Highlights (Key Facts & Solutions)
- The initial diagnosis must verify if the outage is external (use sites like downforeveryoneorjustme.com) or internal (check other devices).
- The most frequent cause of connected-but-no-internet is a corrupted DNS cache, fixed by using platform-specific commands (e.g.,
ipconfig /flushdnson Windows). - To resolve transient errors and force a new external IP address, power cycle the modem and router for at least 60 seconds.
- Router physical placement is critical for Wi-Fi quality; place it centrally, elevated, and away from thick walls or interfering electronics like microwaves.
- When troubleshooting, immediately disable any active VPN to eliminate external server complexity as a potential variable.
- For failed Ethernet connections, prioritize physical checks: ensure the cable is firmly seated and plugged into the LAN port on the router, not the WAN port.
- To check the status of a wired or wireless connection on a PC, Windows users can run
ncpa.cplto quickly access the network connections list.
Overview
Even a short wi-fi or internet glitch can impact your company’s profits. To avoid these risks, it’s crucial to know the necessary troubleshooting skills. When faced with internet connectivity issues, follow these practical network troubleshooting tips to restore your connection swiftly:
When to Check Wireless Network Connection Status
Determining the optimal moment to verify your connection is as crucial as understanding the procedure itself. Inspect the connection when an error message appears on your screen or when you encounter difficulties with network-connected applications that either crash or become unresponsive.
The approach for assessing your network connection status varies based on the specific device in use. Here are some guidelines for different devices:
Computer or Laptop
Windows, macOS, and other operating systems come equipped with built-in connection management utilities. However, the steps to access this specific area of the software may vary depending on the device you’re using.
For example, you can find the Network and Sharing Center in Windows, which shows the status of both wired and wireless networks. To gain access of the list of network connections in Windows, you need to press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box, and then enter the command ncpa.cpl (or netsetup.cpl for Windows XP).
Over different operating systems like macOS, the status bar which is located either at the bottom or top of the screen, features icons that visually represent the connection status.
Moreover, there are third-party applications which are available and offer similar features through alternative user interfaces.
Router
The administrator console of a network router catches important details about both the router’s connection to the outside world and the links for any devices on the Local Area Network (LAN) that are connected to it. To access this information, log in to the router.
If you can access the router by using a mobile app, go to the main screen of the app. Here, you can check whether the entire network is down or if particular devices are disconnected. The app may also display a notification when the network experiences an outage or reconnects to the internet after a power failure or other issues.
Additionally, most routers feature LED lights that indicate the connection status for both the WAN (Wide Area Network) link and any wired connections. Some routers have a single light that turns red when there’s a connection problem. If your router is conveniently located where you can easily see these lights, take the time to learn how to interpret the colors and flashes. This way, you can save time and avoid unnecessary logins to check the connection status.
Reasons Behind Why the Internet is Not Working
Despite the wi-fi symbol indicating a connection, there are several reasons why you might still find yourself without internet access. The most frequent cause is an issue with your router or modem or perhaps a loose cable. However, it’s important to recognize that internet disruptions can also occur due to more intricate technical factors.
Below are the most common reasons why the internet has stopped working:
- If your internet works on one device but not another, the problem may be with the specific device.
- Wi-fi plays an important role in ensuring a stable internet connection. If it is turned off on the device, you won’t be able to connect with any wireless networks.
- Sometimes, websites go down, making it appear as if your internet is faulty. At times, the servers encounter issues, causing challenges when accessing websites through their user-friendly domain names.
- Sometimes, a router causes the actual problem, which leads to an unstable internet connection or no internet connection. Every router has symbols and lights indicating different statuses.
- Ethernet can sometimes lead to no internet access despite being physically connected.
- Incorrect VPN setup or Incorrect proxy server settings can lead to internet problems and disrupt the internet connection.
Troubleshoot Internet Connection Settings
Follow these practical network troubleshooting steps to restore your connection when faced with internet connectivity issues swiftly:
Check Another Device or Website
Let’s start with the basics: Is the problem happening on just one device or all of them? If your computer is acting up, check if your computer or someone else’s laptop can connect to the internet. If it’s only one device causing trouble, focus on that.
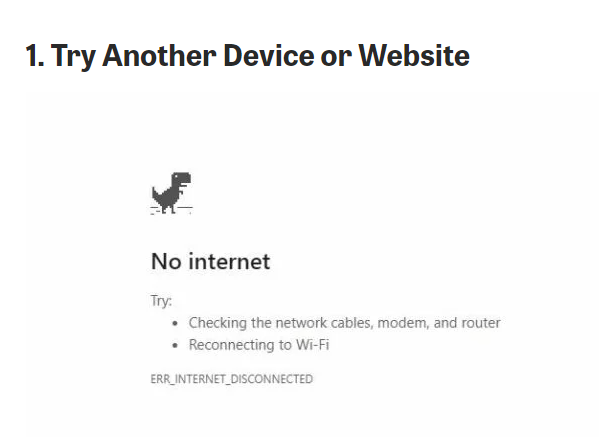
If a specific website won’t load, test another site. If other websites work fine, the issue is probably with the site you’re trying to visit. You might need to wait for them to fix it. To verify if a website is down for everyone or just you, type its address into downforeveryoneorjustme.com or downdetector.com.
If there’s no known outage, it could be your browser’s cache causing trouble. Try opening the site in an incognito window or a different browser.
Verify the wi-fi Settings
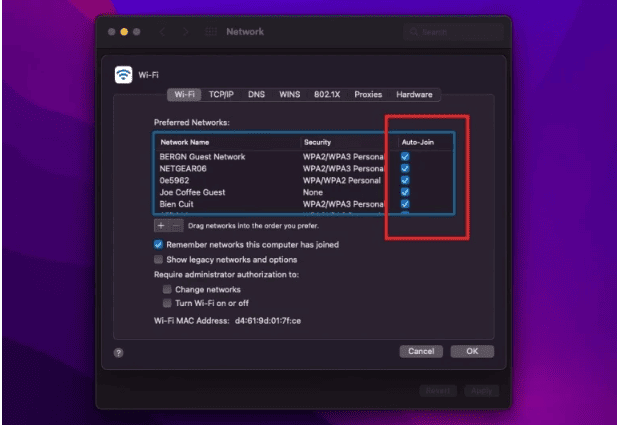
Windows: Look for the wi-fi signal icon in the bottom-right corner of your screen. Click the icon and ensure that you are connected to the correct SSID. If not, you might be unintentionally connected to the wrong network.
If you encounter connectivity issues, consider running the Network Troubleshooter to diagnose and resolve the problem. Follow these steps:
For Windows 10:
- Click the Start button.
- Navigate to Settings > Network & Internet > Status.
For Windows 11:
- Click the Start button.
- Type settings.
- Select Settings > Network & internet.
macOS: Check the wi-fi signal icon in the top-right corner of your screen. Click the icon and confirm that you are connected to the appropriate SSID. If not, you may be connected to the wrong network by default.
Note: An SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the primary name associated with a wireless local area network (WLAN), which includes home networks and public hotspots. It serves as the identification label for your wi-fi network.
Clear the DNS Server
The DNS cache serves as a digital record that your browser relies on to swiftly retrieve web pages you’ve previously visited. However, this cache can lead to technical problems if glitches occur or if online malware inserts unwelcome URLs into it.
Here are the steps to clear your DNS cache on different devices:
Windows:
- Open Command Prompt:
- Typing “cmd” into the search bar.
- Finding the Command Prompt shortcut in the Windows System folder.
- Typing “cmd” into the Run window.
- Type ipconfig /flushdns in the Command Prompt.
- Press Enter to flush the DNS.
Mac:
- Open Terminal in the Utilities folder.
- Search for “Terminal” using the Spotlight function.
- Enter the command to flush the DNS in the Terminal app.
Depending on your Mac operating system (OS), enter one of the following commands in the Terminal app:
- For Yosemite and later: sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
- For Yosemite 10.10–10.10.3: sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache
- For Mavericks, Mountain Lion, Lion: sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
- For Snow Leopard: sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
You’ll be asked to enter your administrator password. Once entered, your cache will be flushed, and any glitches should be resolved.
Check the Router
When it comes to router placement, there are several important factors to consider: distance, elevation, and obstructions.
Central Location and Elevation:
- Choose a spot for your router that is central within your living space.
- Elevate the router relative to your devices. Placing it at a higher position ensures better coverage.
- Avoid placing the router near electronic devices, especially microwaves, which can interfere with the signal.
Wi-fi Signal Strength:
- Wi-fi radio waves weaken as they travel farther. Keep your devices well within the router’s broadcast range.
- Use the Wi-Fi signal meter on your device to assess the strength of the current Wi-Fi signal.
Router Height Matters:
- The router’s signal doesn’t travel in a straight line to your device. Instead, it spreads out like light from a bulb, creating a dome of wi-fi.
- Position the router as high as possible to achieve a wider broadcast and better coverage throughout your home.
Restarting the Router:
- Sometimes, restarting the router can resolve internet connectivity issues.
- If your router has been off for a while, a quick restart may bring it back to working condition.
When to Consider a New Router:
- Hardware and software components in routers and modems can occasionally cause issues.
- If you find yourself rebooting the router frequently to address connectivity problems, consider a new modem or router.
- In such cases, reaching out to your local ISP (Internet Service Provider) for assistance is advisable.
Fix Ethernet Connection
A wired Ethernet connection provides a speedy internet connection. Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to your home router and the other end to the Ethernet port on your Windows PC. If your PC lacks an Ethernet port, you can explore using a USB to Ethernet adapter.
In case you encounter connectivity issues despite using an Ethernet connection, consider the following steps to troubleshoot and regain internet access.
Things to Consider Before Troubleshooting
- Make sure that the Ethernet cable is firmly connected to both the Ethernet port on your router and your Windows 10 and 11.
- On your router, verify that the cable is plugged into the correct Ethernet port, not the one designated for connecting your modem and router.
- If one Ethernet cable doesn’t establish a connection, try using another cable nearby.
- If the second cable works, it may indicate an issue with the initial cable.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Navigate to Settings.
- Go to Network & Internet.
- Click on Status.
- Verify your Ethernet connection status. It should indicate “You’re connected to the Internet” under the Ethernet network connection.
Disable VPN
Using a VPN offers several advantages, but it also introduces an additional layer to your internet setup. Consequently, what appears to be a home network issue might actually stem from your VPN. Occasionally, a VPN may time out if you remain connected for extended periods while your system is idle, or you might be using an overloaded server that struggles to handle your connection.
If you’re currently using a VPN—whether through an app or a manual Windows connection—disable it temporarily and attempt to go online again. If the issue persists, keep the VPN turned off during troubleshooting to simplify the process and reduce variables.
Takeaway
Disruption in Internet Connection can be caused due to hardware malfunction or internet connectivity misconfiguration. In most cases, users face difficulty with network connection when wi-fi is connected but shows no connection error.
To solve your issue quickly, kindly follow the troubleshooting methods that are mentioned above in this article.
FAQs:
Q1. If my Wi Fi icon shows I am connected but I still cannot access the internet, what is the most likely cause?
When your device shows a connection to the local Wi Fi network but cannot reach the internet, the most likely cause is a faulty Domain Name System (DNS) server setting or an outage beyond your local router.
- DNS Failure: The DNS acts as the phonebook for the internet, translating user friendly website names (like
google.com) into numerical IP addresses. If your DNS cache is corrupted or the assigned DNS server is down, your device cannot find the IP address even though it is connected to the Wi Fi signal. - External Outage: The problem is likely with the Wide Area Network (WAN) link, meaning the connection between your modem/router and your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is broken. You should check the lights on your router and modem.
- Fix: Flush your DNS cache (see Q4) and then reboot your router and modem to force a new WAN connection.
Q2. How can I quickly determine if a website is down for everyone or just me, before I start troubleshooting my network?
Before investing time in network troubleshooting, you should confirm the website’s status using external diagnostic tools, which saves unnecessary checking of local hardware.
- External Website Check Tools:
- downforeveryoneorjustme.com: This site checks the website’s status from external servers, confirming if the outage is global.
- downdetector.com: This site tracks user reports and known service disruptions for major websites and services (like Google, Facebook, or your ISP).
- Browser Cache Test: If the external tool confirms the site is up, the problem may be your local browser cache or DNS record. Try accessing the site using an incognito or private browsing window or a completely different browser to bypass the local cache.
Q3. What is the technical reason for restarting my router and modem, and how long should I keep them powered off?
Restarting (or power cycling) your router and modem is necessary to clear their temporary memory (cache) and force them to re establish their connection and configuration with your ISP.
- Technical Reason: Routers accumulate network traffic data, address assignments, and minor errors in their working memory. A restart clears this temporary state, resolving minor glitches and memory leaks. More importantly, it forces the modem to perform a fresh Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) request to the ISP, acquiring a new external IP address and clean connection parameters.
- Recommended Power-Off Time: You should keep both the router and modem completely powered off for at least 60 seconds. This duration ensures all internal capacitors discharge and the temporary memory is fully reset. Power the modem on first, wait for its lights to stabilize, and then power on the router.
Q4. What specific command do I use to clear the DNS cache on a Windows PC, and why does this fix internet issues?
You must use the ipconfig /flushdns command in the Command Prompt to clear the DNS cache on a Windows PC.
- Command and Execution:
- Open the Command Prompt (search for
cmd). - Type the command:
ipconfig /flushdns - Press Enter.
- Open the Command Prompt (search for
- Why it Fixes Issues: Your PC keeps a local record of recently visited websites. If a website’s IP address changes, or if the cache becomes corrupted (e.g., due to malware inserting bad entries), your browser keeps trying to use the old, incorrect IP. Flushing the DNS forces your computer to look up the correct, current IP address from the DNS server again.
Q5. Why is the physical placement of my router important, and what are the three key factors to avoid?
The physical placement of your router directly affects its signal strength and coverage (Signal Strength), as Wi Fi signals are radio waves easily weakened by obstacles.
- Router Placement Factors:
- Central Location: Place the router as centrally as possible, preferably on the main floor, to ensure the signal spreads evenly throughout the home.
- Elevation: Place the router as high as possible (e.g., on a shelf or desk). The signal spreads outwards and slightly downwards, creating a dome of coverage.
- Obstructions to Avoid:
- Thick walls (concrete or brick).
- Large metal objects (refrigerators, filing cabinets).
- Electronic devices that cause interference, especially microwaves, cordless phones, and large speakers.
Q6. If an Ethernet connection fails to connect, what are the three initial checks I must perform before troubleshooting the software settings?
Before checking software settings like the Network and Sharing Center, you must perform three immediate physical checks to rule out a hardware failure.
- Initial Physical Checks:
- Cable Connection: Verify the Ethernet cable is firmly seated (clicked in) at both ends: the router/switch and the computer’s Ethernet port.
- Router Port: Ensure the cable is plugged into a numbered LAN port on the router, not the dedicated WAN port (which is for the modem connection).
- Cable Swap: Try swapping the cable with a known good, working Ethernet cable. A failed or damaged cable is a very common cause of connectivity loss.
Q7. Why should I temporarily disable my VPN when troubleshooting a general internet outage, even if the VPN is not the suspected cause?
You should temporarily disable your Virtual Private Network (VPN) because it introduces an extra layer of complexity and an external server dependency, which can mask the true local cause of the outage.
- Reducing Variables: The VPN creates an encrypted tunnel, meaning your connection is routed through a third party server before reaching the internet. If you turn off the VPN and your internet access is restored, the problem lies with the VPN server or its client application, not your home network.
- Simplifying Diagnostics: If you disable the VPN and the internet still does not work, you have successfully eliminated the VPN as a variable, allowing you to focus diagnostics entirely on your local router, modem, and ISP connection without interference.
Disclaimer: The information outlined above for “How to Verify Internet Connection Settings?” is applicable to all supported versions, including QuickBooks Desktop Pro, Premier, Accountant, and Enterprise. It is designed to work with operating systems such as Windows 7, 10, and 11, as well as macOS.
