Recording payroll accurately in QuickBooks Desktop and Online is crucial for efficient personnel management, timely employee compensation, and strict adherence to tax and legal requirements. This expert guide provides step-by-step instructions for establishing payroll items, processing employee compensation, and handling subsequent liabilities and reporting. It addresses both standard payroll runs and the nuanced process of manually tracking paychecks created outside of QuickBooks using precise journal entries and specific liability accounts within the Chart of Accounts. Furthermore, the content offers advanced customization techniques, including setting up different pay schedules and managing contractor payments separately, along with critical compliance tips for avoiding common errors, reconciling accounts with bank statements, and preparing year-end tax forms like W-2s and 1099s. This authoritative resource is designed to streamline payroll processes, ensure financial accuracy, and maintain audit readiness for all business sizes.
Highlights (Key Facts & Solutions)
- Core Payroll Setup: The process begins with setting up required payroll items and inputting detailed employee data in QuickBooks Desktop, followed by processing payroll, recording liabilities, and generating necessary reports (Payroll Summary, Tax Liability).
- QuickBooks Online (QBO) Manual Tracking: For paychecks created externally, users must create specific Expense accounts (Wages, Taxes) and Liability accounts (Federal Taxes 941/944, SUI, FUTA) in the Chart of Accounts, then record transactions via a Journal Entry to debit expenses and credit liabilities and net wages.
- Tax Payment Resolution: If a tax payment made outside of QBO still appears as due, the user must manually record the payment under the Payroll Tax section to clear the outstanding liability and remove the payment reminder.
- Advanced Customization: QuickBooks allows for customization of paycheck layouts, setting up different pay schedules (weekly, monthly), and accurately managing bonus/commission payments separately from regular wages.
- Contractor vs. Employee: It is vital to manage 1099 Contractor payments via Bills or Expenses (Vendors) and W-2 Employee payments via Payroll to avoid the primary compliance risk of worker misclassification and resulting tax penalties.
- Compliance and Accuracy: Best practices include regularly reconciling payroll accounts with bank statements to detect errors, utilizing Payroll Adjustments to fix submitted errors, and preparing comprehensive Payroll Summary and Tax Liability reports for clean year-end filings.
Calculation of payroll and creation of paychecks
Calculating payroll and creating paychecks in QuickBooks Desktop is essential for confirming the accurate pay of employees and timely compensation.
This process possesses several steps, such as:
- Entering employee work hours
- Reviewing and approving timesheets
- Accounting for overtime and other factors
- Correctly applying taxes and deductions
QuickBooks Desktop shows customizable payroll settings that automate these tasks, including establishing direct deposit, setting up various deductions and contributions, and handling employee benefits. The software also develops detailed payroll reports, helping assure compliance with regulations while delivering valuable insights for financial planning and decision-making.
How to record payroll in QuickBooks Desktop?
To ensure accurate and effective payroll processing, there are numerous essential stages involved in recording payroll in QuickBooks Desktop.
The first important step is to set up payroll items, where you can specify different pay types, contributions, and deductions that are unique to your business. The next step is to input each employee’s personal data, including name, address, tax exemptions, and payment information.
After this data is in place, the system uses the entered data to calculate payroll, accounting for pertinent components such as hours worked and overtime. Payroll creation for employees then happens automatically, and you may check and change the amounts as needed.
Record payroll in QuickBooks Desktop
To record payroll in QuickBooks Desktop, set up payroll with company and employee details, process payroll, record liabilities and expenses, and generate necessary payroll reports.
Following the step-by-step information below:
Step 1: Set Up Payroll in QuickBooks Desktop
- Open the QuickBooks Desktop application on your computer.
- Go to the “Employees” menu at the top of the screen.
- Choose Payroll Setup.
- Click on “Payroll Setup” from the drop-down menu.
- Put Company Information [ You need to provide necessary information about your company, such as business name, address, and federal Employer Identification Number (EIN) ]
- Set Up Payroll Items [ Mention payroll items such as salary, hourly wages, bonuses, and deductions ].
- Enter the details of each employee, including personal information, pay rates, tax withholding preferences, and direct deposit information, if applicable.
Step 2: Process Payroll
- Click on the Payroll Center and then go to the “Employees” menu and choose “Payroll Center.”
- Click on the “Pay Employees” tab, then choose “Start Scheduled Payroll” to begin processing payroll for the current pay period.
- Select the employees for whom you are processing payroll. Ensure all relevant employees are checked.
- Put the Hours Worked by the employees.
- Review and Adjust Paychecks:
- Click “Create Paychecks” to finalize the payroll.
Step 3: Record Payroll Liabilities and Expenses
- Go to the Payroll Center and then choose “Payroll Center” again from the “Employees” menu.
- Click on the “Pay Liabilities” tab to record payroll tax payments and other liabilities.
- Select the liabilities you need to pay, verify the amounts, and click “View/Pay” to record the payments.
- Put Expense Accounts.
Step 4: Generate Payroll Reports
- Click on the “Reports” menu at the top of the screen.
- Select “Employees & Payroll” and then choose the specific payroll reports you need, such as Payroll Summary, Payroll Detail, or Tax Liability reports.
- Customize the date range and other parameters as needed, then run the reports to review payroll information.
How to record payroll in QuickBooks Online?
Creating payroll becomes a smoother process with QuickBooks Online. The platform not only allows you to review and modify employee compensation before finalizing the payroll but also ensures accuracy and compliance with tax filing requirements, giving you peace of mind.
Payroll options, such as payment dates, deductions, and perks, are simple for users to set up. Adding employees is easy, with choices to enter personal information, salary scales, and tax information. The best part is its user-friendly interfaces, which make payroll data entry, including hours worked and overtime.
Record payroll paychecks you create outside of QuickBooks Online
A lot of times, we use other services to run a payroll, but still require to keep track of those paychecks in QuickBooks. We consider those paychecks as “paychecks made outside of QuickBooks”. So, in order to track them manually, follow the below steps:
Steps to create journal entries for paychecks you create outside of QuickBooks
To manually record paychecks in QuickBooks, first create payroll expense and liability accounts. Then, enter journal entries for gross wages, payroll taxes, and net wages using the employees’ payroll details.
Following the step-by-step information below:
Step 1: Create manual Tracking Accounts
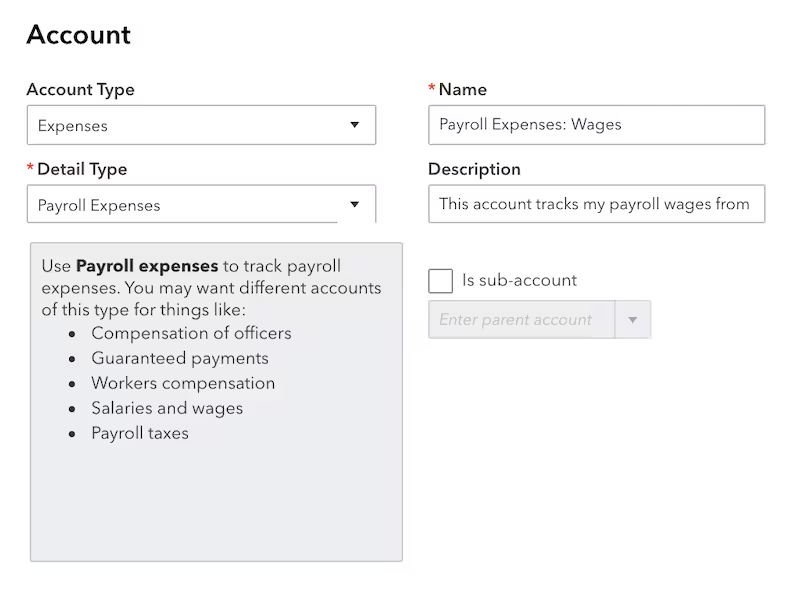
You must have an account in your Charts of Accounts. If you don’t have one, first create a new account by following the steps to add a new account. In your Charts of Accounts, follow the steps to add a new account.
- Then, create the expense accounts and choose the Expense as the account type.
- Payroll Expenses: Wages
- Payroll Expenses: Taxes
- Now, create the liabilities accounts and select liability as the account type:
- Payroll Liabilities: Federal Taxes (941/944)
- Payroll Liabilities: Federal Unemployment (940)
- Payroll Liabilities: [State] SUI/ETT
- Payroll Liabilities: [State] PIT/SDI
Note: These accounts cover common payroll tax situations. Additional accounts may be needed for state or local taxes.
Step 2: Enter the Payroll paychecks
Make sure to retrieve your employees’ payroll pay stubs or a payroll report from your payroll service. You will use this information to create the journal entry.
If you have paid multiple employees for the pay period, you can combine all the paychecks into one journal entry, or you can use individual journal entries if you want to keep the details separate.
Now, you need to create a journal entry by following the steps below:
- Choose + New.
- Click on Journal Entry.
- Mention the paycheck date under the Journal date.
- In case you want to track the paycheck number, enter it in the Journal no. field.
Add gross wages
- Choose the Payroll Expenses: Wages for the account.
- Put the amount as a debit.
Add employer payroll taxes
- Choose the Payroll Expenses: Taxes for the account.
- Put the amount as a debit.
Note: You can combine taxes into one debit or add each tax item as an individual debit. Taxes such as:
- Social Security Employer
- FUTA Employer
- State Job training taxes
- Medicare Employer
- State unemployment insurance
Add taxes paid towards 941 or 944 taxes
- Choose Payroll Liabilities: Federal Taxes (941 or 944) for the account.
- Put the amount as a credit.
Note: You can combine taxes into one debit or add each tax item as an individual debit. Taxes such as:
- Federal Income taxes
- Social Security Employee
- Social Security for Employer
- Medicare for Employee
- Medicare for Employer
Add state unemployment insurance taxes.
- Choose the Payroll Liabilities: [State] SUI/ETT Liability for the account.
- Put the amount as a credit.
Note: You can combine taxes into one debit or add each tax item as an individual debit. Taxes such as:
- State Unemployment Insurance
- State Employment Training Tax
Add state income taxes
- Choose Payroll Liabilities: [State] PIT/SDI for the account.
- Put the amount as a credit.
Note: You can combine taxes into one debit or add each tax item as an individual debit. Taxes such as:
- State Personal Income Tax
- State Disability Insurance.
Add federal unemployment taxes (FUTA)
- Choose Payroll Liabilities: Federal Unemployment (940) for the account.
- Put the amount as a credit.
Add net wages
- Pick the checking account from which you’re paying your employees.
- Instead of combining them, put each paycheck on separate lines. Put the amounts as credits.
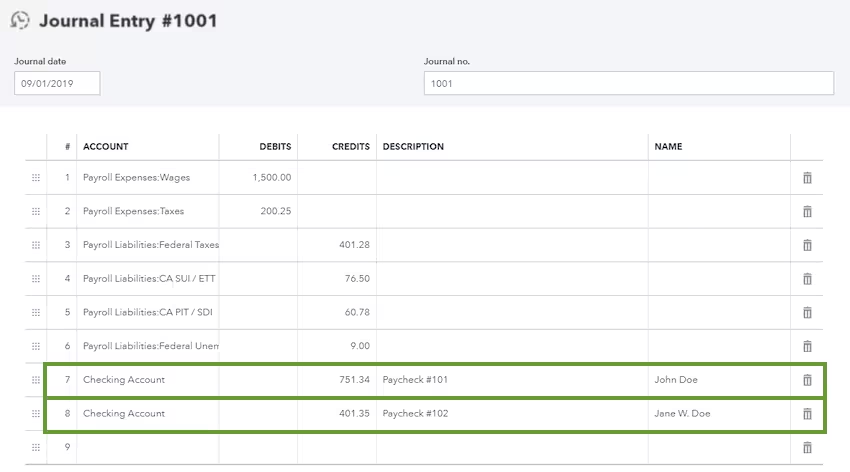
- When you’re done entering the debits and credits, click on the Save option.
Record paid payroll in QuickBooks Online
- Click on Payroll.
- Choose Employees.
- Click on Run Payroll.
- Choose a Pay schedule and Pay date.
- Select the Employee whose payment you want to record
- Click on the Actions button on the screen, then select Edit paycheck to enter the pay details. [ You can add hours, compensation, memos, or any other necessary paycheck information in this section. ]
- Click on Preview Payroll.
- Click on Submit Payroll.
In case you don’t use the QuickBooks Online Payroll; you can then create journal entries for paychecks that you create outside of QuickBooks.
Record a payroll tax from a prior tax period in QuickBooks Online
There are scenarios where some of the taxes go missing. So, now are the steps mentioned below, which include the payment for a tax that no longer appears in the list of due taxes.
Steps to record a tax payment for a prior tax period from QuickBooks Online
- Click on Taxes and choose Payroll Tax.
- Click on Prior tax history.
- Click on Add Payment.
- Put the required payment information.
- Click on OK.
Record a payroll tax that is currently due in QuickBooks Online
If you have already made a tax payment but the payment still appears due, there is a high possibility that the payment was made outside of QuickBooks Payroll.
Steps to remove the tax payment reminder from QuickBooks Online
To record a tax payment:
- Click on Taxes and choose Payroll Tax.
- Click on the Payments tab.
- In the Upcoming tax payments section, select Pay for the tax you want to pay.
- Choose Other and put the actual date the payment was made; for the Payment Date,
- Mention the cheque number.
- Click on Record and Print.
To verify that your tax payment was recorded:
- Click on Reports.
- Choose the Payroll Tax Payments report under the Payroll section,
- Confirm that the tax payment was recorded.
Now that you’ve followed these steps, you can be confident that your payroll tax payments have been recorded correctly.
How to create a new account in the Chart of Accounts?
Before you record the payroll in QuickBooks, it’s crucial to create a new account in the Chart of Accounts. This account is not just a step but a significant responsibility for tracking payroll liabilities and expenses.
Steps to add a new account
- Go to Settings and then click on Chart of Accounts.
- Click on New.
- Now, enter the account name.
- Click on Account type and select the Detail type from the dropdown menu.
- If the account is a sub-account, then click on “Make this a sub account” and then choose the Parent account it should be under.
- Enter the opening balance and mention the starting date in the As of the field if you have selected the Bank, Credit card, liabilities, asset, or equity account.
- Enter the description to add additional information about this account. (This is an optional step).
- Click on Save.
Tips & Best Practices for Recording Payroll in QuickBooks
By keeping correct payroll records, businesses can successfully track employee salaries and ensure compliance with tax requirements.
Following best practices while handling employee paychecks, deductions, and payroll-related activities is necessary for effectively documenting payroll in QuickBooks.
- Efficient payroll recording in QuickBooks demands accurate employee records, regular account reconciliation, and up-to-date tax rates.
- Keep precise records to ensure correct wage calculations, tax compliance, and effective management of deductions and benefits.
- Regularly reconcile payroll accounts to control errors and guarantee financial integrity.
- Utilize payroll reports to attain insights into labor costs, overtime, and payroll liabilities, allowing companies to make informed decisions, and assure compliance with regulations.
- Setting up clear payroll categories and accurate employee information is key for seamless payroll processing.
Advanced Payroll Customization in QuickBooks: Features You Shouldn’t Miss
Once you’ve mastered basic payroll recording in QuickBooks, the next step is customization—where efficiency, compliance, and control truly begin. From managing multiple pay schedules to handling bonuses, QuickBooks offers powerful tools to streamline even the most complex payroll needs. These advanced features let you tailor paycheck formats, track paid time off automatically, and differentiate between employee and contractor payments. Each function saves time, minimizes errors, and improves record accuracy. In this section, we’ll explore five key customizations that make payroll processing smarter, faster, and more aligned with your business structure.
How to Customize Paycheck Layouts and Templates in QuickBooks
Customizing paycheck layouts in QuickBooks improves clarity, ensures compliance, and enhances branding.
- Go to the Payroll Settings, then click Paycheck Printing Preferences.
- Choose between voucher style or standard style paychecks for better format control.
- Add or remove fields like employee ID, pay period, or deduction summary as per your needs.
- You can include the company logo, update font styles, and rearrange pay stub items for a professional look.
- Finalize by clicking Preview and test print before saving changes.
This setup boosts transparency, reduces employee confusion, and reinforces a consistent pay format.
Setting Up Different Pay Schedules for Multiple Employee Types
Creating multiple pay schedules in QuickBooks boosts flexibility, improves accuracy, and saves processing time.
- Go to Employees > Payroll Setup > Pay Schedules to begin the setup.
- Click Add New, then choose pay frequency like weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly.
- Assign each pay schedule to groups like full-time staff, part-time employees, or seasonal workers.
- Customize start and end dates for each schedule to align with actual working cycles.
- Review summaries to avoid overlapping periods or missed payments.
This feature helps streamline payroll runs, ensures timely compensation, and reduces manual errors.
Managing Contractor Payments Separately from Employee Payroll
Handling contractor payments separately in QuickBooks avoids tax mix-ups, ensures legal compliance, and simplifies 1099 reporting.
- Navigate to Expenses > Vendors > Add Contractor to create a separate profile.
- Mark them as 1099 contractors and fill in essential fields like TIN, email, and payment method.
- Use Bill or Expense entries instead of payroll to record payments.
- Assign correct Chart of Accounts categories like Contractor Services to track costs accurately.
- At year-end, generate Form 1099-NEC under the Payroll Tax > Filings section.
This separation avoids payroll tax errors, improves financial tracking, and supports cleaner audits.
How to Handle Bonus and Commission Payments in QuickBooks
Recording bonuses and commissions accurately in QuickBooks improves transparency, motivates employees, and ensures correct tax reporting.
- Go to Employees > Employee Center, then select the employee and click Edit Payroll Info.
- Add a new payroll item as Bonus or Commission using the Add Earnings Item option.
- Enter the exact amount separately from base pay to avoid merging it with regular wages.
- Apply correct tax settings—bonuses are typically taxed at a higher flat rate.
- Review the paycheck preview to confirm proper totals and withholdings before submission.
This method helps you reward fairly, stay compliant, and track incentive payouts clearly.
Tracking Paid Time Off (PTO), Sick Leave, and Vacation Accruals
Accurately tracking PTO, sick leave, and vacation accruals in QuickBooks improves employee trust, ensures policy compliance, and prevents payroll disputes.
- Go to Employees > Edit Employee > Payroll Info and click Sick/Vacation.
- Set up accrual rules—define hours accrued per pay period, maximum limits, and reset conditions.
- Choose whether accrual is based on hours worked, pay periods, or a lump sum.
- Display current balances on each paycheck to promote transparency.
- Run reports like Vacation and Sick Leave Summary to monitor usage patterns.
This system automates leave tracking, reduces manual errors, and supports better workforce planning.
Payroll Accuracy and Compliance: Pro Tips Every QuickBooks User Must Know
Once your payroll system is set up, the real challenge is maintaining accuracy, staying compliant, and avoiding common pitfalls. Even a small payroll error can lead to penalties, employee dissatisfaction, or tax trouble. This section gives you a practical edge with actionable tips that go beyond setup—like fixing incorrect entries, reconciling with bank statements, and meeting state-specific legal requirements. You’ll also learn how to prepare year-end reports without stress. Each topic is designed to strengthen your payroll process and keep your business audit-ready, accurate, and fully compliant in QuickBooks.
Common Payroll Mistakes in QuickBooks and How to Avoid Them
Avoiding payroll mistakes in QuickBooks helps maintain legal compliance, ensures accurate pay, and prevents IRS penalties.
- One common error is forgetting to update tax tables—always refresh them before running payroll.
- Entering incorrect employee classification (e.g., contractor vs. W-2 employee) can lead to audit risks.
- Misreporting overtime hours or skipping PTO accrual settings affects employee trust and accuracy.
- Not reconciling payroll liabilities with actual payments causes accounting mismatches.
- Skipping paycheck previews leads to unnoticed deductions or pay rate issues.
Fixing these early keeps records clean, boosts employee satisfaction, and ensures audit-readiness.
How to Fix Incorrect Payroll Entries in QuickBooks
Correcting payroll errors in QuickBooks restores accuracy, avoids tax issues, and maintains clean financial records.
- Go to Employees > Payroll Center, then locate the incorrect paycheck in the Transaction List.
- Click Void or Delete only if it hasn’t been submitted to tax agencies yet.
- Use Payroll Adjustments to fix taxes, hours, or deduction errors without voiding the entire entry.
- Recreate the paycheck with the correct details and assign it to the same pay period.
- Always document the correction using Memo fields and update reports to reflect changes.
Fixing entries quickly prevents compliance errors, rebuilds trust, and ensures year-end reports stay balanced.
Reconciling Payroll with Bank Statements: Step-by-Step Guide
Reconciling payroll with bank statements ensures financial accuracy, detects payment issues, and supports error-free audits.
- Start by opening Reconcile under the Accounting > Chart of Accounts section in QuickBooks.
- Select your payroll checking account, then enter the statement end date and ending balance.
- Match each payroll transaction, including net pay, tax payments, and benefit deductions, with the bank entries.
- Flag any unmatched items like duplicate checks or missing deposits for investigation.
- Once all entries align, click Finish Now and save a copy of the reconciliation report.
Doing this monthly improves accuracy, prevents fraud, and keeps payroll and banking records in sync.
Tips for Staying Compliant with State-Specific Payroll Laws
Following state payroll laws prevents penalties, protects your business, and ensures employee rights are upheld.
- Always check your state’s minimum wage, overtime rules, and pay frequency laws before running payroll.
- Register for state-specific tax accounts like SUI (State Unemployment Insurance) or PIT (Personal Income Tax).
- Set up proper withholding rates, especially if your business operates across multiple states.
- Use QuickBooks’ automated tax updates to stay aligned with regulation changes.
- Regularly review state payroll reports to catch discrepancies in benefits, leave accruals, or deductions.
This keeps payroll legally sound, reduces audit risks, and strengthens employer-employee trust.
How to Prepare Payroll Reports for Year-End Filing
Year-end payroll reports ensure accurate filings, support tax form generation, and simplify financial reviews.
- Go to Reports > Employees & Payroll, then select Payroll Summary, Tax Liability, or Employee Details.
- Set the date range from January 1 to December 31 to capture the full year’s data.
- Review totals for gross pay, tax withholdings, benefits, and deductions—correct any discrepancies immediately.
- Generate W-2s or 1099s under the Payroll Tax > Filings section for distribution and e-filing.
Archive final reports securely and back them up for compliance and audit preparation.
This process closes the year cleanly, avoids missed filings, and ensures smooth transitions into the new payroll cycle.
Conclusion!
Recording payroll in QuickBooks is an essential procedure that guarantees your company complies with tax regulations and keeps correct financial records. By adhering to systematic procedures, which include setting up payroll items, updating employee details, executing payroll, and recording payroll expenses, you can expedite your payroll process, lower errors, and save time. The control and insight QuickBooks provide not only make accounting responsibilities easier but also give you a comprehensive picture of the financial health of your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between recording payroll in QuickBooks Desktop (QBD) versus QuickBooks Online (QBO) when using a third-party payroll service?
The primary distinction is in the process and the tools used for reconciliation. Both systems require recording a summary of the external payroll to reflect accurate finances, but the method differs.
- QuickBooks Desktop (QBD): Users typically process the payroll summary through a Payroll Liabilities or General Journal Entry transaction, often after manually setting up matching payroll items. The complexity is often managed using summary-level transactions against liability and expense accounts to align the books with the third-party payroll report.
- QuickBooks Online (QBO): The standard method involves creating a Manual Journal Entry. This requires the user to first establish specific Expense accounts (e.g., Payroll Expenses: Wages) and Liability accounts (e.g., Payroll Liabilities: Federal Taxes) within the Chart of Accounts to map the external data accurately. This method provides explicit control over the debits and credits.
When manually recording external paychecks in QuickBooks Online, why is it critical to use both Expense and Liability accounts, and what is the required entry structure?
It is vital to use both account types to adhere to the fundamental accounting equation, which ensures the company’s financial statements are accurate and compliant.
- Expense Accounts (Debits): These record the total cost of payroll to the business, including the gross wages and the employer’s portion of payroll taxes (like FUTA and employer Social Security/Medicare). Debiting these accounts increases the business’s expenses, correctly decreasing its profit on the Profit & Loss Report.
- Liability Accounts (Credits): These record the money the business owes but has not yet paid, such as all withheld taxes (employee and employer portions) and other deductions (like health insurance or 401k) that must be remitted to third parties. Crediting these accounts increases the liabilities on the Balance Sheet.
The basic structure ensures the total Debits equal the total Credits:
- Debits:
- Gross Wages Expense
- Employer Tax Expense
- Credits:
- Payroll Tax Liabilities (All withholdings/contributions)
- Cash/Checking Account (Net Pay)
How can I correct a paycheck in QuickBooks Desktop that was created with the wrong hours or deductions but has not yet been sent to the employee or tax agency?
If the paycheck exists in the system but has not been sent, the recommended process is to Void or Delete the incorrect paycheck and then recreate it correctly.
- Locate the Paycheck: Navigate to the Employee Center or the list of checks/transactions.
- Action: If the check number must be preserved for tracking, Void the paycheck. If the check number does not need to be retained, Delete the paycheck.
- Recreate: Immediately create a new paycheck for the same pay period with the correct hours, rate, and deductions.
Crucial Note: If the paycheck has already been sent to a tax agency or submitted for direct deposit, you must use a Payroll Adjustment to fix the tax liabilities and Year-to-Date (YTD) figures, as simple voiding may cause significant reporting errors.
What are the three crucial pieces of information that must be verified when reconciling payroll with the bank statement monthly?
Bank reconciliation for payroll goes beyond matching the bank’s ending balance; it involves confirming that all payroll-related transfers are accurately recorded. The three crucial items to verify are:
- Net Pay Disbursements: The total amount withdrawn from the bank account for employee direct deposits and cleared paychecks must match the total Net Pay recorded in the payroll summary.
- Total Tax Payments: The withdrawals made by the IRS and state/local tax agencies must align exactly with the amounts recorded as payments against the Payroll Liability accounts.
- Third-Party Service Fees: Any separate fees charged by the payroll provider (e.g., ADP, Gusto) must be accurately accounted for as a Payroll Expense or Bank Service Charge expense in QuickBooks.
When customizing paycheck layouts in QuickBooks, which three fields are most important for employee clarity and compliance?
The primary goal of the paycheck stub is to provide transparency and meet legal mandates. The three most important fields for customization are:
- Accrued Time Off Balances: Clearly displaying the employee’s current available balance for Paid Time Off (PTO), Sick Leave, or Vacation Time is often legally required by state and local laws and prevents disputes.
- Detailed Deduction Breakdown: Showing the exact amount and type of every single deduction (e.g., 401k Employee Contribution, Health Premium Pre-Tax) satisfies legal disclosure requirements and allows employees to easily track their benefits.
- Pay Period Dates: Explicitly listing the Start Date and End Date of the work period covered is necessary to confirm wage compliance and align employee expectations, especially regarding overtime calculation periods.
Why should contractor payments (1099) be managed separately from employee payroll (W-2) in QuickBooks, and what is the primary compliance risk?
The separation is necessary because the two classifications have fundamentally different tax treatment and reporting requirements.
- Primary Compliance Risk: Worker Misclassification. The IRS evaluates the Behavioral Control, Financial Control, and Relationship between the business and the worker. Misclassifying an employee (W-2) as an independent contractor (1099) results in the business failing to withhold and remit Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment taxes, leading to significant fines and penalties.
- QuickBooks Management Difference:
- W-2 Employees: Payments use the Payroll function, involving tax withholding and liability tracking.
- 1099 Contractors: Payments are recorded as Bills or Expenses using the Vendors section, with no tax withholding. The system only tracks the amount paid to generate the year-end Form 1099-NEC.
What is the immediate step to take in QuickBooks Online if a tax payment you already made is still showing up as due in the Upcoming tax payments section?
If a tax payment was made outside of the QuickBooks Online Payroll system (e.g., via check or direct state website payment), it must be manually recorded to clear the liability and remove the false due status.
- Path: Go to Taxes, then select Payroll Tax.
- Action: Click the Payments tab. In the Upcoming tax payments section, locate the tax and select Record Payment.
- Data Entry: Enter the actual date the payment was made (selecting the Other payment option) and the check number or confirmation ID.
- Finalize: Click Record to successfully mark the liability as paid and update your balance sheet.
Disclaimer: The information outlined above for “How to Record Payroll in QuickBooks Desktop and Online?” is applicable to all supported versions, including QuickBooks Desktop Pro, Premier, Accountant, and Enterprise. It is designed to work with operating systems such as Windows 7, 10, and 11, as well as macOS.
