by launching new promotions or pivoting messaging to reflect current customer needs, something physical marketing cannot do.
Use Automation and AI
Automation and AI enable businesses to adapt quickly to changing market conditions, making them more agile and resilient during tough economic times. AI can detect patterns of fraudulent activity in real time, helping businesses protect themselves from financial losses.
Utilizing automation and AI during a recession can help businesses increase efficiency, reduce costs, and stay competitive in a challenging economic environment. AI-driven CRM systems such as Salesforce and HubSpot automate lead scoring, follow-ups, and task reminders, helping sales teams focus on high-value opportunities and close deals faster.
Keep a Check on Accounts Receivable
Businesses should always ensure a timely collection of receivables in order to maintain healthy cash flow into the business. They can offer great deals such as additional discounts for early payments and closely monitoring overdue invoices. To prevent payment delays, businesses can automate reminders and follow-ups.
It is crucial for businesses to closely manage their accounts receivable and encourage timely payments in order to improve cash flow and maintain financial stability during a recession. The key strategies for minimizing payment delays include offering early payment incentives, automating reminders, and enforcing strong credit policies. Every business should keep a close eye on accounts receivable in order to prevent cash flow disruptions and ensure the business can navigate through the challenging economic climate.
Opt for Cloud Based Software
During a recession, businesses can opt for cloud-based software solutions, which can be an effective strategy to achieve this. Cloud-based software eliminates the need for expensive on-premise servers and hardware. Businesses can operate on a subscription-based model, paying only for what they use.
Cloud services provide flexible pricing models, which enable businesses to adjust their resources based on their current needs. This allows companies to pay only for the resources they use without having to commit to unused capacity. Cloud-based solutions typically operate on a subscription basis (monthly or yearly), providing more predictability and manageability for cash flow, especially during economic downturns.
Opt for Subscription Softwares/Services
Businesses should go ahead with subscription-based software instead of purchasing software. The subscription model offers monthly and annual costs, supporting the businesses in budgeting.
Subscription software usually includes automatic updates, maintenance, and customer support, eliminating the need for additional costs for upgrades or system maintenance. This reduces IT expenditures and ensures that the software remains up to date. Subscription software gives access to premium tools that are out of reach if purchased outright. This allows businesses to leverage advanced tools and features without the heavy investment, improving productivity without straining budgets.
Subscription software usually includes customer support, allowing companies to concentrate on their core business activities without having to manage software or deal with technical issues. This is particularly helpful for businesses during a recession.
Layoffs (Inefficient and Duplicate of Work)
Layoffs during a recession may be necessary to reduce costs, especially when there are inefficiencies and duplications in the workforce. By conducting a thorough audit, streamlining roles, utilizing technology, and maintaining transparency, businesses can manage layoffs in a way that improves efficiency and positions the company for long-term survival and success.
Layoffs should be strategic as it helps the business to target the areas where automation or restructuring can replace the manual work.
Utilize Freelancers
Businesses should hire freelancers instead of full-time employees to lower fixed costs during a recession. Freelancers can work remotely, eliminating the requirement for office space, utilities, and equipment and reducing overhead expenses.
Freelancers often offer specialized expertise that may not be available in-house, enabling businesses to finish projects without the need to invest in expensive training or hiring new employees. This access to a wide talent pool can be crucial during a recession when resources are limited.
Freelancers offer flexibility, enabling businesses to adjust their workforce based on project needs. This is especially valuable during economic downturns when business demand fluctuates and hiring permanent staff may not be practical. Freelancers help businesses access a diverse global talent pool, which is particularly useful during a recession when specific skill sets are not available locally or when companies need to adapt to new market demands.
Get less inventory: JIT , EOQ, ABC Costing
Businesses can follow techniques like Just-in-Time (JIT), Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and Activity-based costing. Using these techniques will reduce inventory holding costs by receiving goods only when needed by the business. Businesses can also use mathematical formulas to find the optimal order quantity that minimizes the ordering and holding costs. Along with that to avoid excess inventory, businesses should focus on high-value items and carefully manage low cost items.
Pay Per Project or Milestone Based
Businesses should opt for pay-per-project or milestones during a recession because it provides flexibility, cost control, and risk reduction.
Always ensure that each milestone or project has clearly defined deliverables, timelines, and performance expectations as this avoids misunderstandings and ensures that payments are tied to specific outcomes. For large projects, break them into smaller, manageable milestones. This helps businesses to track progress and ensures that payments are tied to incremental success, reducing the financial risk of project delays or underperformance.
It supports companies in managing their cash flow more effectively by prioritizing the most critical tasks. By clearly defining project goals, deliverables, and payment structures, businesses can ensure that they only pay for work that creates value, making it an ideal strategy during economic uncertainty.
Optimize Your Customer Invoicing
Businesses should optimize customer invoicing during the recession as it improves cash flow and ensures financial stability. Businesses can offer discounts or incentives for early payments, encouraging customers to pay sooner.
Businesses can set automated payment reminders to ensure that customers are regularly notified about upcoming and overdue payments, reducing the chance of missed or delayed payments.
Businesses can reduce the payment terms, which can help businesses get paid faster, and offer a variety of payment options that make it easier for customers to pay on time. By accepting credit cards, digital wallets, and online bank transfers, businesses can remove barriers that may delay payment.
Leverage Tax Advantages
During a recession, businesses can benefit from tax advantages to cut costs, boost cash flow, and maintain financial stability. By making use of available credits, deductions, and deferrals, and by managing income and expenses strategically, businesses can navigate tough economic times while reducing their tax burden.
It’s advisable for businesses to work with a tax advisor or accountant to make sure they take full advantage of these opportunities and don’t miss out on important tax savings during a recession.
By carefully tracking and maximizing deductible business expenses, businesses can lower their taxable income, which in turn reduces their overall tax burden. By deferring income to a later tax year and accelerating deductible expenses into the current year, businesses can lower their current tax liability.
Communication Between Teams & Partners
Businesses must maintain clear, open, and frequent communication between teams and partners. Transparent messaging fosters trust, helps teams stay aligned with strategic priorities, and encourages collaboration and innovation. Effective communication can also boost morale, reduce anxiety, and ensure that everyone is working toward common goals, making it a vital tool for navigating economic uncertainty. By leveraging digital tools, promoting transparency, and focusing on solutions, businesses can create a resilient communication strategy that helps them weather the storm of a recession.
During a recession, businesses need to be more resourceful, and effective communication between departments is essential for fostering collaboration. Cross-functional collaboration can help generate new ideas for cost-saving measures, innovation, or process improvements.
Communication during a recession should focus on more than problems but also on solutions. A business needs to encourage a culture where employees and partners feel empowered to suggest ideas for cost savings, efficiency improvements, or new revenue streams that can lead to innovation.
Seek a Business Loan or Line of Credit
During recessions, many businesses face cash flow shortages because of slower sales, delayed payments from customers, or higher operational costs. A loan or line of credit can offer the necessary funds to cover expenses such as payroll, rent, or inventory. Businesses can also use these financial options to refinance existing high-interest debt into more favorable terms, reducing their monthly payments and improving cash flow.
By strengthening the financial records, building strong relationships with lenders, and exploring all financing options, businesses can improve their chances of securing the funding needed to navigate through the recession successfully. Lenders become more conservative during recessions, increasing their scrutiny of a business’s creditworthiness. They may require higher credit scores, more collateral, or stricter terms.
Diversify your Investments
Diversifying investments and revenue helps businesses reduce their dependence on a single source of income and become more resilient to economic challenges. Businesses can begin by introducing complementary products or services that align with their current offerings.
Businesses can explore opportunities to expand into untapped markets, either domestically or internationally, as this might involve customizing products for new customer demographics or targeting industries that are less affected by economic downturns. Businesses should begin by upgrading their digital infrastructure, such as enhancing their e-commerce platform, improving cybersecurity, or utilizing cloud computing for greater flexibility and cost savings.
How Does a Recession Impact Cash Flow?
During recessions, consumer spending decreases, which decreases demand for businesses’ products and services. When sales decrease, the inflow of cash diminishes. Companies face declining revenues and find it difficult to meet fixed expenses like rent, debt payments, and payroll, leading to liquidity challenges.
When a recession occurs, businesses may have less cash to service their debt, leading to limited cash reserves for operational expenses. Even banks and financial institutions tend to tighten lending standards, making it more difficult for businesses to access credit. Businesses that depend on lines of credit or loans for working capital face liquidity issues when they need access to additional funds.
Unsold inventory in industries like manufacturing and retail can tie up cash that could be used for operational expenses, during recession. Businesses experiencing cash flow difficulties may delay payments to suppliers to save funds.
Businesses frequently fire employees or implement other cost-cutting strategies during a recession to conserve money. Although this may provide immediate financial relief, it affects the company’s long-term growth and staff morale. During a recession, businesses usually cut back on spending on projects, new facilities, and equipment to conserve money.
In the end, if a company is unable to solve its cash flow and liquidity problems during a recession, it may end up insolvent or declare bankruptcy.
Understanding how cash flow works during a recession is crucial for businesses to take proactive steps, such as increasing cash reserves, obtaining financing before it’s necessary, and cutting operational expenses early to fight the economic downturn.
Case Studies and Examples
- In 2008, during the financial crisis, Lehman Brothers, one of the world’s largest investment banks, experienced a significant decrease in asset values, resulting in substantial losses. As its revenues decreased, Lehman was unable to meet its liquidity needs and eventually filed for bankruptcy, which had a significant impact on the overall financial crisis.
- Toys “R” Us filed for bankruptcy in 2017 when they were struggling financially for years but got hit hard by liquidity problems in 2017. The company delayed payments to suppliers to preserve cash, which led to suppliers losing confidence in the business. As a result, some suppliers cut off their deliveries, worsening the company’s cash flow.
- Tesla faced liquidity issues in 2017 due to challenges in ramping up the production of the Model 3. Although the Tesla plant did not close permanently, there were shutdowns and cash flow issues that nearly crippled the company. Tesla had negative free cash flow for at least five consecutive quarters (from Q1 2017 to Q1 2018). Tesla had to raise capital through multiple rounds of financing to stay afloat and avoid bankruptcy.
Conclusion:
Adequate cash management is an essential component of a corporation’s success, guaranteeing liquidity, financial stability, and the capability to invest in growth opportunities. By monitoring, analyzing, and controlling cash flows, businesses can guide both challenges and opportunities with confidence. Cash management is not just about balancing the books, it is about strategic planning, optimizing cash reserves, and ensuring that every financial decision supports long-term objectives.
FAQs:
How Can Technology Help in Cash Management?
Technology streamlines cash management by automating processes, providing real-time data, and enhancing decision-making with tools like treasury management systems.
What are the Risks of Poor Cash Management?
Poor cash management can lead to insolvency, inability to meet financial obligations, and lost business opportunities.
How Does Cash Forecasting Benefit a Business?
Cash forecasting helps businesses predict future cash needs and plan accordingly to avoid liquidity issues.
-
Cash Management During Recession for Small Businesses
This article addresses how businesses can manage financial challenges during an economic recession. It provides strategies such as cutting unnecessary costs, optimizing cash flow through…
-
Cash Disbursement: Definition, How it Works & Example?
Cash disbursement involves the payment of funds by a business to various parties, including vendors, employees, or creditors. It is crucial for maintaining accurate financial…
-
15 Best Cash Management Software: Free and Paid Software?
Cash management software helps businesses efficiently monitor, plan, and manage their cash flow. By integrating with accounting and banking systems, it provides real-time data, ensuring…
-
Cash Advance – Definition, Types and How Does it Work?
A cash advance offers quick access to funds in emergencies, but comes with high fees and immediate interest charges. It’s ideal for urgent, short-term financial…
-
What are Non Cash Expenses? Meaning Examples, and Importance?
Non-cash expenses, like depreciation, amortization, and stock-based compensation, impact a company’s financial statements without involving cash outflows. Understanding these charges is essential for accurate reporting,…
-
Operating Cash Flow (OCF): Definition, Importance & Methods?
Operating Cash Flow (OCF) measures the cash a company generates from its core operations, providing insights into its ability to sustain and grow without external…
-
Cash vs Accrual Accounting: What’s the Difference?
Choosing between cash and accrual accounting depends on your business’s size and complexity. Cash accounting is simpler and works well for small businesses, tracking cash…
-
Cash Basis Accounting – Definition, Example and Uses?
Cash basis accounting simplifies financial tracking by recording transactions only when cash is received or paid. Ideal for small businesses or service-based companies, it offers…
-
Petty Cash: Definition, Types, Process, and Recommendations
Petty cash management is essential for businesses to efficiently handle minor, everyday expenses like office supplies, lunches, and reimbursements. By setting up a structured petty…
-
Working Capital Management: Definition, Components & Types?
Working capital management is essential for businesses to efficiently manage cash flow, meet short-term obligations, and support long-term growth. By optimizing the use of current…
-
Liquidity and Liquidity Ratios: Definition, Types & Example
Liquidity ratios are essential tools to assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations, helping investors, creditors, and analysts evaluate financial health. They provide…
-
Cash Flow Statement: Definition, Uses & Examples?
A cash flow statement is crucial for businesses to track cash inflows and outflows, ensuring liquidity and financial stability. It helps businesses manage cash, forecast…
