Highlights (Key Facts & Solutions)
- Repair Priority: The primary troubleshooting order is to run DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) and SFC (System File Checker) scans first to repair underlying Windows component files, before executing the Microsoft .NET Framework Repair Tool.
- Permissions Required: All command-line fixes (DISM, SFC, PowerShell) require the Command Prompt or PowerShell to be run with elevated permissions (Run as Administrator).
- Manual Forced Repair: A highly effective manual method involves using the Control Panel’s “Turn Windows features on or off” option to disable the relevant .NET Framework version (e.g., 3.5 SP1 or 4.8), restarting the computer, and then re-enabling it to force a clean component reinstallation.
- Integrated Components: Newer .NET Framework versions (like 4.8) are integrated into Windows and cannot be uninstalled like traditional software; they must be fixed using the Repair Tool or the manual disable/enable method.
- Advanced Management: The PowerShell method allows administrators to completely uninstall and reinstall specific .NET Framework package versions, providing granular control necessary for resolving compatibility issues with legacy software.
- DISM Command Roles: The DISM command
checkhealthis diagnostic only (reports corruption status), whilerestorehealthperforms the actual system image repair. - Final Verification: After any repair, the System Boot Configuration should be set to Normal Startup (via
msconfig) to confirm the fix is stable and permanent, without interference from third-party services. - Supported Versions: The official Repair Tool supports versions including .NET Framework 4.8, 4.7.2, 4.7.1, 4.7, 4.6.2, 4.6.1, 4.6, 4.5.2, 4.5.1, 4.5, 4.0 and 3.5 SP1 (which includes .NET 3.0 SP2 and 2.0 SP2).
Overview
The .NET Framework is a software development framework provided by Microsoft Windows that offers a runtime environment and a set of libraries and tools for building and running applications ( Linux, macOS, Windows, iOS, Android) on Windows operating systems. Any issues with the framework result in a malfunction where either the applications (or software) will not be able to run or some of their functionality gets restricted.
Net Framework is the most significant component of the Windows Operating system. By default, it comes with Windows Operating System 10 and 11. Microsoft provides a dedicated repair tool that you can use to repair issues with the .NET Framework and get your apps to run again.
Note:
- These versions of .NET Framework supports the repairing tools: the .NET Framework 4.8, 4.7.2, 4.7.1, 4.7, 4.6.2, 4.6.1, 4.6, 4.5.2, 4.5.1, 4.5, 4.0 and 3.5 SP1 (includes .NET 3.0 SP2 and .NET 2.0 SP2).
- The .NET Framework Repair Tool is only available in English.
- All the integrated platforms and .NET Framework versions are listed under “Affected configurations.”
Quick Fixes for Microsoft .NET Framework Errors
Before moving ahead with other error-specific solutions, first, go through these two quick fixes for .Net Framework, which are highlighted below:
Run a DISM Scan
DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) can be used to repair the Windows image, which contains the core components of the Windows operating system, including Net Framework.
The DISM scan is run using Windows Command Prompt (DOS). This scan tool is available in DOS and can be initiated by running a command. Before running the command, you need elevated permissions for the command prompt. This scan will highlight any possible errors or missing files in the Net Framework.
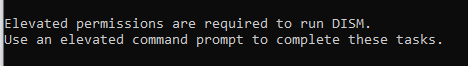
For the elevated permissions, you either need to login as an administrator or have to contact your system administrator. Here’s a command to run DISM scan:
Open an elevated Command Prompt and type DISM /online /cleanup-image /checkhealth

Install the latest Windows Updates
Windows updates are important to stay up to date with all the latest fixes, security patches, and overall improvements offered by Microsoft. Hence, we recommend installing all the latest updates, as they may have fixes to resolve the errors with the .NET Framework. For this, do the following:
- Click on Start and then Settings.
- Now, select Update & Security > Windows Update, and then hit the Check for updates icon.
- If updates are available here, install them at once.
Preferable Ways to Repair Microsoft .NET Framework
Below, we have listed what else you can do to fix Microsoft .NET Framework errors except running the repair tool. Let’s have a look:
Step 1: Run the .NET Framework Repair Tool
Running the .NET Framework Repair Tool helps to identify and automatically fix common issues related to the .NET Framework installation. It detects problems, repairs corrupted files and registry entries and provides a user-friendly interface for effective troubleshooting which makes it an essential first step in resolving .NET errors.
Follow the below given steps to run the .NET Framework Repair Tool:
Step 1: Firstly, navigate to the Microsoft .NET Framework Repair Tool page and then download the tool from the official Microsoft Download Center website.
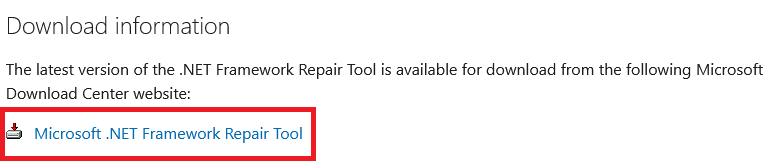
Step 2: Now, scroll down to the Download information section.
Step 3: Click on the Microsoft .NET Framework Repair Tool link to download the executable file.
Step 4: After this, choose the file you want to access and then press Next.
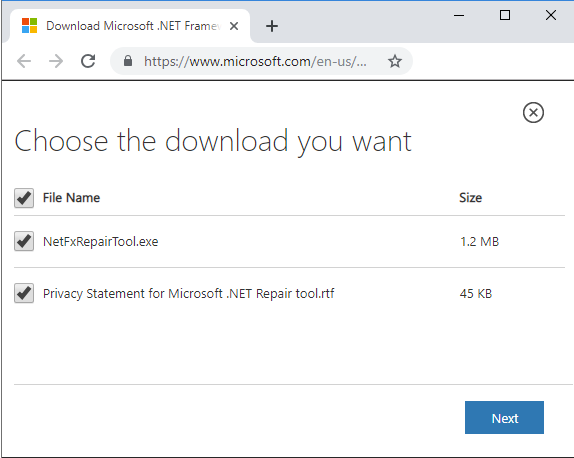
Step 5: Click twice on the Netfxrepairtool.exe to run the repair tool. Then, hit the Yes tab if prompted by User Account Control.
Step 6: Tickmark the I have read and accept the license terms checkbox and click Next.
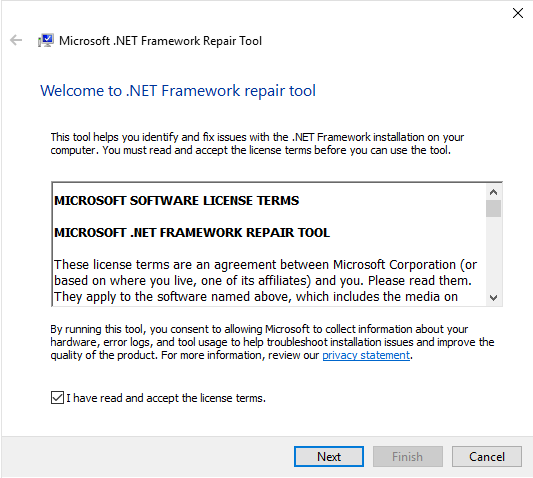
Step 7: Once done, the repair tool will start performing a few tests to diagnose and fix the issues. This will recommend a few changes. Read the description and Press Next to apply the changes.
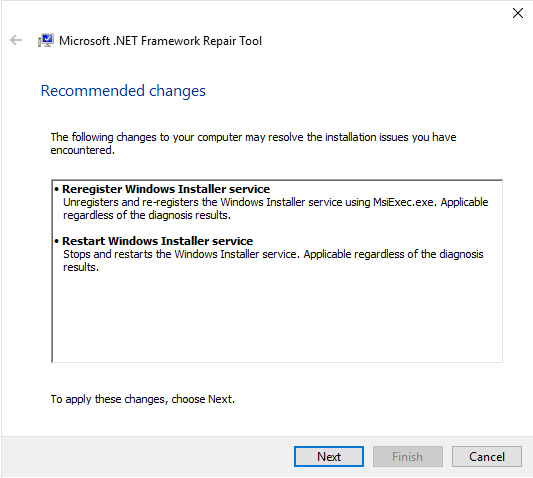
Step 8: After making the changes, instead of selecting the Finish button, click Next.
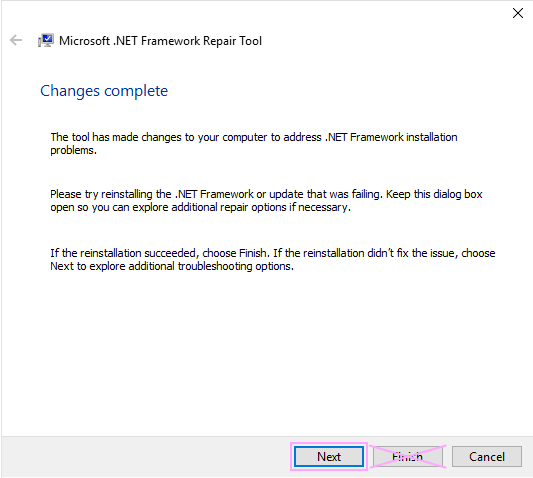
Step 9: At last, hit the Finish icon to close the repair tool.
Step 2: Repair .NET Framework using PowerShell
Repairing the .NET Framework using PowerShell allows for efficient identification and reinstallation of missing or corrupted components through automated commands. This method streamlines the troubleshooting process, making it easier for administrators to manage and fix .NET-related issues across multiple systems with minimal manual intervention.
Follow the below given steps to repair the .NET Framework using PowerShell:
Step 1: To begin with, hold and press the Windows + S keys on your keyboard to open Windows Search and then type PowerShell in the text field.
Step 2: Now, hit right-click on PowerShell and choose Run as administrator.
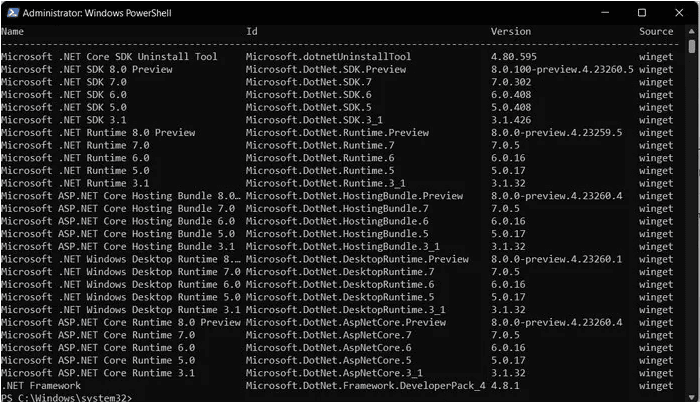
Step 3: Under the PowerShell window, type the following command and then hit the Enter key:

Step 4: After this, if you are prompted to install NuGet – a package manager by .NET Framework, type Y and click Enter.
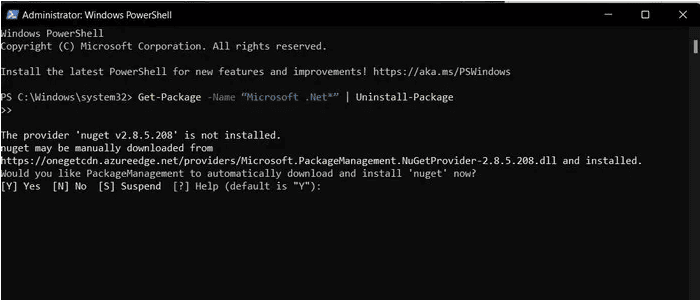
Step 5: PowerShell will now start to uninstall the .NET Framework from your system.

Step 6: Next, execute the following command to install the latest version of Microsoft .NET Framework:

Step 7: Write down the .NET version ID you want to install and then perform the following command. Replace [PackageID] with the ID you noted.
![How to Repair the Microsoft .NET Framework For Windows? 4 Replace [PackageID]](https://ebetterbooks.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/image-15.png)
Step 8: Once done, PowerShell will download and extract the package. Then, you will see a successfully installed message on your screen when the process is complete.
Step 9: Finally, close PowerShell and restart your computer to apply the changes, then check for the error status.
Step 3: Install an Older .NET Framework Version Manually
Installing an older version of the .NET Framework manually can resolve compatibility issues with legacy applications that require specific versions to function correctly. It can also replace corrupted files in the current installation and help bypass problems introduced by recent updates, restoring application functionality.
Follow the steps given below:
Step 1: Head to the .NET Framework download page in the first place.
Step 2: Now, select the .NET Framework version you want to download under the Supported Versions section.

Step 3: Click on Download .NET Framework XX Runtime on the next page.
Step 4: Once the download is completed successfully, go to the download location and run the dotnetfx.exe file to launch the setup. Later, press Yes if prompted by UAC.
Step 5: Afterward, follow the instructions appearing on your screen to complete the setup.
Step 6: Restart your system and then install the app to see if it is working or not.
Step 4: Use the System File Checker Tool
Using the System File Checker (SFC) tool helps repair Microsoft .NET Framework errors by scanning for and replacing corrupted or missing system files. This process restores the integrity of essential components, ensuring that applications relying on the .NET Framework can function properly and efficiently.
To run the System File Checker tool, adhere to the steps below:
Step 1: Press the Windows + X key and then enter CMD into the search box.
Step 2: Now, hit right-click on Command Prompt from the search result and choose Run as Administrator.
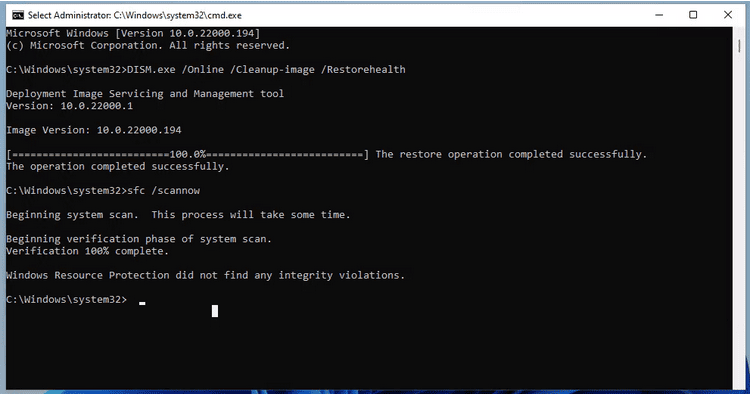
Step 3: Type the following command and then press the Enter key under the Command Prompt window:

Step 4: Before using the System File Checker tool, the above DISM command is recommended to run as it will provide files required to repair system file corruption.
Step 5: When you’re ready, enter the following command in the command prompt window and click the Enter tab.
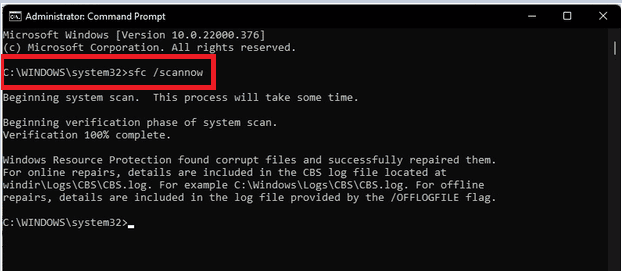
Step 6: The SFC tool will now detect and scan your system files for issues and replace any corrupted files if necessary. Wait for the verification process to complete.
Step 7: Once done, restart your system at the end.
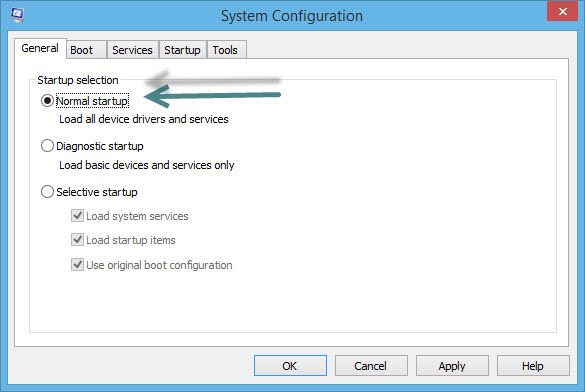
Step 5: Perform System Boot Configuration in Normal Startup
Performing a System Boot Configuration in Normal Startup helps resolve .NET Framework errors by ensuring that all essential Windows services and drivers are loaded correctly. This process eliminates potential conflicts from third-party applications, allowing for a clean environment to identify and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Follow the below given steps :
Steps 1: Initially, hold and press the Windows + R keys on your Keyboard.
Steps 2: Next, type msconfig and Press Enter.
Steps 3: Click on the General tab.
Steps 4: Then, select the Normal startup option.
Steps 5: Hit Apply and then Press OK.
Steps 6: Restart your system.

Manually Fix Microsoft .NET Framework Errors
QuickBooks Desktop basically uses Microsoft programs to run web-based apps, and Microsoft .NET Framework is one of them. The application won’t work properly if there’s an issue with .NET Framework software.
Windows 10 and Newer
- Firstly, shut down all open programs.
- Now, open the Windows Start menu.
- Type Control Panel into the search and then open Control Panel.
- Navigate to Programs and Features.
- After this, choose Uninstall a Program.
Note: Don’t worry; you are not uninstalling anything.
- Choose the option Turn Windows features on or off.
- Search and locate .NET Framework on the list.
Check for both the .NET Framework 4.5 (or later) and .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 Settings.
Note: To fix .NET. Framework 4.5, 4.6, 4.7, and 4.8, you are required to follow the same steps.
Check NET Framework 4.5 (or later)
If the .NET Framework 4.5 (or later) checkbox is unmarked:
- Click on the checkbox to enable .NET Framework 4.5 (or later).
- Now, press OK to save your changes.
- Restart your system.
If the .NET Framework 4.5 (or later) checkbox is already marked:
- Tickmark the checkbox to disable .NET Framework 4.5 (or later). Don’t turn it back on.
- Next, hit the OK tab to save your changes.
- Restart your system.
- When you try to sign in back into Windows, follow the instructions to turn on .NET Framework 4.5 again.
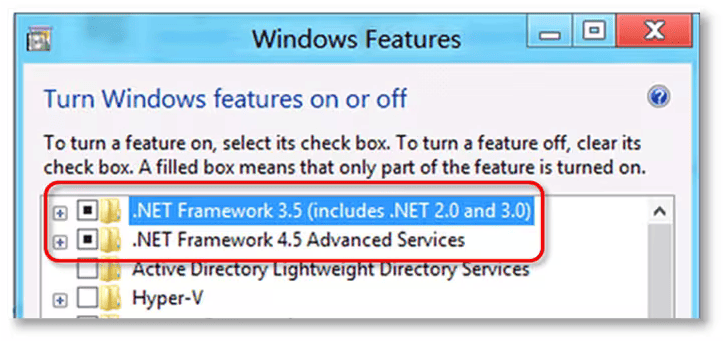
Check NET Framework 3.5 SP1
If the .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 checkbox isn’t marked:
- Hit the checkbox to turn on .NET Framework 3.5 SP1.
- Press OK to save your changes.
- Finally, restart your system.
If the .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 checkbox is already tickmarked:
- Click the checkbox to disable .NET Framework 3.5 SP1. Don’t turn it back on.
- Now, select OK to save your changes.
- Restart your system.
- When trying to sign in back into Windows, adhere to the steps to enable .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 once again.
Recommendation: Immediately contact an IT Professional or Microsoft expert if you encounter the errors when turning .NET Framework on or off, as the issue may be regarding your operating system, not QuickBooks.
FAQs:
1. Why are the DISM and SFC scans listed as “Quick Fixes” before running the official .NET Repair Tool?
The DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) and SFC (System File Checker) scans are recommended first because they are designed to address the root cause of many .NET Framework issues: corruption within the core Windows operating system files.
- DISM’s Role: DISM (specifically the
/restorehealthcommand) repairs the fundamental Windows component store, which holds the original, clean files needed to repair system elements like .NET. - SFC’s Role: SFC (
sfc /scannow) subsequently checks for and replaces corrupted or missing individual system files.
By running these tools first, you ensure the underlying Windows installation is healthy, which significantly increases the likelihood of the specific .NET Repair Tool succeeding.
2. The guide mentions using the Command Prompt with “elevated permissions.” What does this mean, and how do I do it?
“Elevated permissions” means running the Command Prompt or PowerShell with Administrator privileges. This is necessary because commands like DISM and SFC modify core system files and protected areas of the operating system.
- Procedure: You must right-click on the Command Prompt (or PowerShell) application in the Start menu or search results.
- Action: Select Run as administrator.
If you do not run with elevated permissions, the commands will return an “Access Denied” or “You must be an administrator” error, and the repair will fail, as the system protects these critical file operations from standard user accounts.
3. Why is it recommended to turn the .NET Framework feature off, restart, and then turn it back on in the Control Panel?
This manual process forces the Windows operating system to perform a complete re-installation of the core .NET components, which is a powerful troubleshooting method.
- The Goal: When you uncheck the feature, restart, and then re-check it, Windows is required to completely unload the component files and then reload a fresh, clean copy.
- The Benefit: This is the most aggressive way to clear out deeply corrupted files and registry settings that the automated Repair Tool might overlook. It is often the final manual repair step before resorting to full reinstallation.
4. What is the benefit of using PowerShell for .NET repair compared to the official Microsoft Repair Tool?
The PowerShell method is for advanced users and offers greater, granular control over the software components, specifically allowing for precise uninstallation and version management.
- Repair Tool: This tool is user-friendly, diagnosing and automatically fixing common issues within an existing installation.
- PowerShell Method: This method provides an administrative uninstallation and reinstallation capability. It allows an administrator to:
- Force Uninstall: Completely remove the corrupted package.
- Specify Version: Explicitly install the latest, or a specific older version, by using package IDs, which is necessary for legacy application compatibility.
5. The article mentions installing an “Older .NET Framework Version Manually.” Why would I need to do this?
You need to manually install an older version primarily for compatibility with legacy software.
- Legacy Requirements: Many older business or custom applications, including specific versions of software like QuickBooks, were built and tested to run only on a specific, older version of the .NET Framework (e.g. 3.5 SP1).
- Conflict: Even if newer frameworks are technically supposed to be backward compatible, conflicts can arise. Manually installing and enabling the required older version side-by-side with the newest one resolves this compatibility failure, allowing the legacy application to launch.
6. When running DISM, I see the command “DISM /online /cleanup-image /checkhealth.” What is this command doing?
The checkhealth command is the initial diagnostic step within the DISM utility. It quickly scans the integrity of the Windows Component Store.
- Function: It scans the local Windows image (the source of system files) to determine if it is damaged, missing files, or needs repair. It diagnoses the state of the component store.
- Output: It reports the image status as “Healthy,” “Repairable,” or “Non-repairable.” It does not perform any actual fixes.
The subsequent command, typically DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth, is the one that actually attempts to fix the detected corruption by accessing file sources like Windows Update.
7. Why is performing a System Boot Configuration in “Normal Startup” a final repair step?
Using “Normal Startup” is a critical verification step used after performing system fixes to confirm that the repair is stable and not being masked by conflicts.
- Function: Many users perform repairs in a Diagnostic or Selective startup mode to avoid interference from third-party applications (like security software).
- Normal Startup Goal: Returning to the Normal startup configuration (via
msconfig) ensures that all essential Windows services and drivers, along with all third-party programs, load correctly. This verifies that the .NET repair was successful and has eliminated the underlying system instability, confirming the permanent fix.
Disclaimer: The information outlined above for “How to Repair the Microsoft .NET Framework For Windows?” is applicable to all supported versions, including QuickBooks Desktop Pro, Premier, Accountant, and Enterprise. It is designed to work with operating systems such as Windows 7, 10, and 11, as well as macOS.
