The straight-line depreciation method is a type of depreciation method that remains constant over a fixed asset’s useful life.
Straight line depreciation method spread the assets costs evenly over the course of time, it will be used, which is also known as “useful life of an asset”
Key Takeaways
- Straight line basis is a method of calculating depreciation and amortization, which is the process of expending an asset over time.
- It is computed by dividing the difference between an asset’s cost and estimated salvage value by the expected number of years of use.
- The straight-line basis is popular because it is simple to compute and understand, but it does have some limitations.
- To guarantee accurate asset appraisal and financial reporting, master straight-line depreciation.
- Select the appropriate approach for every asset, taking into account units of production or double-declining balance in some situations.
What is the Straight Line Depreciation Method?
Straight line depreciation also known as “ straight-line basis” is a method of depreciation used to measure the depreciation of a fixed asset over a time. Fixed assets include machinery, buildings, computers, equipment, furniture and land improvements, etc.
In the case of fixed assets, the value is reduced over its useful life.
With this method, the depreciation value remains constant over the asset’s useful life because it is assumed that the assets continue to provide the same level of benefit to the company throughout their useful life.
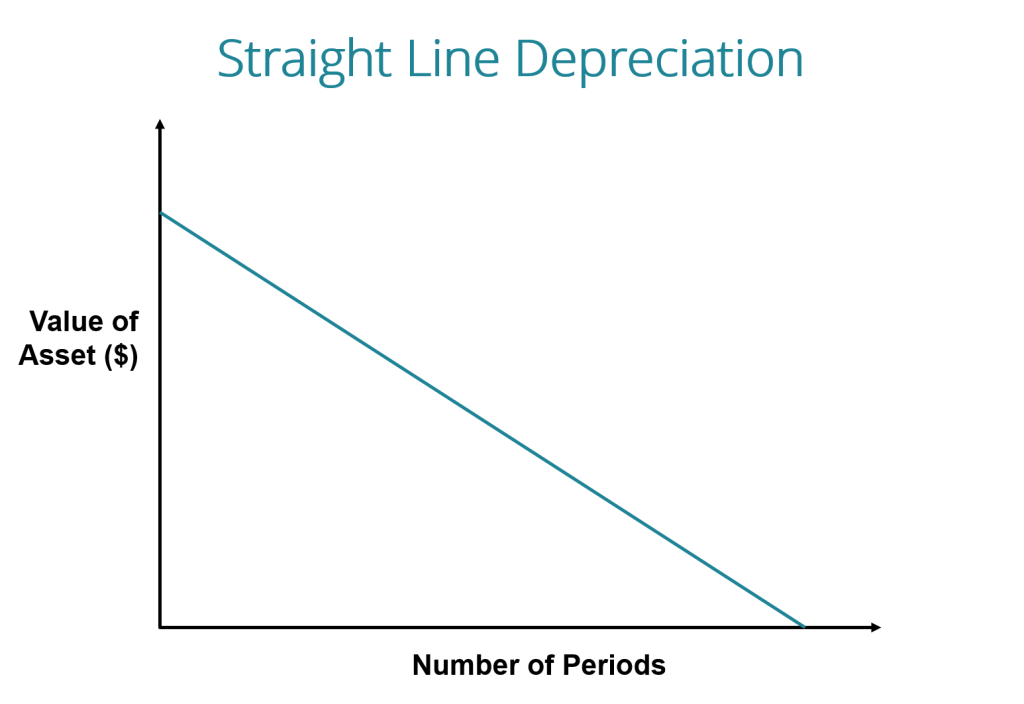
Straight-line depreciation is determined by dividing the difference between an asset’s purchase price and its anticipated salvage value by the number of years it is expected to be in use.
Businesses use amortization for intangible assets such as patents and software and depreciation for physical assets. Both methods spread the cost of an asset over its useful life, helping the company avoid a significant one-time expense that could decrease its income and profitability if the entire cost of the asset were expensed in the year it was purchased.
Formula of Straight-line depreciation method
| Straight-line depreciation = (Purchase Price of Asset – Salvage Value) / Estimated Useful Life of Asset |
OR
| Straight-line depreciation = (Purchase price of Asset – Salvage Value) x Depreciation Rate |
Where:
- Purchase Price of Asset: This refers to the cost of the asset at which it is purchased. It includes the item price and factors such as transportation, commissions, warranties, appraisals, and installation and testing.
- Salvage Value: It refers to the value of a tangible asset at the end of its useful life.
- Estimated Useful Life of Asset: This refers to the number of years the company is expected to use the asset.
- Depreciation Rate: (Annual Depreciation Amount / Useful Life) x 100
What are Other Depreciation Methods?

Straight-line depreciation is the most widely used method; other approaches can be more appropriate in specific situations. Although units of production and double-declining balance provide flexibility, other methods also have their own set of trade-offs.
- Double-Declining Balance: This balance distributes a larger depreciation expense in the early years and a lesser one in the later years, accelerating depreciation. It is helpful for items that lose more value quickly in life.
- Units of Production: Depreciates based on the amount of use of the asset, assigning a higher depreciation amount for increased use. This approach is perfect for assets like machinery or automobiles.
- Sum-of-the years’-digits method: The depreciation method calculates depreciation charges using a fraction. The numerator represents the number of years in the asset’s useful life, while the denominator is the total sum of the digits from 1 to the number of years in the asset’s useful life.
- MACRS (Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System): The U.S. tax-based depreciation technique known as MACRS (Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System) accelerates depreciation over a predetermined recovery period. It applies predetermined depreciation rates to various asset classifications.
Why Does Business Prefer the Straight-line Depreciation Method?
Small businesses prefer to use the straight-line depreciation method, as this helps them free up cash flows for investment, improve overall financial planning, reduce the risk of unexpected tax bills, and plan for future tax liabilities.
Some of the other reasons to choose the straight-line depreciation method are mentioned below:
- Tax Benefits: The straight-line depreciation method considers depreciation expense a deductible expense, reducing taxable income and providing tax benefits to companies.
- Investment Decision: Straight-line depreciation helps businesses improve their investment decisions. The business knows the annual depreciation amount, can calculate net income, and can determine whether the asset is a justified investment.
- Simple: It is one of the easiest ways to calculate the depreciation expense as the depreciation amount remains over the asset’s useful life.
- Compliance: The straight-line depreciation method is accepted under both IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) and GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). Businesses can use this method to ensure compliance with these standards.
- Predictable: The straight-line method offers a consistent depreciation expense over an asset’s useful life, making it easier for businesses to plan and budget for future asset replacement or maintenance needs.
What Numbers Are Included in Straight-Line Depreciation?
Specific factors must be taken into account for each of the three data points—asset cost, salvage value, and usable life—used to compute straight-line depreciation. Costs must be allocated logically and methodically, which requires estimation and judgment.
- Purchase Price/ Original Cost of the assets
The purchase price of an asset covers all labor and material costs, including shipment, installation, taxes, commission fees, and customization required to put it into use.
All fixed assets are recorded on a company’s books at their original cost.
- Salvage or scrap value
It is an approximation of the amount of money that can be obtained upon the asset’s removal from service and subsequent sale or scrapping.
A fixed asset may have a salvage value if the company intends to resell it once it is no longer needed.
- Useful Life
It is a key factor in straight-line depreciation that shows how long the asset is anticipated to remain in operation.
According to the matching principle, the duration over which an asset is depreciated aligns the expense with the revenue it generates in the same period.
How Do You Calculate the Straight-Line Depreciation Method?
Steps to Calculate the Straight-line Depreciation Method
| Straight-line depreciation = (Purchase Price of Asset – Salvage Value) / Estimated Useful Life of Asset |
OR
| Straight-line depreciation = (Purchase price of Asset – Salvage Value) x Depreciation Rate |
Where:
- Purchase Price of Asset: This refers to the cost of the asset at which it is purchased. It includes the item price and factors such as transportation, commissions, warranties, appraisals, and installation and testing.
- Salvage Value: It refers to the value of a tangible asset at the end of its useful life.
- Estimated Useful Life of Asset: This refers to the number of years the company is expected to use the asset.
- Depreciation Rate: (Annual Depreciation Amount / Useful Life) x 100
Steps to Calculate the Straight-line Depreciation Method
Step 1: Find the cost of the asset. Make sure to include the price of the asset along with all the costs included while putting the service into use.
Step 2: Then, subtract the estimated salvage value from the cost of the asset to find the total depreciable amount.
Step 3: Next, determine the useful life of the asset.
Step 4: Finally, divide the depreciable amount by the useful life to calculate the annual depreciation amount.
Example of Straight Line Depreciation Method
Beauty & Beast Private Limited purchases a printer. The salvage value of the printer is $2,000 and its useful life is 4 years. Its purchase price is $20,000.
Solution:
Given:
- Purchase price of the asset = $ 20,000
- Estimated salvage value = $ 2000
- The useful life of the asset = 4 years
| Straight-line depreciation formula = (Purchase price of asset – Salvage Value)/Useful Life |
= (20,000 – 2000) /4
= $4,500
Now,
Annual depreciation = $4,500
Total asset = 4 years
Depreciation Rate = (Annual Depreciation Amount / Useful Life) x 100
= (1/8 ) x 100
= 12.5 %
After calculating the depreciation expense, the depreciation account on the balance sheet will show the accumulated depreciation for the printer over four years:
| Year | Book Value (Beginning year) | DepreciationAmount | Book Value (End of the year) |
| 1 | $20,000 | $4,500 | $15,500 |
| 2 | $15,500 | $4,500 | $11,000 |
| 3 | $11,000 | $4,500 | $6,500 |
| 4 | $6,500 | $4,500 | $2,000 |
Merits of Straight Line Depreciation Method
- Appropriate for Small Businesses: This method is suitable for small and medium-sized businesses because it is easy and quick to calculate, and it does not require specific knowledge to implement.
- Boosts timely asset replacement: By providing an estimated depreciation expense over the asset’s life, businesses can plan to replace depreciable assets at the end of their useful life in a timely manner.
- Helps calculate Profits: Straight-line depreciation offers a consistent depreciation rate, which is valuable for comparing assets among different competitors or industries.
Demerits of Straight Line Depreciation Method
- Not suitable for all assets: Some assets may depreciate more rapidly at the beginning or end of their useful life. This method works best for assets with a predictable and consistent decrease in value.
- Loss of Revenue: The depreciation deducted is not reinvested or utilized outside the company, resulting in no additional revenue or interest for the business.
- Unsuitable for large businesses: The straight-line method may not be suitable for large companies with different operations and various assets having different useful lives.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Straight Line Depreciation
The straight-line depreciation approach has its own advantages and disadvantages, much like any other depreciation technique.
Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of using straight-line depreciation method:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Simplicity: This is easy to apply and understand. | Inaccurate Depreciation: This may not reflect how the asset’s value actually declines |
| Consistency: Provides the same expense amount each period, aiding financial planning. | Overstates Value: Can overstate or understate asset value at different points. |
| Predictability: Helpful for budgeting since expenses are fixed. | Not Suitable for All Assets: Assets with unpredictable usage or wear may require a different method. |
| Widely Accepted: Favored for compliance and tax reporting by authorities. | 5. No Flexibility: Fails to consider an asset’s changing utility over time |
| 5. Minimal Record-Keeping: Requires fewer adjustments, reducing administrative work. | Ignores Usage Patterns: This doesn’t account for high-use periods that may accelerate depreciation. |
Despite its ease of use, the straight-line method may not provide the most accurate picture of an asset’s depreciation. It’s essential to consider whether this method fits your business needs and the asset’s usage pattern.
Conclusion
The straight-line depreciation method is a simple way to calculate the expense of any fixed asset in your business. Every business must know how to calculate straight-line depreciation of its fixed assets, as it is crucial to its success.
With straight-line depreciation, you can reduce the value of a tangible asset and get benefits from that depreciation during tax season.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the other methods of depreciation?
Other options besides straight-line are units of production, falling balance, and sum of the years’ digits. Depending on how assets are used and what the business needs are, each technique offers flexibility in how depreciation is calculated.
How is straight-line depreciation different from other methods?
In contrast to the accelerated decreasing balance, activity-based units of production, and front-loaded sum-of-the-years’ digits methods, straight-line depreciation equally spreads costs over an asset’s useful life, making computations easier and resulting in predictable costs.
What is straight-line amortization?
For intangible assets like patents and copyrights, straight-line amortization applies the idea of straight-line depreciation. Like depreciation for tangible assets, it distributes the cost of the intangible asset equally throughout its useful life.
What is the formula for depreciation?
The formula for a straight line is (Useful Life / Salvage Value—Cost of Asset), which determines the annual depreciation amount. Other techniques modify this formula to reflect their own computations.

