In public companies, it is the Shareholder’s Equity, and in private companies – the Owner’s Equity. In accountancy, the owner’s equity represents the returned value to a company’s shareholders if all the assets get liquidated and all its debts get paid off. Another term that needs to be mentioned in the Statement of Owner’s Equity. The owner arrives at this figure when he/ she writes the Owner’s Equity at the beginning of the period, then adds up the revenue, deducts the withdrawals, and calculates the equity.
In this article, we will learn about Owner’s Equity and the Statement of Owner’s Equity.
What Is Owner’s Equity – Definition
Owner’s Equity is the share of the total asset value owned by the owners(sole proprietorship) and shareholders of the company. You can calculate the total equity of a business by deducting the total assets from the total liabilities (Equity = Assets – Liabilities).
The amount that the company’s owner has to pay to its lenders, creditors, and investors is called liabilities. The sole difference between Owner’s Equity and Shareholder’s Equity is if the owners or the shareholders hold the company.
Is Owner’s Capital the Same as Owner’s Equity?
Owner’s capital and owner’s equity are closely related but differ in scope:
Owner’s capital is defined as the capital brought by the owner at the beginning of the business to carry on the business from which he expects to earn his profit. It is the tangible items that the owner puts into the business, such as cash, equipment, or other properties.
Owner’s Equity is a more extensive concept as it refers to the owner’s investment and any profits earned and reinvested in the business after reducing all expenses, plus any further investment made by the owner or a withdrawal made from the business. In other words, owner’s equity is calculated as the total share by the owner in the business after all the business contributions, earnings, and owner withdrawals have been factored in.
In simpler terms, the owner’s capital is part of the owner’s equity. In contrast, owner’s equity provides an additional overall picture of the owner’s investment in the business at any one time.
Understanding Owner’s Equity: What It Is and How to Calculate It?
You can calculate the owner’s equity by computing all the business assets (property, pieces of equipment, goods, etc.) and subtracting them from all your liabilities (payrolls, loans, wages, etc.). Here is how to find equity from assets and liabilities:
Owner’s Equity = Assets – Liabilities.
How do you calculate owner’s equity?
Suppose Sara owns a beauty salon in Boston and is wondering how much equity she has in the business. Last year, according to her balance sheet, her salon cost $1.5 million, the equipment she used cost $1 million, beauty products cost $800,000, and her receivable amount was $400,000. However, Sara owes $500,000 to the bank, $700,000 to the creditors, and $700,000 as reserves for salaries and wages.
Therefore, the calculation for equity would be:
Owner’s Equity = Assets – Liabilities
Assets = 1,500,000 + $1,000,000 + $800,000 + $400,000 = $3,700,000
Liabilities = $500,000 + $700,000 + $700,000 = $1,900,000
Sara’s Equity = $3,700,000 – $1,900,000 = $1,800,000
Therefore the value of Sara’s worth in the company is = $1.8 million.
George owns a fashion retail business. Its total assets would amount to $4 million, including a building, inventory, a vehicle for home delivery of products, and other long-term and short-term assets.
He also needs to pay back part of the loan he took for the building, overdue inventory payments, and other short-term/long-term liabilities, totaling $3 million.
Assets = $2,000,000 (building) + $1,000,000 (inventory) + $500,000 (vehicle) + $500,000 (others) = $4,000,000.
Liabilities = $1,000,000 (loan on building) + $500,000(payment of inventory) + $1,500,000 = $3,000,000
George’s Equity = $4,000,000 – $3,000,000 = $1,000,000
Therefore the value of George’s worth in the company is = $1 million.
Elements of Owner’s Equity
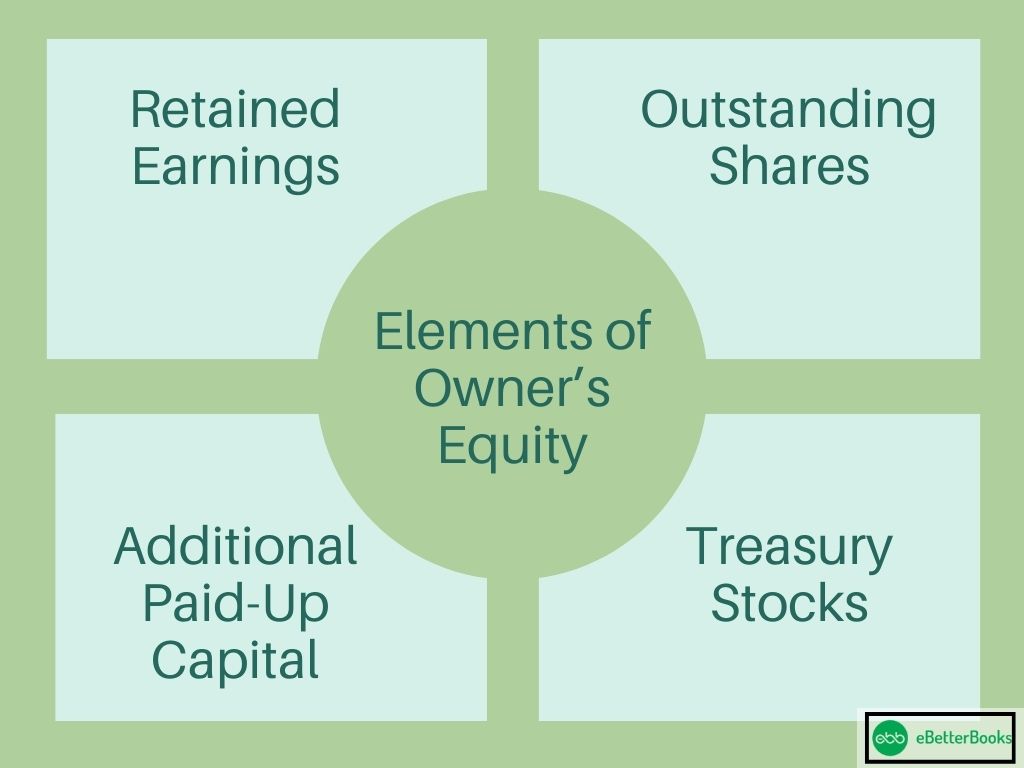
The primary elements of the owner’s equity are given below.
1) Retained Earnings
The amount shown as retained earnings in the balance sheet rather than paid off as dividends to the shareholders is called retained earnings. Retained earnings are the total revenue generated from operations and other activities that reflect the gains on shareholder investments repaid into the business rather than distributed as dividends. The volume of retained earnings increases with time as the firm reinvests a proportion of its earnings. It may represent a giant portion of shareholder value for firms that have been in operation for a lot longer.
The sum of stock sold to buyers but not yet repurchased by the company is called outstanding securities. The amount of outstanding shares is considered when calculating the price of a Shareholder’s Equity.
3) Treasury Stock
The number of securities repurchased from customers and shareholders is named treasury stock. To determine the number of shares issued to investors, subtract the sum of treasury stock from the firm’s overall Equity.
4) Additional Paid-in Capital
The additional paid-in cost is the capital that owners have spent on purchasing shares more than the declared stock’s par value. To calculate this figure, the company subtracts the market price of preferred stock from its par value, sales price, and the number of newly sold shares.
How to Calculate Owner’s Equity On A Balance Sheet?
Since owner’s equity comes after deducting total liabilities from total assets, it is calculated and recorded in a balance sheet at the end of the accounting period. Also, we know that assets are mentioned on the left column, and liabilities are shown on the right side.

Hence, the owner’s equity will reflect on the right side of the balance sheet.
We know that a businessperson infuses capital into a business and can withdraw a sum of money as well. The overall owner’s equity will be reflected as a net figure on the balance sheet.
What Is A Statement Of Owner’s Equity?
Statement of owner’s Equity depicts variation in the capital balance of a business within a specific duration. Generally, sole proprietors apply concepts where they add earned revenue to the capital and deduct total withdrawal from the company.
The result is the Statement of the owner’s Equity. Its value can rise with the owner’s income and contribution. Similarly, losses and withdrawals subtract from the remaining balance.
How To Prepare A Statement Of Owner’s Equity?
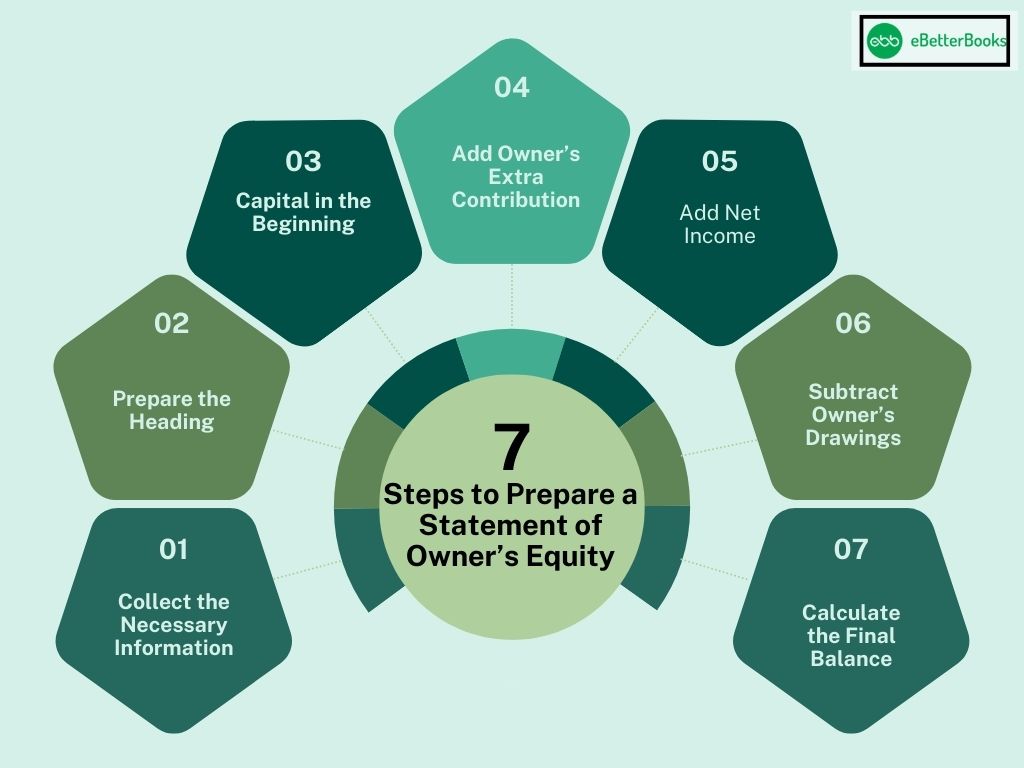
Given below are the steps describing how to prepare the owner’s Equity Statement :
1. Collect The Necessary Information
The Statement of Owner’s Equity comes after the Income Statement. We would continue to depend on the same information source.
Thus, the adjusted trial balance is the best source of knowledge when drafting financial statements. Regardless, any document containing a detailed list of modified accounts must be included. The Income Statement is included later in the process.
2. Prepare the Heading
Like any financial statement, the headline consists of three lines. The company’s name appears on the first sheet.
Subsequently, the report’s title appears on the second side. Statements of Changes in Equity, Statements of Owner’s Equity, or simply Statements of Changes in Equity would also be appropriate in this situation.
The third line depicts the period. Since the report spans time, we use Annual, for the Quarter Ended, for the Month Ended, etc. Any annual financial statements lack the term “for the Fiscal Year Ended.”
Therefore, Gray Electronic Repair Services Statement of Ownership Equity Changes for the Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 2020
3. Capital in the Beginning
Enter the capital that existed initially at report time or the remaining of the previous year, as last year’s final balance is the current year’s initial capital.
4. Add the Owner’s Extra Contribution
The owner’s additional contribution raises the capital and impacts the Statement of owner’s Equity.
5. Add Net Income
When the net income is added to the initial amount, it increases the capital. You can calculate net income by subtracting total revenues from the expenses.
6. Subtract the Owner’s Drawings
The owner’s withdrawals are recorded separately from the net income within the Statement of owner’s Equity. You can adjust it as either owner drawings or owner withdrawals. Withdrawals are made from the capital and hence deducted, so they are subtracted.
7. Calculate the Final Balance
Calculate the final value of the capital account by the end of the reporting period and draw the lines. A single horizontal line depicts the completion of a mathematical operation. At the same time, two horizontal lines are drawn below the result.
Statement Of Owner’s Equity Formula
The statement of owner’s equity is an essential part of the organization and has to be calculated properly. The formula of owner’s equity can easily be understood from the below template for the Statement of Owner’s Equity:
| Statement of Owner’s Equity | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| Beginning Owner’s Equity Balance | xxx |
| Add: | |
| Income Earned | xxx |
| Owner’s Contribution | xxx |
| Less: | |
| Losses Incurred | xxx |
| Withdrawals by the Owner | xxx |
| Ending Owner’s Equity Balance | xxx |
Statement Of Owner’s Equity Example:
Suppose a company has 100,000 capital at the beginning of a reporting time. The earnings compute $15,000, and the owner draws $5,000 from the capital. The Statement of owner’s equity would look like this:
as the beginning capital of $100,000
revenue +$15,000
Withdrawal -$5,000
Therefore, the ending Capital Balance= $110,000
How To Find Net Income On Statement Of Owner’s Equity?
Net income: It is the profit earned by a company in a financial period. To put it simply, subtract expenses from revenue to arrive at a company’s net income.
A company mentions its net income on its owner’s equity statement and income statement. If the net income is high, it will enhance the company’s value. However, if the institution has suffered a net loss (expenses more than revenue), it will reduce the company’s worth.
For instance, we will assume that the net income is $40,000. Hence, the owner’s equity will directly increase by $40,000. Also, when comparing the statement of owner’s equity of two accounting periods, if you find an increase in the net income figure, it means that the company has generated more profit over time.
The net income on the statement of owner’s equity is shown below:
(Image from the previous article)
How do you Find Owner’s Withdrawals in the Statement of Owner’s Equity?
Withdrawals by the owner are calculated by evaluating the business records involving the amount that the owner has legally taken from the business for private use during a particular period. It should be noted that withdrawals do not represent an Expense but rather a decrease in the owner’s equity account.
The formula for calculating Owner’s Withdrawal is:
Owner withdrawal = Liability + Owner Capital + Revenue – Expenses
To calculate the owner’s withdrawals:
- Review Financial Statements: The withdrawals are normally captured within the framework of the Statement of Owner’s Equity, or the drawings account in the general ledger. They will be recorded as a reduction from the total stockholder’s equity.
- Identify Withdrawals: Search for payments made under ‘drawings’ or ‘owner’s withdrawals’ in the accounts because these refer to cash that the owner has withdrawn from the business.
- Sum All Withdrawals: Sum up all the withdrawals made throughout the mentioned period. These can be actual cash, employee expenses that the business owner has had to put his or her hand in the business pocket to sort out, or any other business property the owner has taken.
The total is the owner’s withdrawal, which is subtracted from the owner’s equity on the balance sheet.
How to Calculate the Net Increase in Owner’s Equity?
The net increase in owner’s equity depends on changes in the equity from a certain base at a certain period, considering factors such as profits, capital supplements, and deductions like withdrawals or losses.
Here are the steps:
- Start with the Beginning Owner’s Equity: This is the owner’s equity as per the balance sheet of the previous period or as per the opening balance as per accounting records.
- Add Net Income or Profit: If the business has made a profit in the period, this amount is credited to the owner’s equity. Net income is normally located on the income statement.
- Include Additional Capital Contributions: If the owner injected more capital during the period, this is also included in the owner’s equity.
- Subtract Withdrawals: Subtract all withdrawals that the owner may have must have made for their use. These are normally captured in the statement of owner’s equity.
The formula is:
Net Increase in Owner’s Equity = Beginning Ownership Equity + Net Income + Additional Capital – Withdrawal
The end product is the net addition or subtraction to the owners’ equity of that period.
Is Owner’s Equity An Asset?
From the business owner’s perspective, the Owner’s equity is an asset. However, it isn’t placed in the asset section of the balance sheet. Why?
The answer lies in the basic accounting principle: A business and its owner are two different parties. Hence, Equity is theoretically an advantage to the company’s owner rather than the company itself.
The balance sheet reflects all the possessions of a company, not of the business owner. Assets are valuable products held by the company. However, the owner’s equity is something of a loss to the company. It reflects the owner’s rights to the money left over if the company sold most of its properties and cleared off all of its debts.
When Does The Owner’s Equity Turn Negative?
Equity becomes negative when there are more liabilities than assets. In situations like this, the owner may have to invest an additional amount to cover up losses.
When a company has negative owner’s Equity yet decides to withdraw more, those draws may become taxable as capital gains on the owner’s tax return.
Therefore, the owners must ensure that they don’t draw funds from the company’s funds until the balance is positive.
What Is Equity Financing?
Quite often, organizations sell their company’s shares to raise more finance for their operations. This method is known as Equity Financing. Companies raise funds when they need to pay short-term bills and expand their businesses. By selling shares, a company sells its ownership in exchange for cash.
Multiple equity financing sources exist, such as the owner’s friends and family, outside investors, or an initial public offering.
An initial public offering (IPO) is the process of offering a company’s shares to the public in a new stock issuance. In a public share issuance, the company raises its funds from the public. Huge industries such as Google and Facebook have raised billions of funds via IPOs.
What is Equity Ownership?
Equity Ownership refers to the percentage of ownership and control accelerated by individuals within a Company.
For example, if you own 10% of a company’s shares, then you would receive 10% of any profits made by that company.
The company owns a building where it conducts its business and leases it out to its tenants. The tenant is currently paying rent for this building but does not own any part of it as yet. The tenant has requested that he be allowed to purchase 20% of the equity in the building from the current owners of the building.
Variety of Uses for the Word “Equity”
The principle of equity has various uses beyond analyzing firms. Therefore, we should think of equity more broadly as the degree of ownership of any asset after deducting all debts linked to that asset.
We have mentioned many other common equity variants below:
1. Private Equity
Usually, we apply private equity to appraise those firms that aren’t listed publicly. The accounting equation also holds where declared equity on the balance sheet remains after deducting liabilities to the assets to settle at a calculation of book value. Privately owned firms will then attract buyers by actively selling shares in private placements. Institutions such as retirement funds, university endowments, and insurance firms, as well as qualified individuals, might be among these remote equity participants.
Private equity is often offered to funds, and individuals specialize in direct acquisitions in private firms or leveraged buyouts (LBOs) in publicly traded companies. In an LBO deal, an organization accepts a loan from a private equity group to finance the purchase of a subsidiary or another business. Typically, we secure debts by the cash flows and investments of the company under purchase.
Mezzanine debt is a form of private lending often issued by a commercial bank or a mezzanine venture capital fund. Mezzanine deals sometimes have a debt-equity ratio in the form of a subjugated loan, warrants, common stock, or preferred stock.
2. Home Equity
Home equity is approximately equivalent to the valuation of owning a house. In other words, it is the sum of equity one has with them that reflects how much of the home they entirely possess by deducting the mortgage debt. Equity in a house or residence is derived from interest premiums plus a down payment, along with changes in property valuation.
Home equity is often an individual’s most valuable form of leverage. It may be used to obtain a home equity loan, also known as a second mortgage or a home equity line of credit. An equity takeout occurs as capital is taken out of a property or borrowed against it.
3. Brand Equity
When calculating an asset’s equity, it is vital to remember that these assets can include both physical assets, such as land, and intangible assets, such as its image, brand recognition, etc. A company’s identity will gain intrinsic credibility over years of advertisement and consumer growth. Market equity calculates the worth of a brand compared to a generic or store-brand equivalent of a good.
Owner’s equity and shareholder’s equity are the same thing. The former applies to private and small-scale businesses, while the latter applies to companies that have made their shares available to the general public (Alphabet, Microsoft). Owner’s equity is often known as a company’s book value. It is a metric used to analyze a firm’s valuation and financial health.

Shareholders equity= Total assets- total liabilities.
Owner’s Equity In Your Business
The owner’s equity can fluctuate regularly. Continued acquisitions and a rise in earnings generally result in the growth of the owner’s equity. Increased production and revenue, particularly when combined with lower expenditures, can demonstrate this high growth.
Owners of businesses should be mindful of the effect their actions have on their equity. It is likely, for instance, to get a negative balance of equity where an owner has drawn more than they have paid.
Negative owner equity isn’t a negative thing. Since the owner’s equity fluctuates, variables such as asset depletion may affect the figures over a specified time.
Owner’s Equity Vs. Business Fair Value
Owner’s Equity is the owner’s share of the business and is the difference between total assets and total liabilities. This form represents the book value figure of the business based on the original cost of the assets, which is applied at the time of filing the accounts and in internal business decisions. Owner’s equity pertains to contribution, return on business, and profit and consists of contribution, retained earnings, and net income of the business; it presents a more or less unchanging picture of the financial position of the business.
Business Fair Value, on the other hand, is the value attributed to the economic reality of the business, which is the price that the buyer would have to pay for the business in the current market. It takes into account such things as the business’s future profit-making ability, market forces, and other hard and soft assets such as goodwill.
The key difference lies in valuation: owner’s equity is grounded in accounting books, while fair value captures market prices, and the two are generally distinguishable. Even though owner’s equity gives shareholders and other interested parties a valuable picture of net worth, fair value offers a more extensive and promising view of long-term and short-term sales, mergers, and investments.
How To Improve Your Owner’s Equity?
The two prime contributors to owner’s equity are revenue and gains. Boosting them would boost the owner’s equity. Consider these options:
1. Upgrade your Property
Your place of operations plays a significant role in boosting profits and increasing sales. It can also help improve the owner’s equity. Minor changes can bring remarkable results.
If you revamp its look, like getting a paint job done, adding new cabinets, changing lights and furniture, and other things, it adds lots to aesthetics. These minor interior design changes add to your liabilities, so keep changes under budget to cover the cost and help improve the Owner’s equity.
2. Not Just Upgrade, Maintain it Too
Not maintaining the assets will rapidly depreciate them, consequently reducing the owner’s equity. Conduct routine assessments and follow all legal parameters.
3. Clear off Debts as Soon as Possible
Debt accumulation can seriously impact a business. Advance payments, regular checks on pending payments, and paying more than the minimum balance keep the accumulation of debts away from your business.
4. Increase your Margin
Small businesses can hire freelancers instead of full-time workers, work on aesthetics and service to justify their products’ high prices, and keep product quality high to attract more customers. These simple measures can greatly increase their profit margins.
5. Reduce your Cost of Manufacturing
Small businesses can reduce their manufacturing costs by looking for the cheapest source of raw material (without compromising quality) and increasing their scale of operations. Cheap raw materials of high quality aren’t available without effort, so bargain hard and make regular payments.
Large sales must precede scaling up operations, or it will only add to your debt. Track spending habits to avoid incurring extra costs, and choose inventory carefully.
Conclusion
In this article, we tried our best to explain what owner’s equity is and provide a statement of the owner’s equity. We mentioned various formulas supported by different examples. We also noted the primary elements of Owner’s Equity and how it can be an asset or a liability. You learned what Equity financing is and how to prepare its statement.
FAQs
Do owner’s equity and capital mean the same thing?
Equity is the sum of money a shareholder or business owner would get if they sold their holdings and settled all of the business’s debt. Capital refers to a company’s readily available financial assets.
How do you calculate the Owner’s Equity in a business?
Owner’s Equity may be calculated by adding all of the company’s assets and subtracting or deducting all of its liabilities. The formula for owner’s Equity is Owner’s Equity = Assets – Liabilities.
Is it possible for the owner’s equity to be a negative amount?
Owner’s Equity may be negative if the company has more liabilities than assets. In this situation, the owner might have to make additional investments to make up the difference.
Does owner’s equity appear on the balance sheet?
The owner’s Equity is noted on the balance sheet at the end of the company’s accounting period. It is calculated by subtracting all liabilities from all assets.
What causes an owner’s equity to decrease?
- A decline in owner equity is brought on by a drop in assets or a rise in liabilities due to company activities.
- Financial resources or assets are removed from a firm for the owner’s benefit.
- The impacted account is when money is received from the owner for investment purposes.
How do you calculate additional paid-in capital?
By applying the below formula to all public offerings, you will be able to calculate an organization’s APIC.
Additional Paid-In Capital = (Issue Price – Par Value) * Number of Shares Outstanding.
