Cost-volume profit analysis helps small businesses formulate pricing strategies, forecast profit when the volume of production changes, track costs related to production, and assess the impact on profits.
It calculates how much you must sell to cover all costs and turn a profit. Knowing your break-even point and how adjustments to price, expenses, or sales volume impact your bottom line allows you to make more intelligent choices about pricing, production, and marketing.
CVP analysis has the advantage of being comparatively easy to utilize, even for someone with little prior financial knowledge. You can obtain a comprehensive view of how various elements affect your organization by computing important metrics such as sales prices, contribution margins, and fixed and variable costs. In order to boost profitability, this tool can assist you in determining areas for improvement, cutting expenses, and setting appropriate prices.
CVP analysis is especially crucial for small firms since it gives you the confidence to make decisions. CVP offers the data-driven insights you need to make sure your decisions are in line with your financial objectives, whether you’re thinking about raising prices, introducing a new product, or changing your sales approach. This clarity can mean the difference between success and failure in a market that is highly competitive.
What is CVP Analysis?
At its core, CVP analysis assists small business owners in gaining a comprehensive understanding of sales volume, cost, and profit. By implementing this analysis, the overall cost is split into fixed and variable categories which determine the units that need to be sold out in order to have a breakeven and evaluate the variations in pricing, sales volume, or cost that affect the profitability.
- Fixed Costs: These are the costs that do not change with the number of units sold and remain constant. Such costs include insurance, rent, and salaries.
- Variable Costs: These costs correspondingly vary with the number of units sold out or produced. Such costs include direct labor, direct expenses, or direct materials.
- Sales Price: The amount at which the product or service is sold to customers.
- Contribution Margin: The variation among sales revenue and variable costs, which contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit.
The key formulas are:
- Contribution Margin (CM) = Sales Price per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit
- Break-even Point (BEP) = Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin per Unit
Importance of CVP Analysis for Small Businesses
Small businesses always face financial issues due to fewer resources, less stable sales volumes, and more volatile market conditions. CVP analysis reduces the severity of such financial challenges by making a clear relationship among the most key financial factors available for better decision-making and better financial planning.

Here’s why CVP analysis is particularly important for small businesses:
- Better Financial Planning: With this understanding of the cost structure, a small business owner can, to a greater extent, predict profit levels and future growth. The budgeting in relation to CVP analysis ensures the financial health of the business at any point when the sales experience fluctuation.
- ForecastingProfitability: Small business owners can use CVP analysis to forecast how variations in costs or sales volumes affect profitability, and make all the adjustments accordingly.
- Effective Pricing Strategy: Comprehending the effect of pricing on prevailing profitability enables businesses to set competitive yet profitable prices for their services or products.
- Management of cost or expenses: CVP analysis indicates which costs are driving profitability and which ones must be reduced or optimized for better margins.
Key Benefits of CVP Analysis for Small Businesses
Better Pricing Strategy
CVP analysis is valuable for developing pricing strategies because it shows the amount of contribution margin on each product or service offered. By determining the contribution margin, a business owner can be well aware of what he/she can sell for in order to break even, meaning that there would be an equal amount of contribution margin in comparison to both fixed and variable costs.
In addition, CVP analysis enables businesses to evaluate the impact of price change on overall profitability. It gives a clear picture of how price adjustments will affect their bottom line.
Additionally, it helps owners determine what price to set in order to reach specific financial goals, for example, desired profit level or sales targets. By considering such factors, a small business could refine its price strategy to still be competitive without compromising its financials.
In fact, CVP analysis enables any business to have better decision-making in terms of where to balance demand with the possibility of long-run profitability.
Break-Even Clarity
Break-even analysis is an important part of CVP, indicating the point at which total revenues equal total costs. This means the business is neither making a profit nor a loss. This point is termed the break-even point. It allows small business owners to know how many sales they need to start to make a profit.
- How to calculate the break-even point:
- Break-even point (units) = Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin per Unit
- For example, if fixed costs are $20,000 and the contribution margin per unit is $100, the break-even point is 200 units ($20,000 / $100).
Once the break-even point has been identified, it can be used for business owners to check if the current sales goals are achievable or not, thus helping them reach closer to viable targets. In the case of budgeting, financial planning, and sustainability, this is very essential.
Informed Decision-Making
CVP analysis provides data-driven insights that help business owners make informed decisions.
Here’s how it aids decision-making:
- Sales Volume Decisions: The CVP can help businesses determine realistic sales targets by analyzing how changes in sales volume affect profitability and avoid overestimating the potential income.
- Cost Control: Small businesses can identify where costs can be lessened. For illustration, investigating variable costs can direct to identifying cheaper suppliers or optimizing production processes.
- Product Line Decisions: If a small business trades more than one service or product, CVP can be utilized to compare the profitability of each line. The corporation can know which products contribute the most to fixed costs and develop the most profit so that it focuses on the most profitable offerings.
How to Perform CVP Analysis
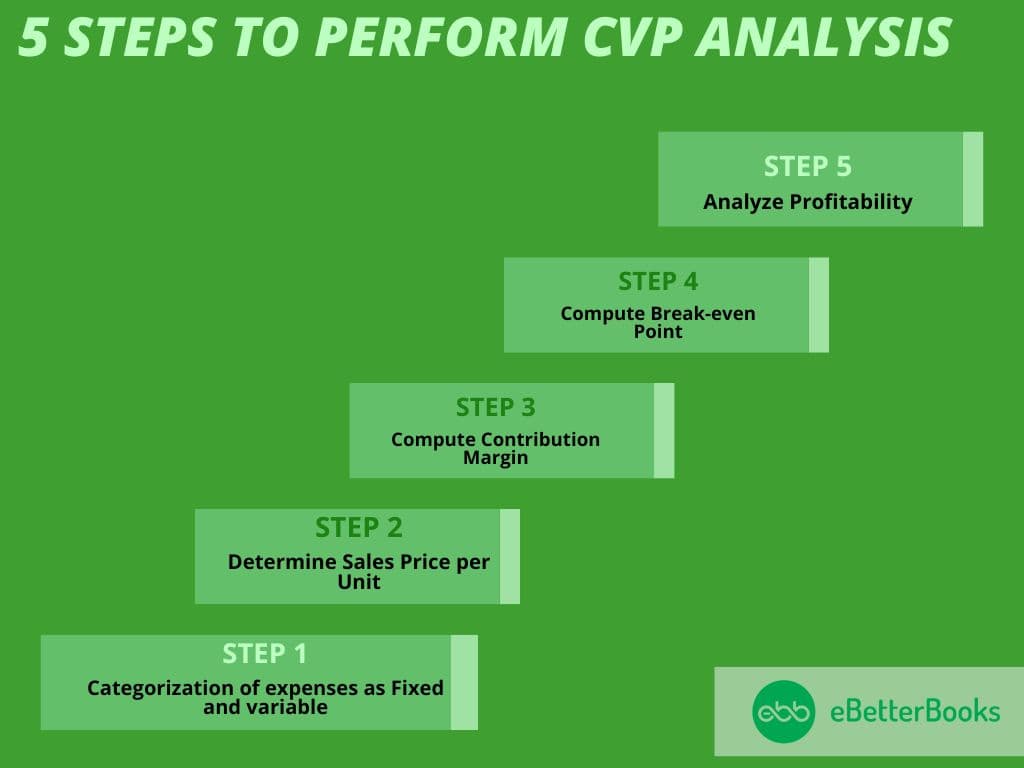
To do this simple CVP analysis, note these few key steps:
- Categorization of expenses as Fixed and variable: Costs never fluctuate while business production and volume of its selling goes along variable cost is changing at this rate.
- Determine Sales Price per Unit: Set pricing on how you want to sell.
- Compute Contribution Margin: Contribution margin is obtained by subtracting the variable cost per unit from the sales price per unit.
- Compute Break-even Point: Break-even point formula is used to calculate the units required to recover the fixed costs.
- Analyze Profitability: Consider various scenarios like changes in pricing, volume, or costs, and analyze the impact on profitability.
Let’s consider an example for better understanding:
- Fixed Costs = $15,000
- Sales Price per Unit = $100
- Variable Cost per Unit = $60
- Contribution Margin = $100 – $60 = $40
- Break-even Point = $15,000 / $40 = 375 units
This means the business needs to sell 375 units to break even.
CVP in Action: Real-World Examples
A small bakery owner, for example, can use CVP analysis to determine the optimal price for their pastries. Let’s say the bakery’s fixed costs (rent, salaries, etc.) are $2,000, the cost of ingredients for each pastry is $2, and they want to sell each pastry for $5. Using CVP, the bakery owner can calculate how many pastries they need to sell to cover their fixed costs and start making a profit.
If the bakery wants to make a profit of $1,000 per month, CVP analysis can help them set a clear sales target and evaluate whether their pricing strategy is realistic based on market conditions.
Challenges of CVP Analysis for Small Businesses
While CVP analysis is a valuable tool, small businesses may encounter certain challenges:
- Accurate Cost Estimation: It is difficult to classify all costs accurately, especially for companies whose expenses vary or are just starting to use cost accounting.
- Market Fluctuations: Variations in market demand, competition, or customer behavior may affect the pricing or volume assumptions used in CVP analysis.
- Complexity in Multi-product Businesses: Multiple-product businesses can face difficulties in applying CVP to each of the products offered since their cost structures vary.
Conclusion
CVP analysis is an important tool for small businesses to improve profitability and make decisions based on data. Understanding the relationship between costs, volume, and profit helps business owners set the optimal price, manage costs, and better predict their profits.
Although CVP analysis has its challenges, the benefits of using it in pricing strategy, clarity of break-even, and making informed decisions are invaluable for small businesses that want to be successful in the long term. Small business owners, with CVP analysis embedded into the framework of their financial plans, have the chance to focus more deeply on their operations and take more confident steps toward growth and sustainability.
FAQs!
What is CVP Analysis?
CVP (Cost-Volume-Profit) analysis helps businesses understand the relationship between costs, sales volume, and profit.
Why is CVP Analysis Important for Small Businesses?
It helps small businesses determine the break-even point and make informed decisions on pricing, costs, and profitability.
How Do Fixed and Variable Costs Impact CVP Analysis?
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of sales, while variable costs change with sales volume, affecting profitability.
What is the Break-Even Point in CVP Analysis?
The break-even point is the level of sales where total revenues equal total costs, resulting in no profit or loss.
