Hard inquiries impact credit scores; soft inquiries don’t. Hard checks are for in-depth due diligence; soft inquiries check credit scores.
A hard credit inquiry, or “hard pull,” occurs when you apply for a credit card, loan, or cell phone plan, which allows a lender to check your credit report with your permission. That can temporarily lower your score negligibly and stay on your report for up to two years.
A soft inquiry, or “soft pull,” happens when you check your credit or a company reviews it for marketing, with no impact on your score.
While Hard Inquiries are a Common Part of:
- Credit Application Process
- Loan Process (Car, Home Loan, Personal Loan, etc.)
- Renting and Leasing
- Line of Credit.
Soft Inquiries are Commonly Used for:
- Background Checks,
- Pre-Approved Credit Offers, and
- Personal Credit Monitoring
- Job Processing.
Recognizing the difference might help you manage your credit and avoid unnecessary score declines.
What are Hard and Soft Credit Inquiries?
Credit inquiries occur when someone (a lender, creditor, employer, or other entity) checks your credit report. There are two types of inquiries, known as hard credit inquiry and soft credit inquiry.
Hard Credit Inquiry
A hard credit inquiry, also known as a hard credit check or hard pull, is when a lender checks your credit after you apply for a credit card, a line of credit, or a loan.
Pulling one or more of your credit reports is usually a step in the process of evaluating your previous and present financial activity, including loan and credit card balances and payment histories.
Every credit report the lender looks at will have a record of the credit check added to it.
This might result in a slight decline in your credit score, as scoring algorithms take into account how frequently and recently you’ve applied for credit.
Hard inquiries can stay on your credit report for up to two years, although those older than a year usually have little to no influence on your score.
Common Hard Inquiry Examples:
Applying for a New Credit Card
A hard inquiry is often the result of every credit card application.
Applying for an Automobile Loan
When determining your creditworthiness for financing a vehicle, lenders or banks make hard inquiries.
Applying for a Mortgage
In order to assess your financial stability, mortgage applications require hard pulls.
Applying for a Personal Loan
To determine a borrower’s eligibility, lenders conduct hard inquiries.
Asking for a Credit Limit Increase
When you request a larger credit limit, some creditors could perform a hard inquiry.
Creating a New Utility Account
When establishing new services, utility companies may run a hard credit inquiry.
Applications for Apartment Rentals
As part of the tenant screening procedure, landlords or property management firms may ask direct questions.
How a Hard Credit Inquiry Works?
A hard credit inquiry is a legal credit check performed by a lender or financial institution when you apply for a credit card, loan, or other type of financing.
It allows the lender to examine your creditworthiness before accepting or rejecting your application.
Here’s how the process works:
1. Credit Application Submission
You start a hard inquiry by applying for a new line of credit, like this:
- A credit card.
- A personal loan.
- A mortgage, or house loan
- An auto loan
- A line of credit
During the application procedure, the lender requests personal and financial information such as:
✅ Full name
✅ Social Security number (SSN)
✅ Employment details
✅ Annual income
✅ Existing debts.
2. The Lender Requests your Credit Report
After receiving your application, the lender will request a credit report from one or more of the main credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax, or TransUnion).
This request is referred to as a hard pull since it gives the lender a complete credit history, including:
- Your credit score
- Opened and closed credit accounts.
- Outstanding amounts and debt usage.
- Payment history, including missing or late payments.
- Public records, like bankruptcies and foreclosures.
This complete report assists lenders in determining whether you are a low- or high-risk borrower.
3. The Lender Assesses your Creditworthiness
The lender assesses your credit profile based on the facts in your credit report and chooses whether or not to approve your application.
Important factors include:
- Credit Score: Higher scores raise the likelihood of acceptance.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): A lower DTI indicates a greater ability to repay debt, measured by monthly debt to income.
- Credit use: Excessive credit use may be a sign of financial stress.
- Payment History: The likelihood of acceptance is increased by a history of on-time payments.
4. The Lender Makes a Decision
Based on their risk assessment, the lender will:
- Approve the application with specified loan terms (interest rate, credit limit, loan amount, etc.).
- Deny the application if the borrower does not meet the required criteria.
Note: An adverse action notification outlining the reasons for the denial—such as a poor credit score, excessive debt, or inadequate income—must be sent by the lender if your application is rejected.
5. Your Credit Report Has a Hard Inquiry Logged
The inquiry is noted and stays on your credit report for a maximum of two years after the lender pulls your credit report.
Its impact on your credit score, however, fades with time and usually lasts little more than a year.
Soft Credit Inquiries
A soft credit check, also known as a soft inquiry or soft pull, is when you or a firm analyzes your credit record without applying for credit.
Soft inquiries are commonly used to determine eligibility for preapproved credit offers, such as credit cards or loans, background checks, employment screenings, and personal credit monitoring.
Soft inquiries, unlike hard inquiries, do not affect your credit score, which lenders use to determine your trustworthiness.
These checks may still appear on your credit record, but they are solely viewable to you and have no impact on loan decisions.
Common Soft Inquiry Examples:
Personal Credit Checks
These are when you review your credit report or score.
Pre-Approval Credit Checks
To determine whether you’re eligible for pre-approved credit card or loan offers, lenders assess your credit.
Employment Background Checks:
With your authorization, potential employers may run a credit check on you as part of the recruiting process.
Insurance Quotes
In order to give you an accurate rate quotation, insurance companies may check your credit.
Account Reviews by Current Creditors
In order to manage your current accounts, current creditors may conduct periodic credit checks.
Opening Utility Services or Bank Accounts
When you open new services or accounts, certain banks and utility companies do soft inquiries.
While both hard and soft inquiries review your credit record, their impact on your credit score varies greatly.
Hard queries might temporarily damage your score, especially if they occur frequently. Soft inquiries, on the other hand, do not influence your credit score, making them handy for risk-free credit monitoring.
Understanding how these inquiries influence your credit allows you to make more educated financial decisions and avoid avoidable credit score decreases.
How Does Soft Credit Inquiry Work?
1. Initiate a Soft Credit Inquiry
Soft inquiries can happen in a variety of settings, including:
| Personal Credit Checks | Pre-Approved Offers | Employer Background Checks | Insurance Quotes | Current Account Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| When you review your credit record using services such as Experian or Credit Karma. | Credit card issuers or lenders use creditworthiness to establish eligibility for pre-approved offers. | Potential employers may perform credit checks during the recruiting process with your explicit authorization. | Insurance firms may use soft pulls to assess risk and calculate premium prices. | In order to manage your current accounts, your creditors may examine your credit on a regular basis. |
2. Recording in Your Credit Report
Soft inquiries appear on your credit record but do not affect your credit score. They are only visible to you, not potential lenders.
3. Information is Provided in a Soft Inquiry
A soft inquiry usually delivers a summary of your credit profile, which includes:
✅ Your credit score.
✅ Basic account information.
✅ Payment History Overview.
✅ Public records, such as bankruptcy .
It provides less thorough information than a hard inquiry.
4. Consent Requirements
| Personal Credit Checks | Employer Checks | Pre-Approved Offers |
|---|---|---|
| You may see your credit report at any time without harming your score. | Employers must obtain your explicit permission before conducting a soft inquiry. | Lenders may conduct soft inquiries for pre-approval causes without your express authorization. |
How do hard and soft inquiries impact your credit score?
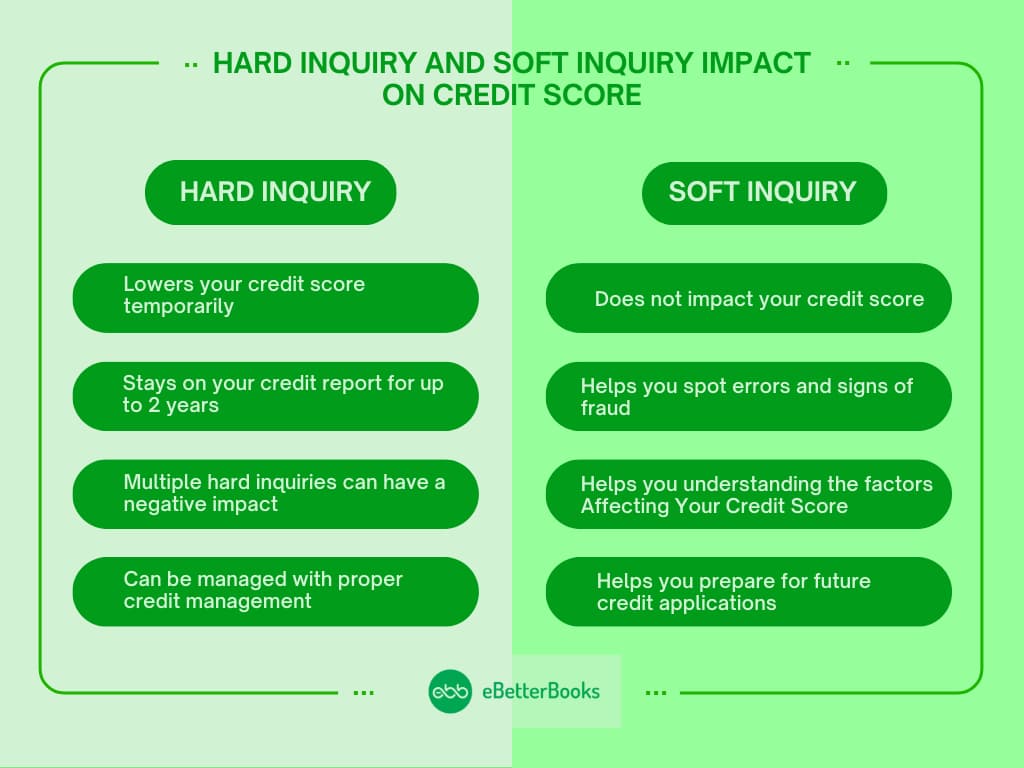
Impact of Hard Credit Inquiries
A hard credit inquiry happens when a lender or creditor checks an individual’s credit record as part of the selection procedure for giving credit.
While such inquiries are a common element of credit applications, they might have a short-term influence on the credit score.
Effect on Credit Score
A single hard inquiry can lower a credit score by a few points, usually not more than five. The exact impact depends on the individual’s credit history and total credit profile.
Duration of Impact
Hard inquiries can stay on a credit report for up to two years, although their impact on the credit score typically lasts just 12 months.
Multiple Hard Inquiries
When applying for a mortgage, auto loan, or student loan, several hard inquiries within a short period (usually 14 to 45 days, depending on the credit scoring model) are regarded as a single inquiry. This enables you to compare rates without adversely affecting your credit score.
Long-Term Considerations
While hard inquiries have a minimal influence, proper credit management—such as making on-time payments and keeping credit utilization low—is significantly more important in maintaining a decent credit score.
Impact of Soft Credit Inquiries
A soft credit inquiry, also known as a soft pull, is when you or an entity examines your credit report without submitting a formal credit application.
These inquiries do not affect your credit score and are commonly used for pre-approval credit checks, background screenings, or personal credit monitoring.
Detect and Correct Errors
Your credit report includes important information such as your personal information, current and closed credit accounts, and payment history.
Errors in any of these components, such as misspelled names, incorrect amounts, or missed loan payments, might harm your credit score.
Regular checks help you to identify and dispute discrepancies before they affect your financial situation.
Protect Yourself from Identity Theft
Reviewing your credit report might help you spot signs of fraud, such as illegal credit card accounts or loans issued in your name.
If you observe any unusual behavior, you may report it to the credit bureaus and freeze your credit if required.
Understand the Factors Affecting Your Credit Score
Your credit report contains information about what is helping or damaging your credit score. Missed payments, heavy credit use, or repeated recent hard inquiries can all reduce your credit score.
To enhance your credit health, analyze these indicators and take remedial action, such as paying bills on time, lowering your amount of debt, or spacing out credit applications.
Prepare for Future Credit Applications
If you want to apply for a mortgage, auto loan, or a new credit card, examining your credit report beforehand will help you determine your eligibility.
A solid credit profile boosts your chances of getting approved at a lower interest rate.
Real-World Examples for Hard Vs Soft Inquiries
Filling Out Several Credit Card Applications within a Short Period.
Sarah applies for five separate credit cards in two months in an effort to maximize her credit card perks. Every time she applies for a card, her credit report is subject to a hard inquiry.
Impact: Because every inquiry stays on her record for a maximum of two years, lenders can perceive her as a higher risk individual, presuming she is overextending herself financially or in need of credit. She may thus be subject to increased interest rates or have her future credit applications rejected.
Choosing an Auto Loan vs Applying for Several Loans at Once.
Jake is seeking a vehicle loan and applies to three different lenders over two weeks. Because credit scoring models identify loan shopping, these inquiries are combined as one inquiry, reducing the impact on his credit score.
Impact: Unlike many credit card applications, Jake’s grouped auto loan inquiries do not dramatically disrupt his credit score, which allows him to compare rates without penalty.
Emma checks her credit score weekly.
Emma utilizes a credit monitoring tool, such as Experian, to check her credit score once a week. Because these are soft inquiries, her grade remained unchanged.
Impact: Emma is more aware of her credit health and is less concerned about potential score decreases. She may monitor developments, discover fraud early, and strategically plan future credit applications.
John receives several pre-approved credit card offers.
John begins receiving several pre-approved credit card offers in his inbox. Lenders conducted gentle inquiries to assess his eligibility.
Impact: While such inquiries do not affect John’s credit score, he should exercise caution when creating new accounts since this may damage his credit use and average account age.
How to reduce hard credit inquiries?
Hard inquiries happen when lenders analyze your credit record throughout the loan or credit application procedure. While a single hard inquiry may only drop your score by a few points, many inquiries over a short period have a greater impact.
Here’s how you can minimize them:
1. Only Apply for Credit When Necessary
Each hard inquiry remains on your credit record for up to two years and might modestly reduce your credit score. If you apply for many credit accounts in a short period, lenders may consider you a higher-risk borrower.
Before applying for a new credit card or loan, ask yourself these questions:
- Do I truly need this credit?
- Will I qualify with my present credit?
- Can I afford the payments?
2. Prior to Applying, Use Pre-Qualification
Prequalification or preapproval credit checks, which employ a soft inquiry rather than a hard one, are provided by several lenders. Your credit score is not affected by a soft inquiry. This enables you to determine your eligibility for a credit card or loan prior to filing an official application.
3. Combine Rate Shopping in a Limited Amount of Time
Credit scoring algorithms like FICO Score and VantageScore usually count several hard inquiries made in a short period as a single inquiry when you’re looking for a mortgage, auto loan, or student loan.
Note: To reduce the influence on credit scores, it is best practice to finish all loan applications within 14–45 days.
4. Inquire About the Credit Check Type
Find out if the lender conducts a hard or soft investigation before applying for a loan product. Certain financial organizations let you examine rates without making a formal inquiry or provide soft pull loans.
5. Keep an Eye Out for Unauthorized Inquiries on your Credit Report
By routinely checking your credit report, you can identify fraudulent inquiries that can indicate identity theft. Contact the credit bureau right once to dispute any inquiries you don’t recognize.
Tip: Visit AnnualCreditReport.com to view your credit report for free once a year from each of the three main credit agencies.
Tips for Maintaining a Good Credit Score
The duration of your credit history, credit usage, and payment history are some of the variables that go into calculating your credit score.
Here’s how to maintain your score high or raise it:
1. Make On-Time Bill Payments (35% of your Score)
The most significant aspect of your credit score is your payment history. Your score may be lowered by even one late payment.
Tip:
- To prevent missing deadlines, set up automated payments or reminders.
- If you unintentionally forget to make a payment, do it right away since credit bureaus are notified when payments are more than 30 days past due.
2. Don’t Use Too Much Credit (30% of Your Score)
The percentage of your available credit that you are utilizing is known as credit usage. Your score will improve with a lower utilization rate.
Tip:
- To keep your credit use below 30%, strive to utilize less than $3,000 if your entire credit limit is $10,000.
- For the greatest effect on your credit score, try to maintain utilization below 10%.
- To lower reported utilization, settle balances prior to the statement closure date.
3. Keep Your Credit History Long (15 Percent of your Score)
Lenders prefer borrowers with a solid credit history.
Tip:
- Even if you don’t use your previous credit accounts frequently, keep them open.
- Your credit history is shortened when you close an account, and it may also result in higher use.
4. Diversify your Credit Mix (10% of your Score)
Having several sorts of credit accounts, such as credit cards, installment loans, and mortgages, might improve your credit score. However, only incur debt that you can manage properly.
5. Limit New Credit Inquiries (10% of your Score)
As previously indicated, answering too many difficult questions in a short amount of time might damage your score. Apply for new credit only when required.
6. Dispute Credit Report Errors
Mistakes on your credit report, such as wrongly reported late payments or fraudulent accounts, might lower your credit score. If you uncover any mistakes, dispute them with the credit bureaus.
Tip: How To Dispute an Error: Contact the credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax, or TransUnion) via email, phone, or letter. Provide accompanying documentation to help rectify the mistake.

Final Thoughts
Consistent financial discipline, knowledge of possible fraud, and smart credit management are necessary to maintain a high credit score.
You may safeguard and enhance your financial situation by reducing the number of hard inquiries, keeping an eye out for identity theft on your credit report, and adhering to recommended practices like on-time payments and minimal credit use.
Better loan terms, reduced interest rates, and more financial flexibility are all made possible by having a high credit score. Being proactive now will contribute to long-term financial security and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a hard and soft credit pull?
A hard pull is when a lender assesses your credit for a loan or credit application, which might slightly reduce your credit score. A soft pull occurs when you check your credit or when employers run background checks; it does not affect your credit score.
Do multiple hard inquiries reduce my score?
Yes, having multiple hard inquiries in a short period will temporarily reduce your credit score. However, if you’re looking for car loans, mortgages, or student loans within a 14-45 day period, these inquiries are combined to reduce the impact they have.
How long do inquiries stay on my credit report?
Hard inquiries remain on your credit report for up to two years, but their impact on your score usually fades after 12 months. Soft inquiries appear on your report but are only visible to you and do not affect your score.
