When operating a small or large business, comprehending your costs is essential for maintaining profitability and guaranteeing long-term success. Two significant classifications of business expenses that every entrepreneur should be mindful of are overhead costs and operating expenses. While they might seem similar at first glance, differentiating between the two is crucial for accurate financial planning and budgeting.
Understanding the difference between overhead and operating costs can support you in effectively controlling your budget, enhancing profitability, and making knowledgeable financial decisions. In this article, we’ll examine how to categorize these costs, provide examples of operating expenses in businesses, and discuss how to track them utilizing software to simplify financial management.
A Glance: Overhead Costs vs Operating Expenses
| Aspect | Overhead Costs | Operating Expenses |
| Nature of Costs | Indirect costs are not tied to production or sales. | Direct costs are linked to manufacturing or service delivery. |
| Fixed vs. Variable | Includes both fixed (e.g., rent) and variable (e.g., office supplies). | Includes fixed (e.g., production salaries) and variable (e.g., materials) costs. |
| Impact on Profitability | Affects profits even with low sales or production. | Affects profit margin; and increases with higher production or sales. |
| Examples | Rent, insurance, utilities. | Production wages, raw materials, packaging. |
What Are Overhead Costs?
Overhead costs are necessary expenses incurred in the course of running a business but do not directly contribute to the generation of goods or services.
Such costs are not directly involved in the process of generating revenues but are certainly incurred in the general operations. These costs also guarantee that all the activities involved in the operation process must be carried out smoothly.
It is essential for business owners to understand overhead costs since they are an essential determinant of pricing strategies and profitability.
Overhead costs can be classified into several types. The most common overhead costs include rent, utilities, office supplies, employee salaries for non-production staff, insurance, and depreciation of equipment.
These are expenses that businesses have to incur on a regular basis, regardless of how much product is sold or how many services are provided.
Types of Overhead Costs
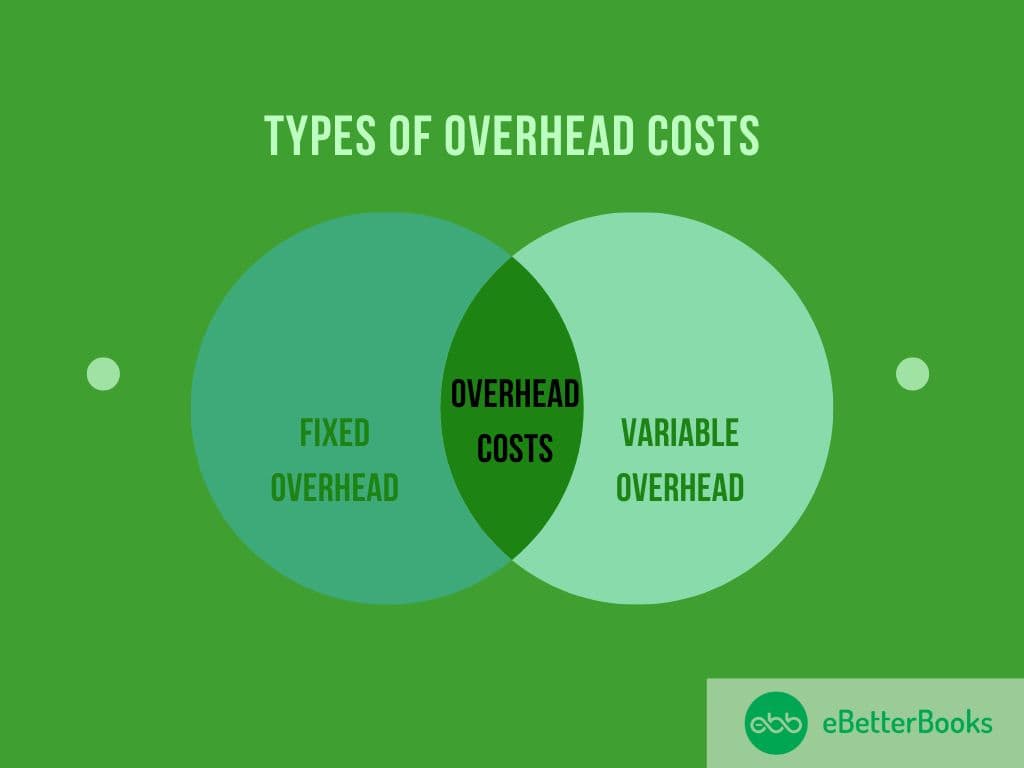
Overhead costs can be classified into two main types:
- Fixed Overhead: Such overheads remain constant irrespective of the level of production. It includes rent, insurance premiums, or salaries of administrative staff. These costs are not exposed to business performance and must be paid regularly even when the business has low sales or no production at all.
- Variable Overhead: Unlike fixed overhead, variable overhead expenses vary with each level of production. That means that these overhead costs fluctuate with an increase or decrease in volume or sales of products. The most common example is the supply of raw materials where a variation in the product manufacturing will trigger the supply of raw materials. Variable overheads are directly dependent on the level of production; however, they still support the operational needs of the business.
Importance of Managing Overhead Costs
Controlling overhead costs is the biggest challenge to profitability in businesses. Though overhead costs are inevitable, they can consistently eat away at profits if left unchecked. Business owners must track both fixed and variable overhead to ensure expenses are being kept about revenue and the business is financially sound.
This would balance the cutting of overhead costs against the need to maintain quality in service or product. The company can reduce expenses on some costs, such as administrative staff or office supplies, but with careful consideration not to affect the operation negatively.
Overhead costs, in the broad sense of the word, are part and parcel of a business; although they contribute towards the daily activities of a firm, they don’t add any value to revenues. A differentiation between fixed overhead and variable overhead is required. Managing these properly ensures the long-term profitability of an enterprise.
What Are Operating Expenses?
Let’s talk about operating expenses. All the costs involved in your company’s core business activities—that is, costs that are directly connected to the creation of goods or services sold.
Let’s keep using the example of the coffee shop. Among the operating expenses would be the cost of:
- Cost of coffee beans, milk, and other ingredients
- Wages for baristas and other employees who are directly engaged in the creation and selling of coffee
- Packaging items, for example cups, lids, napkins, and stirrers
- Advertising and marketing costs, including any ads running online or flyers announcing your existence
Operating costs tend to be rather less predictable and are far more directly related to the volume of business. The more espresso and coffee you sell, the more working dollars you will have. These costs vary with sales volume.
Operating expenses can be divided into two categories:
- Fixed Operating Expenses: These are the costs that are recurring and do not vary with the volume of production. These include employee salaries (for those directly involved in operations) and rent for space used for operations.
- Variable Operating Expenses: These expenses vary according to the volume of production or sales. They include, among others, the cost of raw materials, commission to salespersons, and utilities like water and electricity that depend on consumption.
Why Are Operating Expenses Important?
Every operating expense is important strictly because it reduces your ability to make money. If you are not conscious of the cost of manufacturing and getting your products to the market, you might soon discover that you are bearing unnecessarily high costs.
For instance, costs of raw materials, and human resource costs can greatly reduce your profitability.
Controlling operating expenses is a crucial aspect in ensuring that the business achieves sustainable results that can be explained by the operating revenues/Operating expenses are critical factors that determine the ability of a business to generate sustainable revenues.
Overhead Costs vs Operating Expenses – Key Differences
While overhead costs and operating expenses may seem similar, some key differences can affect how you manage your business’s finances:
Nature of Costs:
- Overhead Costs: They are indirect costs that are closely related to the general business activities. It doesn’t have a direct correlation with the production or sale of products or services which are likely to be the main products of the company.
- Operating Expenses: They include the straight costs related to the manufacturing or service delivery process. They change depending on the levels of sales and production.
Fixed vs. Variable:
- Overhead costs consist of both fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs include rent, insurance, shipping costs, and other expenses, while variable costs include shipping costs, office supplies, and other expenses used in proportion to usage.
- However, operating expenses may also be fixed expenses, such as expenses incurred for the salaries of production staff, and variable expenses which could include the cost of production materials.
Impact on Profitability:
- Overhead costs: Even when you’re not enjoying high amounts of production or sales, high overhead costs cut down your profits. It is, therefore, important to strive to contain these costs.
- Operating expenses: These costs are direct cost that falls under the cost of goods sold (COGS). If the operating expenses are too large it influences the amount of money you earn per pound of product, but they also increase when total sales increase because more ingredients or people are required.
Common Misconceptions and Mistakes
Small businessmen and women especially commit the mistake of categorizing their expenses in the wrong way, which can cause a lot of problems concerning taxes and/or financial planning.
Here are some of the most common misconceptions and mistakes when it comes to categorizing expenses:
- Misclassifying Operating Expenses as Overhead: At times, expenses that should be considered under operating expenses such as raw materials or employees’ wages may be somehow grouped under overheads. This is often likely to cause problems related to inadequate financial reporting as well as misstated profitability analysis.
For instance, if you are in the retail business and you by mistake sign the cost of your inventories under overhead, you will have factored up the cost of the goods sold hence, you will get a lower margin than it appears.
- Not Accounting for Depreciation Correctly: Amortization, particularly on fixed assets such as equipment and machinery, is usually misinterpreted. It depends on the classification some businesses may treat depreciation as an operating expense rather than an overhead cost. The correct depreciation method affects balance sheets; misclassification of depreciation affects the earnings statements and tax deductions.
- Not Tracking Variable Costs Properly: This is why you have to track fluctuating variable costs such as inventory or shipping costs if you want accurate financial predictions. It is also possible, that if these costs are not classified well, you can’t determine how much of a profit you make per unit sold.
- Ignoring Tax Implications: Costs can be properly classified and this classification can lead to huge tax issues. For instance, you have overhead expenses where the business may reduce its taxable income and if done wrongly, then the business is penalized and some of the deductions may not be allowed. Incorrect classification of expenses also leads to wrong preparation of tax return and hence the taxpayers may remit more or less taxes than required.
- Failing to Adjust for Changing Costs: The costs are dynamic in nature depending on the business environment in operations currently. Thus, it is crucial to revisit the listed cost categories and expenses more often, based on the current financial environment. For instance, inflation may lead overhead costs such as rent or power expenses to go high and if they are not well handled, the profit margins may be affected.
Practical Applications and Tools
Managing overhead and operating expenses can be a complex task, but there are various tools available to help you stay on top of it.
Here are some practical applications and tools for tracking these costs effectively:
Accounting Software for Expense Tracking
Controlling overhead and operating costs is a challenging activity, however, there are various techniques that can be used.
Here are some practical applications and tools for tracking these costs effectively:
1. Software for Recording Traveling Expenses
- When it comes to tools used to manage overhead and operating expenses small businesses QuickBooks’ features are reputable in the market.
QuickBooks allows you to:
- Organize your expenses and track them according to the category you want.
- Prepare its income statements and balance sheets.
- It is easy to also differentiate between fixed and variable expenses.
- Prepare financial reports for easy preparation of taxes
Other similar software tools comprise Xero and FreshBooks which can also be used for expense tracking, invoicing, and reporting.
2. Expense Categorisation Templates
- For organizations that can afford to manage their costs individually, or for those who do not wish to establish an expense report procedure yet, templates may be used to begin. Record keeping needs to be accurate and well organized and the use of templates while categorizing your expenses might be of assistance.
Here’s a simple template for categorizing expenses:
| Expense Type | Overhead Costs | Operating Expenses |
| Rent | Yes | – |
| Utilities | Yes | – |
| Salaries (Admin) | Yes | – |
| Salaries (Production) | – | Yes |
| Raw Materials | – | Yes |
| Marketing & Advertising | Yes | – |
This basic table lets you quickly sort expenses into their respective categories, helping you understand where your money is going.
3. Day-to-Day Layouts for Intricate Tracking
- However, if specific details on expenses are more your thing, then it can be helpful to use a Google Sheet or Excel spreadsheet. You can create a spreadsheet with columns organized with overheads and operating expenses which can be updated from time to time as you make payments or spend money on the business. It is even possible to input some fields with formulas that automatically calculate totals and also across time, changes occurring.
Conclusion
Therefore, it should be kept in mind that overhead costs and operating expenses are both significant parts of your business’s financial organization, though they play different roles. Overhead expenses are the costs incurred to keep the business in operation other than direct manufacturing costs while operating expenses refer to costs concerning the manufacture of the product or provision of the service.
Understanding the differences between these two categories—and actively managing them—can make a world of difference in your business’s financial health.
FAQs!
What is the difference between overhead costs and operating expenses?
Overhead costs are indirect expenses necessary to run a business while operating expenses include both direct and indirect costs associated with daily operations.
Are overhead costs part of operating expenses?
Yes, overhead costs are a subset of operating expenses.
Can Overhead Costs Include Salaries?
Yes, overhead costs can include salaries, especially for support roles not directly involved in production.
Do operating expenses include cost of goods sold (COGS)?
Yes, operating expenses include COGS, which are direct costs of producing goods or services.
