Digital Wallets are applications installed on your mobile device that store copies of your credit and debit cards. Such apps include Apple Pay®, Samsung Pay® and Google PayTM. But, for your security, your card number and other details are not kept on record.
Digital wallets are convenient, secure, and easy to track. In 2021, a survey revealed that approximately 150 million users are active smartphone users who’ve used digital wallets in their lifetime.
What is a Digital Wallet?
A digital wallet is a software application that enables an individual to store their payment details and information within a connected device such as a smartphone, tablet, or computer. It allows users to complete electronic transactions offline and/or online without using credit/debit cards or cash. Digital wallets merge several modes of payment to make transactions easier and more convenient and make it easier for a user to get financial assistance within one app.
Features of Digital Wallets
- Secure Payment Storage
Digital wallets save your payment details, including your credit and debit cards, on your machine. Data privacy is well maintained within these wallets since they do not store your actual card numbers but only hold encrypted tokens.
Example: Apple Pay® retains information about your card on your phone and does not require physical cards.
- Contactless Payments
Mobile payment solutions let you make payments without contact with others by touching a button at compatible merchants through NFC. You can check or wave your phone or smartwatch near a payment terminal to pay without using a traditional card.
Example: In-store payments in Apple Pay® and Samsung Pay® leverage NFC technology.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Payments
Most digital wallets allow immediate cash transfers between users and can be used to split bills, send gifts, or pay someone, even when cash and checks are not preferred. Depending on the dominant platform, such exercises can attract or sometimes even have zero fees.
Example: Venmo and Cash App allow users to send money to friends and family using emails or phone numbers.
- Biometric Authentication
Most mobile wallets, in addition to PIN or passcode protection, allow users to verify their identity with fingerprint scanning or facial recognition before they can use the wallet to pay for anything. This feature locks the wallet and only sends an unlock signal to those who meet the requirement of being authorized to conduct transactions.
Example: Apple Pay® offers consumers easy payment options, such as fingerprint identification, also known as touch ID, and face identification, commonly known as face ID.
- Multi-Platform Access
Digital wallets are always available online. You can operate the wallet and generate transactions on your smartphone, smartwatch, or desktop, regardless of which one you prefer.
Example: PayPal can be easily imported into any Web browser, installed as a convenient application on a smartphone, or used as an added tool for other platforms.
- Loyalty & Reward Programs
Most digital wallets support loyalty points, coupons, and gift cards so that every reward point can be stored and redeemed from the same wallet. This feature assists users in making payments with less money.
Example: Currently, Apple Pay® enables users to link store-specific cards within an app, and these may be used to apply an instant or permanent discount to the total billing amount at the time of payment.
- Bill Payments & Subscriptions
Most digital wallets allow you to schedule regular payments, such as monthly subscriptions, bill payments, or membership fees. This feature eliminates the need to worry about missed payments, and most financial activities are handled on the application.
The Role of Credit Cards in Digital Wallets
How Credit Cards Can Be Linked with Digital Wallets
Credit cards are one type of money, and the integration of digital wallets is based on them. History shows that credit cards are the most common way of payment when it comes to digital wallets.
Users can even connect their credit card details to e-wallets such as Apple Pay® or PayPal, through which they can make purchases without even using the credit card.
These wallets safely store credit card details in encrypted forms and carry out tokenization to avoid security issues during payments.
The Symbiotic Relationship
Digital wallets and credit cards complement each other:
- Digital wallets require credit cards as the base instrument in the context of funding transactions.
- Wallets benefit from integrating credit cards since they offer utility for the cards in digital transactions.
This partnership makes transactions easier, whether conducted online or at the physical store and, among other things, helps foster a contactless payments society.
Benefits for Consumers
- Rewards and Incentives
Traditional credit cards connected to digital wallets can still provide cashback, points, or even miles, depending on the purchases made. Digital wallets don’t mess with traditional credit card reward programs and allow users to accrue even more.
Example: Here are a few ideas for utilizing Apple Pay® with a rewards credit card and earning points on every purchase.
- Credit-Building Opportunities
Through mobile payment using a credit card, whenever the user makes a payment to buy something, the user’s credit scores are built or boosted depending on the payments that the user has made on time.
- Convenience and Speed
Credit cards in digital wallets include the convenience of fast payments when no card details have to be entered at the checkout or the physical card is not needed.
Example: Promoting your phone to a card reader with Google Pay™ is faster than swiping or inserting a card.
- Enhanced Security
Mobile payments also minimize fraud risks since credit card transactions are secured further by biometric authorization and tokenization.
Example: Samsung Pay® guarantees that the actual card number is not transmitted through the transaction.
- Global Acceptance
One of the most important benefits of such cards is that they can be used for domestic and international purchases because they integrate with most mobile wallets.
- Expense Management
Many digital wallets offer real-time spending insights, allowing users to trace transactions done with their credit cards.
PayPal provides full transaction history.
How the Digital Wallet Trend Looks in the United States
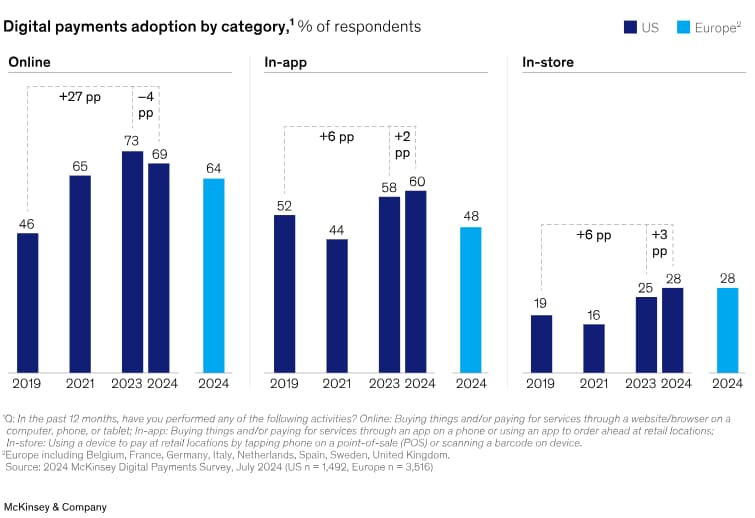
The use of digital wallets has continued to grow over the past few years, changing the way shoppers in the United States and Europe pay for goods and services.
As highlighted in the graph:
Key Insights from the Data
- Online Payments: Digital wallets continue to lead the online payment preference, rising 27 percentage points from 2019 to 2024 within the United States. This is a stark contrast to the use of credit cards and goes a notch higher to wallets such as PayPal and Apple Pay.
- In-App Transactions: More than half of the users in both regions favor digital wallets for in-app purchases, highlighting their role in app-based shopping.
- In-Store Payments: Store adoption has been less pronounced yet continues at a relatively decent rate. In the United States, 27.4% of payments are now being made through digital wallets, illustrating the growing comfort consumers have with contactless payments.
Regional Variations
In-store payments using digital wallets, the United States takes the lead, probably because of the advanced availability of payment terminals equipped with NFC. Europe, on the other hand, continues to have positive growth in online and app-based payments, which are increasingly adopting digital wallet methodologies.
Pros and Cons of Integrating Digital Wallets with Credit Cards

Pros of Linking Digital Wallets with Credit Card
- Increased Mobility for the users
- Digital wallets are a version or alternative way that enables credit card users to perform transactions using their cards without the need to hold a physical card.
- One of the benefits that electronic wallets give consumers is that they can download their cards in one application.
- Increased Security
- Tokenization, encryption, and biometric authentication provide security for transactions made through digital wallets.
- Card information is not disclosed at the time of purchase, which lowers the chances of credit card fraud.
- Improved User Engagement
- Consumers can interact with digital wallets, which allows card issuers to send instant transaction alerts and updates on rewards.
- Making such tagged offers available through the featured wallet apps will help increase traffic and spending.
- Opening A Gateway To Younger Demographics
- Consumers in the younger generation, who are familiar with technology, prefer possessing digital wallets. Including credit card benefits assists issuing companies in reaching this audience.
- Global Payment Flexibility
- Digital wallets can accommodate international payments, ensuring cardholders can effortlessly transact in foreign markets without dealing with currencies.
- Efficient and Covid-safe Payments
- Contactless payments were needed during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. Engaging the consumption from wallet integration is consistent with this transition.
Cons of Linking Digital Wallets to Credit Cards
- Reduced Brand Visibility
- As with a digital wallet, credit card branding is less of an issue because people primarily engage with the digital wallet application rather than the card company.
- Reliance On Third Party Sites
- For the latter, the card issuers depend on the wallet providers (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay) for functionality, updates, and customers’ communications.
- Even simple technical problems with the wallet or technical problems within the wallet platform can cause transaction halts.
- Risk of Customer Retention
- Users can easily switch between cards, as indicated by the use of digital wallets, which means that cards issued cannot easily build loyalty.
- Increased Competition
- It is interesting to note that many digital wallets offer opposing financial products or different kinds of payments, such as BNPL.
- Integration costs and complexity
- Using and being compatible with many digital wallet solutions demands a rigorous commitment of resources to technology and structures.
- Due to the constantly evolving wallet technologies, change has become frequent.
- Fraud and Liability Risks
- In spite of this, digital wallets will come with secure features, while any loophole in the wallet system may indirectly affect the linked credit cards.
- Conflicts and fraud problems may take more time to resolve whenever third-party wallet companies are involved.
Major Differences Between Digital Wallets and Credit Cards
| Features | Digital Wallets | Credit Cards |
| Technology | Software-based, stored on mobile devices (smartphones, tablets, smartwatches). | Physical card with magnetic strip or chip. |
| Payment Method | Uses NFC, QR codes, or app-based transactions for contactless payments. | Requires swiping, inserting, or tapping the physical card |
| Security | Advanced security features like biometrics (fingerprint/face recognition) and tokenization. | Relies on physical security features, PIN, or signature. |
| Convenience | It can be used directly from your smartphone. | You must carry the physical card; it can be inconvenient if lost. |
| Accepted Locations | Accepted where contactless payment is supported but only sometimes available. | Widely accepted at almost all physical and online retailers. |
| Integration with Other Services | It can integrate with loyalty programs, tickets, and other apps. | Primarily used for financial transactions; limited integration. |
Digital wallets and traditional credit cards serve similar functions in that they both enable you to make payments, but they differ in several key aspects:
Technology
- Digital Wallets: These are apps or software-based mobile payment solutions that enable payment with the added convenience of having the payment information stored on a smartphone, tablet, or smartwatch. They include Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay.
- Credit Cards: These are plastic cards fitted with magnetic strips or chips, normally utilized by swiping or insertion into payment devices.
Payment Method
- Digital Wallets: Payment is made via Near Field Communication (NFC), QR codes, or anything digital in nature. The wallet lets you keep your credit card, debit card, or bank account data and enter into a transaction without the need for the actual card.
- Credit Cards: Payments can only involve the physical card, which is slid, inserted, or tapped on the terminal. You can also enter card details for online purchases directly; that is, you don’t need to scan card numbers.
Security
- Digital Wallets: Biometrics (fingerprint or face recognition) and some form of tokenization (replacing the actual data with a token for each transaction) are routinely used.
- Credit Cards: This minimizes security, which is only based on the plastic card, a secret number, or the signature on the back of the card. If the card is misplaced or stolen, unauthorized usage is likely until the card owner informs the service provider.
Convenience
- Digital Wallets: These are built into your phone or smartwatch and provide greater comfort. They do not require you to carry any physical cards and can be used to make contactless or internet payments.
- Credit Cards: You have to carry the actual plastic card with you, which may be a nuisance if you need to place it.
Accepted Locations
- Digital Wallets: These are common in most stores and are readily used, especially in stores that support contactless payment. However, mobile payment may only be possible in some locations.
- Credit Cards are used globally, both for Internet buying and in conventional stores, and they do not require any advanced technology.
Integration with Other Services
- Digital Wallets can be easily linked to other apps and services, including loyalty programs, tickets, and cryptocurrency wallets, meaning that they perform multiple functions.
- Credit Cards: Most of the time, they are designed for payments and can offer various incentives, but they don’t allow you to use other applications except for payment.
Challenges and Limitations of Digital Wallets
| Challenge / Limitation | Description |
| Device Dependence | Digital wallets rely on smartphones, tablets, or smartwatches. If the device is lost, stolen, or out of battery, access to the wallet is restricted. |
| Limited Merchant Acceptance | Not all merchants, especially small businesses or those in less tech-savvy areas, support digital wallet payments. |
| Privacy and Data Concerns | Digital wallets store sensitive financial information, raising concerns about data security and the potential for breaches. |
| Fees | Some digital wallets may charge fees for linking a credit card, transferring funds, or making international transactions. |
| Limited Support for All Cards | Not all financial institutions or cards are compatible with digital wallets, limiting options for users. |
| Technological Barriers for Older Generations | Older consumers may need help with adopting or understanding digital wallet technology, creating a barrier to usage. |
The Bottom Line
Digital wallets continue to replace traditional methods of payment as they are easy to use and secure, and they allow the use of other financial interfaces. However, the statistics have their weaknesses. They include the state’s dependence on technology, limited acceptance by some merchants, privacy issues, and other hidden fees. Still, it has to be noted that digital wallets are still an important and constantly developing means of payment with a number of striking advantages for those who use them.
