The card issuer sets the credit card limit based on various factors, which can be increased by requesting the bank to review your income information to reflect any financial improvements.
What is a Credit Card Limit?
A credit card limit is the highest amount of money you can borrow or spend on your credit card during a billing cycle. The credit card issuer sets the limit of the credit card on the basis of various factors such as the your creditworthiness, income, and credit history.
Once your credit limit is reached, any further transactions will typically be declined unless the issuer allows over-limit spending which may charge you an additional fees.
Importance of Credit Limits in Managing Finances
It is important for you to understand your credit limit for an effective financial management due to several key factors:
- Budgeting:
Credit card limits are set on the basis of how much you can spend on a credit card or line of credit without getting charged with additional fees. If you know your credit limit, it will help you to plan your monthly expenses and avoid overspending.
A credit card limit helps you better manage your finances and ensures you live within your means which prevents unnecessary debt accumulation.
- Credit Utilization Ratio:
A credit card limit helps you to keep your credit utilization ratio lower which indicates reliable credit usage and it positively impact your credit score. It is recommended that you must maintain a utilization ratio below 30%.
For instance, if you have a $1,000 limit then keeping your balance below $300 is advisable. High utilization can lead to lower credit scores and may signal to lenders that you need to be more leveraged.
- Avoiding Fees:
If you go over your credit limit during your billing cycle it may lead to several other charges such as over the limit fees, this will also cost you some extra fees. Going over your credit limit can also result in declined transactions when making purchases that cause inconvenience and even embarrassment. It is for this reason that you should endeavour to stick to the credit limits set to help you keep off such additional charges and have a healthier credit status.
- Financial Planning:
Credit card limits also influence long-term financial planning. A good understanding of your credit limits helps you in forecasting future borrowing capabilities whether for loans or mortgages.
A higher credit card limit can provide you more flexibility during emergencies or unexpected expenses that allows you to manage cash flow effectively without resorting to high-interest loans.
Moreover, responsible management of credit limits contributes to maintain a positive credit history which is important for obtaining favourable loan terms in the future.
Average Credit Card Limits Based on Age Group
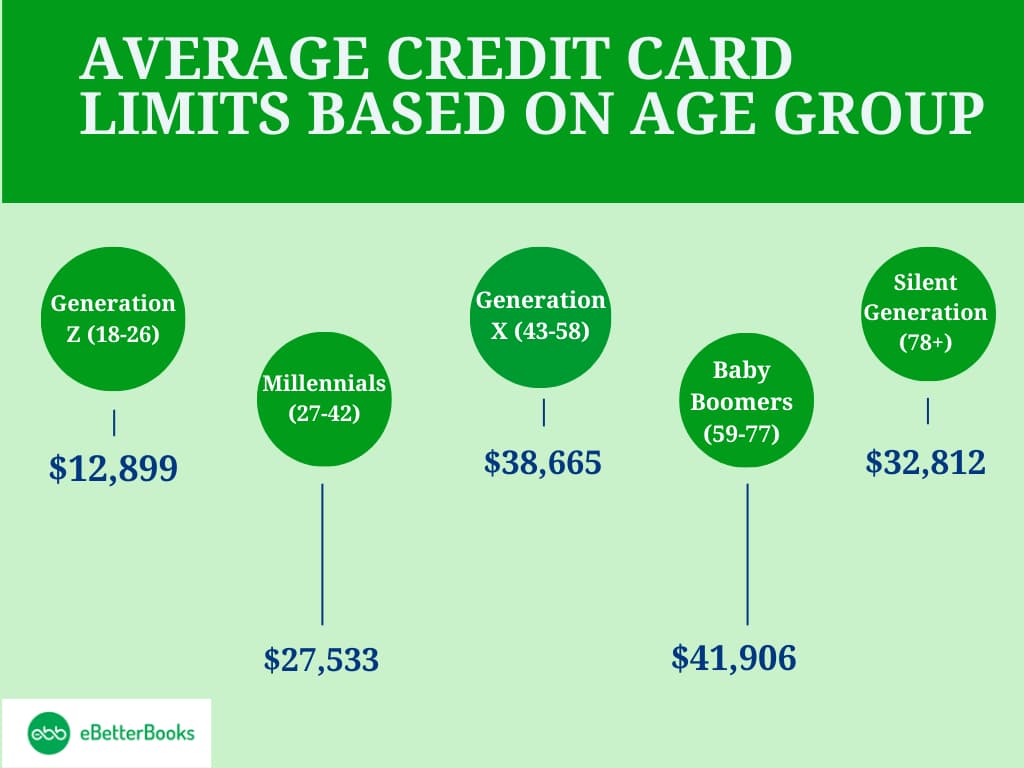
The average credit card limits in the U.S. vary significantly by age group, reflecting the financial maturity and credit history of different generations.
Generation Z (ages 18-26) had the lowest average limit at $12,899, despite a substantial year-over-year increase of 14.3%. Millennial’s (ages 27-42) followed with an average limit of $27,533, while Generation X (ages 43-58) had a higher limit at $38,665. The Baby Boomers (ages 59-77) topped the list with an average limit of $41,906. Interestingly, the Silent Generation (78+) saw a slight increase to $32,812.
These disparities are largely attributed to factors such as income levels, credit history length, and credit scores, which tend to improve with age due to more extensive financial experience and stability.
Types of Credit Limit Determination
Credit card issuers use various methods to set the credit card limits assigned to new cardholders.
These methods are classified into three different types:
Predetermined limits, Customized limits, and Credit-based limits.
01. Predetermined Limits:
Predetermined limits refers to the specific amount set by the credit card issuers for a specific card irrespective of the individual applicant’s creditworthiness. These credit card limits are often based on the type of card for which an applicant has applied.
Examples:
- Starter Cards: A standard starter credit card typically has a limit of $500 and it is aimed at individuals who are new to credit.
- Premium Cards: However, premium credit cards might have higher predetermined credit limits such as $5,000 which are usually for the consumers with better financial profiles.
Issuers provide these limits based on general criteria rather than personalized assessments which makes them less reflective of an individual’s creditworthiness.
02. Customized Limits:
Customized limits are designed according to every individual applicant based on a complete analysis of their financial profiles. Issuers consider multiple factors to minimize risk when extending credit.
How Issuers Analyze Profiles:
- Credit Score
The credit score is an important factor that determines the credit limit offered to an individual. It usually ranges from 300 to 850 that evaluates a person’s creditworthiness based on their borrowing and repayment history.
A higher credit score shows lower risk to lenders that often results in higher credit limits. However, a low credit score significantly restrict the amount of credit extended.
- Income
Income is another primary factor which influences the credit limits. Lenders may consider an applicant’s income to determine the ability to repay the funds they have borrowed.
A higher income of an individual generally associates with a higher credit limit, as it suggests greater financial stability and capacity to manage debt.
- Existing Debts and Liabilities
Lenders also consider if the individual is having any existing debts or liabilities when setting a credit limit. It includes ongoing loans, mortgages or other financial responsibilities that may affect an applicant’s disposable income.
A high debt-to-income ratio can signal potential risk to lenders which lowers the offered credit limit of the applicant.
03. Credit-Based Limits:
Credit card limits are mainly decided by an applicant’s credit history and credit score. This process involves considering different factors which are influenced by the applicant’s financial behaviour.
Factors Influencing Credit-Based Limits:
- Credit Utilization Ratio: Lower credit utilization ratio of an individual indicates that an individual is using a small portion of their available credit which reflects careful credit management and can lead to higher credit limits.
- Length of Credit History: A longer credit history provides more data on an applicant’s borrowing behaviour which showcases their experience with managing credit which can result in higher credit card limits.
- Payment History: If an individual consistently makes timely payments then it proves their reliability and financial responsibility. It also impacts an individual’s credit score and leads to a higher credit card limit.
- Recent Inquiries and Accounts: A high number of recent inquiries for new credit or newly opened accounts may indicate potential risk to lenders which could result in lower credit limits as they assess the applicant’s financial stability.
Steps to Request a Credit Limit Increase
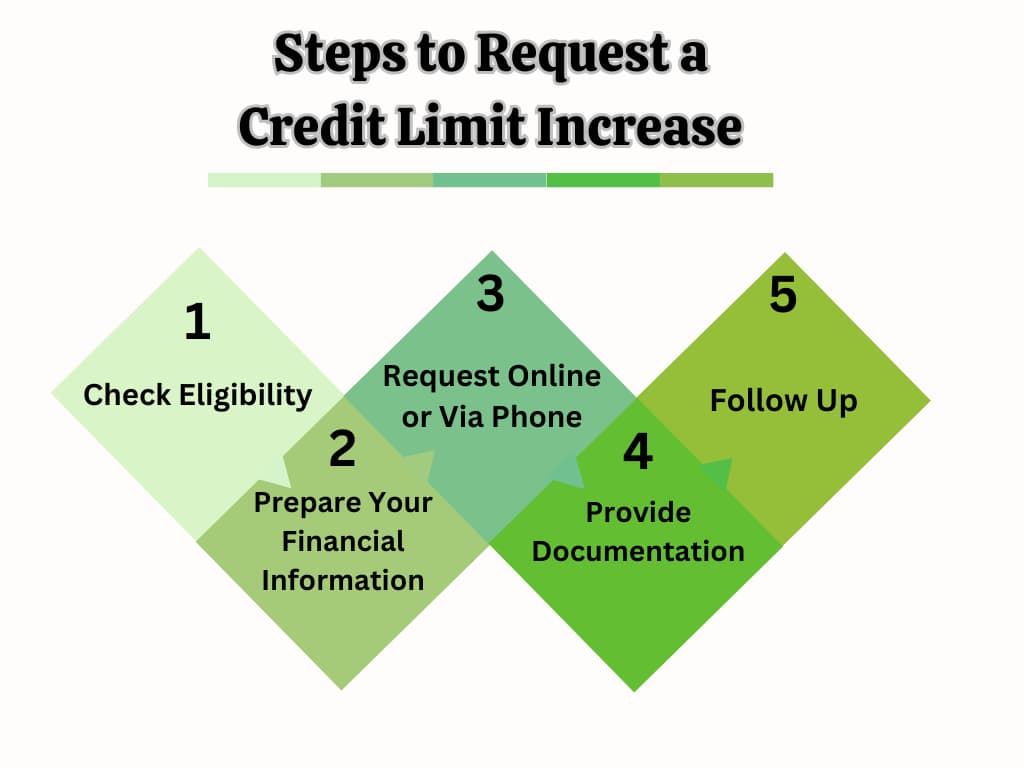
You must follow these steps to request a credit limit increase and ensure a smooth and successful application process:
01. Check Eligibility
Check your eligibility to increases the credit limit before initiating a request. Many banks automatically consider cardholders for the increase based on factors such as their credit card usage patterns, payment history, and overall creditworthiness. Review your account to see if you qualify for an automatic increase which may not require any action on your part.
Key Considerations:
- Payment History
- Credit Utilization Ratio
- Income Changes
02. Prepare Your Financial Information
Gather relevant financial documentation that may be required during the request process. This typically includes details about your income and any other financial obligations.
Documentation May Include:
- Recent pay stubs or tax returns if you are self-employed.
- A summary of existing debts and monthly expenses, if applicable.
03. Request Online or via Phone
Most banks offer multiple ways to request a credit limit increase. You can do this either online or over the phone.
Phone Request:
- Call the customer service number provided by your bank.
- Speak directly with a representative who can guide you through the request process and answer any questions you may have.
Online Request:
- Log into your bank’s online banking platform or mobile application.
- Navigate to the section for credit card services and look for options related to credit limit increases.
- Complete any required fields, such as updated income information, and submit your request.
04. Provide Documentation
If you are seeking a significant increase beyond what is typically allowed or if prompted by the bank, be prepared to submit documentation supporting your request.
Common Documents Required:
- For Salaried Individuals: Last two months’ salary slips.
- For Self-Employed Individuals: Latest income tax return and bank statements from the last three months.
05. Follow Up
After submitting your request, monitor your account for updates regarding the status of your application. Some banks may notify you via email or through their app once a decision has been made.
Tips for Successful Follow-Up:
- Keep track of any confirmation numbers or reference IDs provided during your request.
- If you are still waiting to receive feedback within a reasonable time frame (typically a few days), consider contacting customer service again for an update.
Implications of High Credit Limits
- Increased Risk of Overspending
Risk of increased overspending is one of the most significant drawbacks of having a high credit card limit is the increased temptation to overspend. Individuals are expected to get indulge in unnecessary spendings that they might otherwise avoid if their limit were lower. It can end up borrowing beyond their means and this create some pressure on their financial position.
Consumers may get trapped in a cycle of debt As consumers spend beyond their means, where they are unable to pay off their balances in full each month. The psychological effect of having access to more credit can reduce the perceived value of money that makes it easier to justify unnecessary expenditures.
- Potential Negative Impact on Credit Score
While increasing your credit limit enhances your credit score by just lowering your credit utilization ratio, there are potential downsides if mismanaged. If individuals start carrying high balances relative to their new limits or miss payments, it can have a bad effect on their credit score.
Lenders often interpret high balances as a sign of financial distress, which may lead to higher interest rates on future loans or the rejection of your credit applications. A lower credit score can affect various aspects of life such as the ability to secure housing or employment, as many landlords and employers conduct credit checks.
Therefore, while high limits can provide flexibility they also carry the risk of negatively impacting one’s financial reputation if not handled responsibly.
- Higher Interest Charges
Another significant disadvantage of high credit card limits is the increased chances of getting higher interest charges. If an individual can be charged with higher intrest if they does not pay off their full balance on time which leads to substantial debt over the time. This situation is particularly concerning for cards with high-interest rates, where even small balances can escalate into large amounts due to accruing interest.
As debts grow larger because of these charges, individuals may find it difficult to manage their finances properly and pay off what they owe. This can result in a vicious debt cycle where they rely on credit for everyday expenses while struggling under the weight of accumulating interest.
- Need for Financial Discipline
A strong sense of financial discipline and effective budgeting skills is required to manage a higher credit limit. Without these essential tools, individuals risk falling into debt traps that can be challenging to escape.
High credit limits can create a misleading sense of security due to which people may think they have more disposable income than they actually possess. People may have poor fuinancial discipline due to this mindset which results in poor spending habits and inadequate planning for future expenses or emergencies.
Individuals must actively monitor their spending, create realistic budgets, and adhere strictly to payment schedules to avoid these poor spending habits. Failure to exercise this discipline can result in overwhelming debt and long-term financial consequences that could have been avoided with better management practices.
Conclusion
Understanding credit card limits is essential for effective financial management. These limits, determined by factors such as creditworthiness and income, play a crucial role in budgeting and maintaining a healthy credit utilization ratio. While higher limits can provide flexibility and potential benefits for credit scores, they also pose risks of overspending and accumulating debt if not managed responsibly.
Therefore, individuals must exercise financial discipline, carefully monitor their spending, and adhere to payment schedules to avoid the pitfalls associated with high credit limits. Ultimately, a balanced approach to credit management can lead to improved financial health and better borrowing opportunities in the future.
FAQs!
How Do Credit Cards Decide your Limit?
Credit card limits are determined by issuers based on several factors such as your debt-to-income ratio, credit score, income, and repayment history. Lenders aims to set limits that encourage usage while minimizing the risk of default by keeping them within a manageable range for the borrower.
Why are Credit Limits Important?
Your credit utilization ratio can be influenced by your credit limits which is an important factor in calculating your credit score. Maintaining a low utilization ratio can enhance your creditworthiness that makes it easier to obtain loans or favorable interest rates in the future.
What are the Average Credit Card Limits?
Average credit card limits can vary widely based on factors like credit score and income but typically range from $1,000 to $5,000 for most consumers. Higher-risk borrowers may have lower limits, while those with excellent credit histories might receive limits exceeding $10,000.
How to Increase the Set Credit Card Limit?
You can request a credit limit increase from your issuer which may consider your payment history and income changes. Alternatively, consistently paying off your balance in full and maintaining a low utilization ratio can also prompt issuers to raise your limit over time automatically.
