In the contemporary business world, the efficiency and reliability of accounting software are essential, especially for small businesses, where record keeping is crucial, and these businesses need to adhere to tax laws.
Traditional bookkeeping can be tedious and sometimes even results in mistakes, but using the software for business items such as invoicing, managing expenses, or preparing reports can be a big plus, as it helps save a lot of time.
Implementation of accurate software can help business owners understand their financial position and make wise decisions that can increase business revenue and profitability.
Software like QuickBooks Online, Xero, and FreshBook provide easily navigable solutions for small businesses. Some of these tools come with facilities like auto feed from the business bank, basic financial statement generation, and business app compatibility.
From issues related to cash management to taxation, finding the right accounting software helps small businesses manage their financial engagements properly and efficiently.
Who Needs Accounting Software?
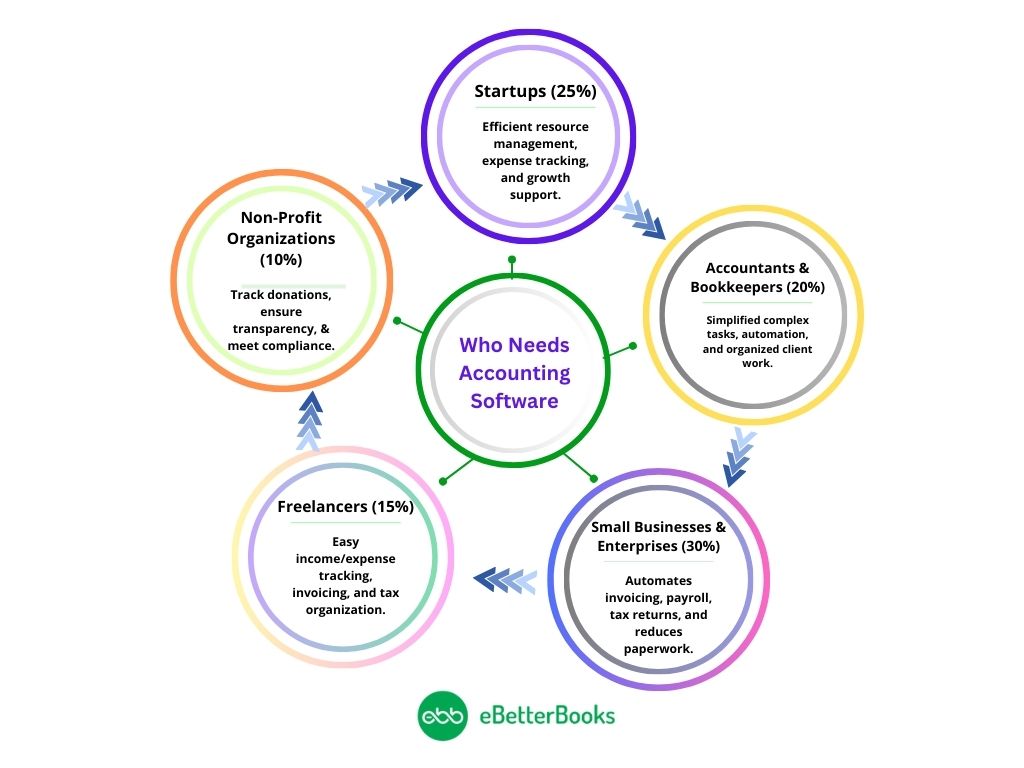
Accounting software is essential for different individuals and organizations.
1. Startups
To the startups, proper accounting and utilization of their scarce resources are made easier by accounting software. It assists them in the management of their expenditure, controlling the flow of cash, and ensuring overall accountability for their financial records from the initial stage.
With the growth of startups, accounting tools are used to give information on the financial situation, and they help in making the right decisions to support the growth of the businesses.
2. Accountants and Bookkeepers
It is also very beneficial to use specialized software because accounting, including the work of a bookkeeper, involves complex calculations, better results are achieved, and work with several clients of several businesses can be clearly and easily organized.
The automation features alleviated manual inputs, served the purpose of faster results, and enabled the professionals to focus on delivering strategic financial solutions to their clients.
3. Small Businesses and Enterprises
Accounting software is essential in the management of small businesses and enterprises as it reduces the number of daily tasks to be performed, including preparing invoices, payroll, and tax returns. These tools help to minimize the paper burden and, at the same time, ensure legal compliance for businesses.
When financial operations are optimized, business owners have more time to work on strategic development solutions and, hence, come up with better-informed decisions.
4. Freelancers and Independent Professionals
There is a quote for freelancers and independent workers who are satisfied with a simple and easy-to-use accounting tool to record their income, expenses, and receipts of the client.
They also let you create polished invoices, log project hours, and organize your finances for taxes without any manual documentation required. The automation and the simplicity enable the freelancers to focus on their core work because the issue of a book of accounts will not squeeze their time.
5. Non-Profit Organizations (NPOs) and Associations
Accounting software is a friend when it comes to tracking and managing donations, grants, and the expenses of non-profit organizations.
Such organizations are required to practice transparency and accountability in their financial transactions; accounting aids enable such firms to manage their finances, prepare and submit reports to the concerned stakeholders, and conform to the legal requirements.
Appropriate accounting software assists NPOs in the most efficient way to utilize their available resources and have the least distraction in pursuing their missions.
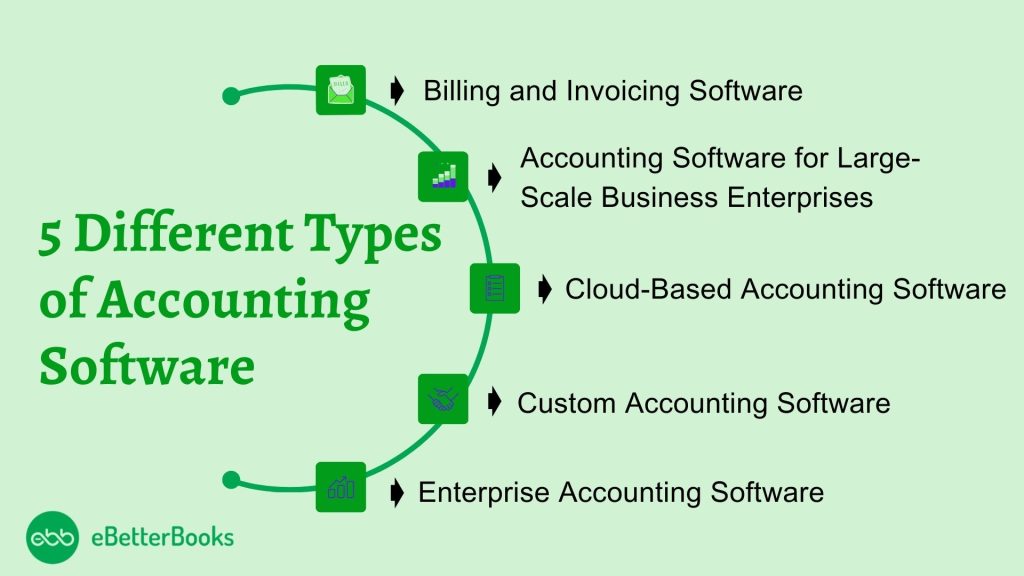
Different Types of Accounting Software
There are various categories of accounting software based on the nature of the business, its size, and its functions, as explained below:
1. Billing and Invoicing Software
This type of accounting software is specific to billing and invoicing forms; hence, it may not contain some of the basic features that are present in general accounting software. I enable users to generate invoices, dispatch and organize invoices, manage payments, and be on top of unpaid dues and balances.
It is particularly useful for entrepreneurs, freelancers, and other service providers as it eliminates the need for manual creation of invoices and follow-ups regarding payments. Some of the well-known ones are FreshBooks and Zoho Invoice.
2. Accounting Software for Large-Scale Business Enterprises
Intended for midsize to large companies, this software contains sophisticated account vantage services such as stock management, payroll, and tax.
It deals with humongous financial records and offers flexibility in reporting. Such systems are often designed to provide solutions to the requirements of large corporations. Some of the most recommended ones are QuickBooks Enterprise and Sage Intacct.
3. Cloud-Based Accounting Software
With cloud-based accounting, you can access the company’s financial data at any time using an internet connection. This type of software is particularly suitable where there is a need for flexibility, teleworking, or several people in an organization who might be involved in the accounting processes.
Some of the benefits of cloud software include updates, greater security, and flexibility, which makes it suitable for small- to medium-sized businesses. Some of them are Xero and QuickBooks Online, among many others in the market.
4. Custom Accounting Software
These are those accounting solutions that are made to order for a certain business establishment. It is best suited for embedding into the existing environment, working with some unique financial processes, or meeting certain sector requirements.
Such software is most frequently employed by companies that have intricate approaches to the management of their finances or specific needs while fostering flawless adherence to the business’s functioning model.
5. Enterprise Accounting Software
Enterprise accounting software can thus be described as an elaborate program meant for managing extreme major operations. It coordinates functions such as budgeting, forecasting financial statements, financial reporting, asset management, and financial compliance.
Such systems are usually deployed as components of the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, which unifies all the company’s crucial processes.
SAP, Oracle NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamic 365 are examples of the software used by multinational companies to address complex accounting needs in different regions and departments.
How to Pick the Best Accounting Software for a Business?
Different metrics will be considered before making the decision.

1. Assess Your Business Needs
The first step one needs to take is to determine the particular accounting needs of the particular enterprise one is running. Some of the factors include the size of the firm, industry classification, and the nature and complexity of the organization’s operations.
Decide whether you require simple tools like invoicing and expense tracking or more complex ones, such as payrolls, inventories, taxes, and many more.
For instance, a small company that operates in the service industry might require only invoicing solutions, while a big company would need them as a part of the ERP system.
2. Set a Budget
Find out your balance and how much you are willing or able to spend on the accounting software. This is true based on the type of software being subscribed, whether cloud-based or on-premise, the number of users that the software will cover, and other requested features.
As the functionality offered is directly proportional to the price being paid, one needs to be very careful while choosing the software that would be most beneficial to your business.
For instance, an emerging startup or a freelancer will be comfortable using a tool that costs nothing or is affordable. At the same time, large organizations may have to spend more and opt for enterprise solutions.
3. Consider Ease of Use
Select a program for implementation that is not very complicated and does not need much training for your team. The software must be easy to use so it can be easy to make invoices, create reports, and track costs.
If the workers are required to learn the software, this may take some time, and if the curve is steep, this can lead to poor performance and utilization of the software or even mistakes.
Other web-based solutions that are quite popular are QuickBooks Online and Xero, as these two programs differ in being rather simple.
4. Evaluate Features and Integrations
When choosing the software to use, ensure that it considers your particular business requirements. For instance, the software must support automating payroll, tax computations, or inventory management.
Furthermore, it should be compatible with the other important applications you utilize, such as CRM, payment processors, and project management software.
5. Scalability
In effectively managing the needs of your business, you will find that your accounting needs will also be changing. Select software that can grow along with your business and is capable of additional features like handling larger numbers of users, using different currencies, or meeting international tax laws.
Other applications can be Zoho Books or NetSuite, which guarantee that the accounting software will remain appropriate for the company’s growth.
6. Security and Compliance
Ensure that the accounting software you purchase has strong features to address the security concerns of financial data. Implement solutions that can include features such as encryption for security, access to solutions for specific clients, and frequent backups.
For those who work in a highly legalized sphere or are oriented in several countries, the software must comply with the standards set by the legislation, whether they are GDPR or the requirements of the particular industry, for instance.
7. Customer Support and Training
Good customer care services are vital because it is always disheartening to find yourself struggling with technical hitches on your learning applications or needing help understanding certain options in your software.
Ensure that the software suppliers include technical support, Live Chat, or a dedicated Account Manager available around the clock. Further, they should be in a position to offer your team training aids, tutorials, or even user forums that can assist in harnessing the full potential of the software.
8. Test Before You Buy
Most accounting software providers provide free trial or demo versions of their software. Use these to assess the effectiveness and usability of such software in your business.
Next, test to determine the software’s compatibility with your needs and integration with other systems. This trial period also enables one to have an idea of the quality of customer support to expect in the future.
Following this approach will guarantee suitable accounting software for business needs, cost, and tenable development.
Most Popular Accounting Softwares


































Most Popular Comparisons
QuickBooks Online
- QuickBooks Online vs Epicor ERP
- QuickBooks Online vs DEXT
- QuickBooks Online vs Cosmolex
- QuickBooks Online vs Cognos
- QuickBooks Online vs Classe365
- QuickBooks Online vs Caseware Working Papers
- QuickBooks Online vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- QuickBooks Online vs Bill
- QuickBooks Online vs Basware
- QuickBooks Online vs Spreadsheet Server
- QuickBooks Online vs Avidxchange
- QuickBooks Online vs Avalara
- QuickBooks Online vs Aplos
- QuickBooks Online vs Expensify
- QuickBooks Online vs Financialforce
- QuickBooks Online vs Fiserv
- QuickBooks Online vs Freshbooks
- QuickBooks Online vs Holded
- QuickBooks Online vs Kashflow
- QuickBooks Online vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- QuickBooks Online vs Workday Financial
- QuickBooks Online vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- QuickBooks Online vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- QuickBooks Online vs Multiview
- QuickBooks Online vs Myob
- QuickBooks Online vs Netsuite
- QuickBooks Online vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- QuickBooks Online vs Quickbooks Desktop
- QuickBooks Online vs Anaplan
- QuickBooks Online vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- QuickBooks Online vs XERO
- QuickBooks Online vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- QuickBooks Online vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- QuickBooks Online vs Sage 50cloud
- QuickBooks Online vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- QuickBooks Online vs Sage Intacct
- QuickBooks Online vs Sap Cash Management
- QuickBooks Online vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- QuickBooks Online vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- QuickBooks Online vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- QuickBooks Online vs Spendesk
- QuickBooks Online vs Zoho Books
Epicor ERP
- Epicor ERP vs QuickBooks Online
- Epicor ERP vs DEXT
- Epicor ERP vs Cosmolex
- Epicor ERP vs Cognos
- Epicor ERP vs Classe365
- Epicor ERP vs Caseware Working Papers
- Epicor ERP vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Epicor ERP vs Bill
- Epicor ERP vs Basware
- Epicor ERP vs Spreadsheet Server
- Epicor ERP vs Avidxchange
- Epicor ERP vs Avalara
- Epicor ERP vs Aplos
- Epicor ERP vs Expensify
- Epicor ERP vs Financialforce
- Epicor ERP vs Fiserv
- Epicor ERP vs Freshbooks
- Epicor ERP vs Holded
- Epicor ERP vs Kashflow
- Epicor ERP vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Epicor ERP vs Workday Financial
- Epicor ERP vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Epicor ERP vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Epicor ERP vs Multiview
- Epicor ERP vs Myob
- Epicor ERP vs Netsuite
- Epicor ERP vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Epicor ERP vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Epicor ERP vs Anaplan
- Epicor ERP vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Epicor ERP vs XERO
- Epicor ERP vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Epicor ERP vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Epicor ERP vs Sage 50cloud
- Epicor ERP vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Epicor ERP vs Sage Intacct
- Epicor ERP vs Sap Cash Management
- Epicor ERP vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Epicor ERP vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Epicor ERP vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Epicor ERP vs Spendesk
- Epicor ERP vs Zoho Books
DEXT
- DEXT vs QuickBooks Online
- DEXT vs Epicor ERP
- DEXT vs Cosmolex
- DEXT vs Cognos
- DEXT vs Classe365
- DEXT vs Caseware Working Papers
- DEXT vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- DEXT vs Bill
- DEXT vs Basware
- DEXT vs Spreadsheet Server
- DEXT vs Avidxchange
- DEXT vs Avalara
- DEXT vs Aplos
- DEXT vs Expensify
- DEXT vs Financialforce
- DEXT vs Fiserv
- DEXT vs Freshbooks
- DEXT vs Holded
- DEXT vs Kashflow
- DEXT vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- DEXT vs Workday Financial
- DEXT vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- DEXT vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- DEXT vs Multiview
- DEXT vs Myob
- DEXT vs Netsuite
- DEXT vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- DEXT vs Quickbooks Desktop
- DEXT vs Anaplan
- DEXT vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- DEXT vs XERO
- DEXT vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- DEXT vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- DEXT vs Sage 50cloud
- DEXT vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- DEXT vs Sage Intacct
- DEXT vs Sap Cash Management
- DEXT vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- DEXT vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- DEXT vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- DEXT vs Spendesk
- DEXT vs Zoho Books
Cosmolex
- Cosmolex vs QuickBooks Online
- Cosmolex vs Epicor ERP
- Cosmolex vs DEXT
- Cosmolex vs Cognos
- Cosmolex vs Classe365
- Cosmolex vs Caseware Working Papers
- Cosmolex vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Cosmolex vs Bill
- Cosmolex vs Basware
- Cosmolex vs Spreadsheet Server
- Cosmolex vs Avidxchange
- Cosmolex vs Avalara
- Cosmolex vs Aplos
- Cosmolex vs Expensify
- Cosmolex vs Financialforce
- Cosmolex vs Fiserv
- Cosmolex vs Freshbooks
- Cosmolex vs Holded
- Cosmolex vs Kashflow
- Cosmolex vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Cosmolex vs Workday Financial
- Cosmolex vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Cosmolex vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Cosmolex vs Multiview
- Cosmolex vs Myob
- Cosmolex vs Netsuite
- Cosmolex vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Cosmolex vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Cosmolex vs Anaplan
- Cosmolex vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Cosmolex vs XERO
- Cosmolex vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Cosmolex vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Cosmolex vs Sage 50cloud
- Cosmolex vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Cosmolex vs Sage Intacct
- Cosmolex vs Sap Cash Management
- Cosmolex vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Cosmolex vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Cosmolex vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Cosmolex vs Spendesk
- Cosmolex vs Zoho Books
Cognos
- Cognos vs QuickBooks Online
- Cognos vs Epicor ERP
- Cognos vs DEXT
- Cognos vs Cosmolex
- Cognos vs Classe365
- Cognos vs Caseware Working Papers
- Cognos vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Cognos vs Bill
- Cognos vs Basware
- Cognos vs Spreadsheet Server
- Cognos vs Avidxchange
- Cognos vs Avalara
- Cognos vs Aplos
- Cognos vs Expensify
- Cognos vs Financialforce
- Cognos vs Fiserv
- Cognos vs Freshbooks
- Cognos vs Holded
- Cognos vs Kashflow
- Cognos vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Cognos vs Workday Financial
- Cognos vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Cognos vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Cognos vs Multiview
- Cognos vs Myob
- Cognos vs Netsuite
- Cognos vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Cognos vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Cognos vs Anaplan
- Cognos vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Cognos vs XERO
- Cognos vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Cognos vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Cognos vs Sage 50cloud
- Cognos vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Cognos vs Sage Intacct
- Cognos vs Sap Cash Management
- Cognos vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Cognos vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Cognos vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Cognos vs Spendesk
- Cognos vs Zoho Books
Classe365
- Classe365 vs QuickBooks Online
- Classe365 vs Epicor ERP
- Classe365 vs DEXT
- Classe365 vs Cosmolex
- Classe365 vs Cognos
- Classe365 vs Classe365
- Classe365 vs Caseware Working Papers
- Classe365 vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Classe365 vs Bill
- Classe365 vs Basware
- Classe365 vs Spreadsheet Server
- Classe365 vs Avidxchange
- Classe365 vs Avalara
- Classe365 vs Aplos
- Classe365 vs Expensify
- Classe365 vs Financialforce
- Classe365 vs Fiserv
- Classe365 vs Freshbooks
- Classe365 vs Holded
- Classe365 vs Kashflow
- Classe365 vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Classe365 vs Workday Financial
- Classe365 vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Classe365 vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Classe365 vs Multiview
- Classe365 vs Myob
- Classe365 vs Netsuite
- Classe365 vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Classe365 vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Classe365 vs Anaplan
- Classe365 vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Classe365 vs XERO
- Classe365 vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Classe365 vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Classe365 vs Sage 50cloud
- Classe365 vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Classe365 vs Sage Intacct
- Classe365 vs Sap Cash Management
- Classe365 vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Classe365 vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Classe365 vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Classe365 vs Spendesk
- Classe365 vs Zoho Books
Caseware Working Papers
- Caseware Working Papers vs QuickBooks Online
- Caseware Working Papers vs Epicor ERP
- Caseware Working Papers vs DEXT
- Caseware Working Papers vs Cosmolex
- Caseware Working Papers vs Cognos
- Caseware Working Papers vs Classe365
- Caseware Working Papers vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Caseware Working Papers vs Bill
- Caseware Working Papers vs Basware
- Caseware Working Papers vs Spreadsheet Server
- Caseware Working Papers vs Avidxchange
- Caseware Working Papers vs Avalara
- Caseware Working Papers vs Aplos
- Caseware Working Papers vs Expensify
- Caseware Working Papers vs Financialforce
- Caseware Working Papers vs Fiserv
- Caseware Working Papers vs Freshbooks
- Caseware Working Papers vs Holded
- Caseware Working Papers vs Kashflow
- Caseware Working Papers vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Caseware Working Papers vs Workday Financial
- Caseware Working Papers vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Caseware Working Papers vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Caseware Working Papers vs Multiview
- Caseware Working Papers vs Myob
- Caseware Working Papers vs Netsuite
- Caseware Working Papers vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Caseware Working Papers vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Caseware Working Papers vs Anaplan
- Caseware Working Papers vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Caseware Working Papers vs XERO
- Caseware Working Papers vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Caseware Working Papers vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Caseware Working Papers vs Sage 50cloud
- Caseware Working Papers vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Caseware Working Papers vs Sage Intacct
- Caseware Working Papers vs Sap Cash Management
- Caseware Working Papers vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Caseware Working Papers vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Caseware Working Papers vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Caseware Working Papers vs Spendesk
- Caseware Working Papers vs Zoho Books
Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs QuickBooks Online
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Epicor ERP
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs DEXT
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Cosmolex
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Cognos
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Classe365
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Caseware Working Papers
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Bill
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Basware
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Spreadsheet Server
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Avidxchange
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Avalara
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Aplos
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Expensify
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Financialforce
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Fiserv
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Freshbooks
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Holded
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Kashflow
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Workday Financial
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Multiview
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Myob
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Netsuite
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Anaplan
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs XERO
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Sage 50cloud
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Sage Intacct
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Sap Cash Management
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Spendesk
- Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt vs Zoho Books
Bill
- Bill vs QuickBooks Online
- Bill vs Epicor ERP
- Bill vs DEXT
- Bill vs Cosmolex
- Bill vs Cognos
- Bill vs Classe365
- Bill vs Caseware Working Papers
- Bill vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Bill vs Basware
- Bill vs Spreadsheet Server
- Bill vs Avidxchange
- Bill vs Avalara
- Bill vs Aplos
- Bill vs Expensify
- Bill vs Financialforce
- Bill vs Fiserv
- Bill vs Freshbooks
- Bill vs Holded
- Bill vs Kashflow
- Bill vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Bill vs Workday Financial
- Bill vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Bill vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Bill vs Multiview
- Bill vs Myob
- Bill vs Netsuite
- Bill vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Bill vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Bill vs Anaplan
- Bill vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Bill vs XERO
- Bill vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Bill vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Bill vs Sage 50cloud
- Bill vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Bill vs Sage Intacct
- Bill vs Sap Cash Management
- Bill vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Bill vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Bill vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Bill vs Spendesk
- Bill vs Zoho Books
Basware
- Basware vs QuickBooks Online
- Basware vs Epicor ERP
- Basware vs DEXT
- Basware vs Cosmolex
- Basware vs Cognos
- Basware vs Classe365
- Basware vs Caseware Working Papers
- Basware vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Basware vs Bill
- Basware vs Spreadsheet Server
- Basware vs Avidxchange
- Basware vs Avalara
- Basware vs Aplos
- Basware vs Expensify
- Basware vs Financialforce
- Basware vs Fiserv
- Basware vs Freshbooks
- Basware vs Holded
- Basware vs Kashflow
- Basware vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Basware vs Workday Financial
- Basware vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Basware vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Basware vs Multiview
- Basware vs Myob
- Basware vs Netsuite
- Basware vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Basware vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Basware vs Anaplan
- Basware vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Basware vs XERO
- Basware vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Basware vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Basware vs Sage 50cloud
- Basware vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Basware vs Sage Intacct
- Basware vs Sap Cash Management
- Basware vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Basware vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Basware vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Basware vs Spendesk
- Basware vs Zoho Books
Spreadsheet Server
- Spreadsheet Server vs QuickBooks Online
- Spreadsheet Server vs Epicor ERP
- Spreadsheet Server vs DEXT
- Spreadsheet Server vs Cosmolex
- Spreadsheet Server vs Cognos
- Spreadsheet Server vs Classe365
- Spreadsheet Server vs Caseware Working Papers
- Spreadsheet Server vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Spreadsheet Server vs Bill
- Spreadsheet Server vs Basware
- Spreadsheet Server vs Avidxchange
- Spreadsheet Server vs Avalara
- Spreadsheet Server vs Aplos
- Spreadsheet Server vs Expensify
- Spreadsheet Server vs Financialforce
- Spreadsheet Server vs Fiserv
- Spreadsheet Server vs Freshbooks
- Spreadsheet Server vs Holded
- Spreadsheet Server vs Kashflow
- Spreadsheet Server vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Spreadsheet Server vs Workday Financial
- Spreadsheet Server vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Spreadsheet Server vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Spreadsheet Server vs Multiview
- Spreadsheet Server vs Myob
- Spreadsheet Server vs Netsuite
- Spreadsheet Server vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Spreadsheet Server vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Spreadsheet Server vs Anaplan
- Spreadsheet Server vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Spreadsheet Server vs XERO
- Spreadsheet Server vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Spreadsheet Server vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Spreadsheet Server vs Sage 50cloud
- Spreadsheet Server vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Spreadsheet Server vs Sage Intacct
- Spreadsheet Server vs Sap Cash Management
- Spreadsheet Server vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Spreadsheet Server vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Spreadsheet Server vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Spreadsheet Server vs Spendesk
- Spreadsheet Server vs Zoho Books
Avidxchange
- Avidxchange vs QuickBooks Online
- Avidxchange vs Epicor ERP
- Avidxchange vs DEXT
- Avidxchange vs Cosmolex
- Avidxchange vs Cognos
- Avidxchange vs Classe365
- Avidxchange vs Caseware Working Papers
- Avidxchange vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Avidxchange vs Bill
- Avidxchange vs Basware
- Avidxchange vs Spreadsheet Server
- Avidxchange vs Avalara
- Avidxchange vs Aplos
- Avidxchange vs Expensify
- Avidxchange vs Financialforce
- Avidxchange vs Fiserv
- Avidxchange vs Freshbooks
- Avidxchange vs Holded
- Avidxchange vs Kashflow
- Avidxchange vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Avidxchange vs Workday Financial
- Avidxchange vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Avidxchange vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Avidxchange vs Multiview
- Avidxchange vs Myob
- Avidxchange vs Netsuite
- Avidxchange vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Avidxchange vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Avidxchange vs Anaplan
- Avidxchange vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Avidxchange vs XERO
- Avidxchange vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Avidxchange vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Avidxchange vs Sage 50cloud
- Avidxchange vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Avidxchange vs Sage Intacct
- Avidxchange vs Sap Cash Management
- Avidxchange vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Avidxchange vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Avidxchange vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Avidxchange vs Spendesk
- Avidxchange vs Zoho Books
Avalara
- Avalara vs QuickBooks Online
- Avalara vs Epicor ERP
- Avalara vs DEXT
- Avalara vs Cosmolex
- Avalara vs Cognos
- Avalara vs Classe365
- Avalara vs Caseware Working Papers
- Avalara vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Avalara vs Bill
- Avalara vs Basware
- Avalara vs Spreadsheet Server
- Avalara vs Avidxchange
- Avalara vs Aplos
- Avalara vs Expensify
- Avalara vs Financialforce
- Avalara vs Fiserv
- Avalara vs Freshbooks
- Avalara vs Holded
- Avalara vs Kashflow
- Avalara vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Avalara vs Workday Financial
- Avalara vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Avalara vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Avalara vs Multiview
- Avalara vs Myob
- Avalara vs Netsuite
- Avalara vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Avalara vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Avalara vs Anaplan
- Avalara vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Avalara vs XERO
- Avalara vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Avalara vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Avalara vs Sage 50cloud
- Avalara vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Avalara vs Sage Intacct
- Avalara vs Sap Cash Management
- Avalara vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Avalara vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Avalara vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Avalara vs Spendesk
- Avalara vs Zoho Books
Aplos
- Aplos vs QuickBooks Online
- Aplos vs Epicor ERP
- Aplos vs DEXT
- Aplos vs Cosmolex
- Aplos vs Cognos
- Aplos vs Classe365
- Aplos vs Caseware Working Papers
- Aplos vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Aplos vs Bill
- Aplos vs Basware
- Aplos vs Spreadsheet Server
- Aplos vs Avidxchange
- Aplos vs Avalara
- Aplos vs Expensify
- Aplos vs Financialforce
- Aplos vs Fiserv
- Aplos vs Freshbooks
- Aplos vs Holded
- Aplos vs Kashflow
- Aplos vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Aplos vs Workday Financial
- Aplos vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Aplos vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Aplos vs Multiview
- Aplos vs Myob
- Aplos vs Netsuite
- Aplos vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Aplos vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Aplos vs Anaplan
- Aplos vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Aplos vs XERO
- Aplos vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Aplos vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Aplos vs Sage 50cloud
- Aplos vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Aplos vs Sage Intacct
- Aplos vs Sap Cash Management
- Aplos vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Aplos vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Aplos vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Aplos vs Spendesk
- Aplos vs Zoho Books
Expensify
- Expensify vs QuickBooks Online
- Expensify vs Epicor ERP
- Expensify vs DEXT
- Expensify vs Cosmolex
- Expensify vs Cognos
- Expensify vs Classe365
- Expensify vs Caseware Working Papers
- Expensify vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Expensify vs Bill
- Expensify vs Basware
- Expensify vs Spreadsheet Server
- Expensify vs Avidxchange
- Expensify vs Avalara
- Expensify vs Aplos
- Expensify vs Financialforce
- Expensify vs Fiserv
- Expensify vs Freshbooks
- Expensify vs Holded
- Expensify vs Kashflow
- Expensify vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Expensify vs Workday Financial
- Expensify vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Expensify vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Expensify vs Multiview
- Expensify vs Myob
- Expensify vs Netsuite
- Expensify vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Expensify vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Expensify vs Anaplan
- Expensify vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Expensify vs XERO
- Expensify vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Expensify vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Expensify vs Sage 50cloud
- Expensify vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Expensify vs Sage Intacct
- Expensify vs Sap Cash Management
- Expensify vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Expensify vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Expensify vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Expensify vs Spendesk
- Expensify vs Zoho Books
Financialforce
- Financialforce vs QuickBooks Online
- Financialforce vs Epicor ERP
- Financialforce vs DEXT
- Financialforce vs Cosmolex
- Financialforce vs Cognos
- Financialforce vs Classe365
- Financialforce vs Caseware Working Papers
- Financialforce vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Financialforce vs Bill
- Financialforce vs Basware
- Financialforce vs Spreadsheet Server
- Financialforce vs Avidxchange
- Financialforce vs Avalara
- Financialforce vs Aplos
- Financialforce vs Expensify
- Financialforce vs Fiserv
- Financialforce vs Freshbooks
- Financialforce vs Holded
- Financialforce vs Kashflow
- Financialforce vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Financialforce vs Workday Financial
- Financialforce vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Financialforce vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Financialforce vs Multiview
- Financialforce vs Myob
- Financialforce vs Netsuite
- Financialforce vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Financialforce vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Financialforce vs Anaplan
- Financialforce vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Financialforce vs XERO
- Financialforce vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Financialforce vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Financialforce vs Sage 50cloud
- Financialforce vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Financialforce vs Sage Intacct
- Financialforce vs Sap Cash Management
- Financialforce vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Financialforce vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Financialforce vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Financialforce vs Spendesk
- Financialforce vs Zoho Books
Fiserv
- Fiserv vs QuickBooks Online
- Fiserv vs Epicor ERP
- Fiserv vs DEXT
- Fiserv vs Cosmolex
- Fiserv vs Cognos
- Fiserv vs Classe365
- Fiserv vs Caseware Working Papers
- Fiserv vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Fiserv vs Bill
- Fiserv vs Basware
- Fiserv vs Spreadsheet Server
- Fiserv vs Avidxchange
- Fiserv vs Avalara
- Fiserv vs Aplos
- Fiserv vs Expensify
- Fiserv vs Financialforce
- Fiserv vs Freshbooks
- Fiserv vs Holded
- Fiserv vs Kashflow
- Fiserv vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Fiserv vs Workday Financial
- Fiserv vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Fiserv vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Fiserv vs Multiview
- Fiserv vs Myob
- Fiserv vs Netsuite
- Fiserv vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Fiserv vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Fiserv vs Anaplan
- Fiserv vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Fiserv vs XERO
- Fiserv vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Fiserv vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Fiserv vs Sage 50cloud
- Fiserv vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Fiserv vs Sage Intacct
- Fiserv vs Sap Cash Management
- Fiserv vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Fiserv vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Fiserv vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Fiserv vs Spendesk
- Fiserv vs Zoho Books
Freshbooks
- Freshbooks vs QuickBooks Online
- Freshbooks vs Epicor ERP
- Freshbooks vs DEXT
- Freshbooks vs Cosmolex
- Freshbooks vs Cognos
- Freshbooks vs Classe365
- Freshbooks vs Caseware Working Papers
- Freshbooks vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Freshbooks vs Bill
- Freshbooks vs Basware
- Freshbooks vs Spreadsheet Server
- Freshbooks vs Avidxchange
- Freshbooks vs Avalara
- Freshbooks vs Aplos
- Freshbooks vs Expensify
- Freshbooks vs Financialforce
- Freshbooks vs Fiserv
- Freshbooks vs Holded
- Freshbooks vs Kashflow
- Freshbooks vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Freshbooks vs Workday Financial
- Freshbooks vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Freshbooks vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Freshbooks vs Multiview
- Freshbooks vs Myob
- Freshbooks vs Netsuite
- Freshbooks vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Freshbooks vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Freshbooks vs Anaplan
- Freshbooks vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Freshbooks vs XERO
- Freshbooks vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Freshbooks vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Freshbooks vs Sage 50cloud
- Freshbooks vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Freshbooks vs Sage Intacct
- Freshbooks vs Sap Cash Management
- Freshbooks vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Freshbooks vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Freshbooks vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Freshbooks vs Spendesk
- Freshbooks vs Zoho Books
Holded
- Holded vs QuickBooks Online
- Holded vs Epicor ERP
- Holded vs DEXT
- Holded vs Cosmolex
- Holded vs Cognos
- Holded vs Classe365
- Holded vs Caseware Working Papers
- Holded vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Holded vs Bill
- Holded vs Basware
- Holded vs Spreadsheet Server
- Holded vs Avidxchange
- Holded vs Avalara
- Holded vs Aplos
- Holded vs Expensify
- Holded vs Financialforce
- Holded vs Fiserv
- Holded vs Freshbooks
- Holded vs Kashflow
- Holded vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Holded vs Workday Financial
- Holded vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Holded vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Holded vs Multiview
- Holded vs Myob
- Holded vs Netsuite
- Holded vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Holded vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Holded vs Anaplan
- Holded vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Holded vs XERO
- Holded vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Holded vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Holded vs Sage 50cloud
- Holded vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Holded vs Sage Intacct
- Holded vs Sap Cash Management
- Holded vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Holded vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Holded vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Holded vs Spendesk
- Holded vs Zoho Books
Kashflow
- Kashflow vs QuickBooks Online
- Kashflow vs Epicor ERP
- Kashflow vs DEXT
- Kashflow vs Cosmolex
- Kashflow vs Cognos
- Kashflow vs Classe365
- Kashflow vs Caseware Working Papers
- Kashflow vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Kashflow vs Bill
- Kashflow vs Basware
- Kashflow vs Spreadsheet Server
- Kashflow vs Avidxchange
- Kashflow vs Avalara
- Kashflow vs Aplos
- Kashflow vs Expensify
- Kashflow vs Financialforce
- Kashflow vs Fiserv
- Kashflow vs Freshbooks
- Kashflow vs Holded
- Kashflow vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Kashflow vs Workday Financial
- Kashflow vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Kashflow vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Kashflow vs Multiview
- Kashflow vs Myob
- Kashflow vs Netsuite
- Kashflow vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Kashflow vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Kashflow vs Anaplan
- Kashflow vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Kashflow vs XERO
- Kashflow vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Kashflow vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Kashflow vs Sage 50cloud
- Kashflow vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Kashflow vs Sage Intacct
- Kashflow vs Sap Cash Management
- Kashflow vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Kashflow vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Kashflow vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Kashflow vs Spendesk
- Kashflow vs Zoho Books
Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs QuickBooks Online
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Epicor ERP
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs DEXT
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Cosmolex
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Cognos
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Classe365
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Caseware Working Papers
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Bill
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Basware
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Spreadsheet Server
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Avidxchange
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Avalara
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Aplos
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Expensify
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Financialforce
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Fiserv
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Freshbooks
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Holded
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Kashflow
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Workday Financial
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Multiview
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Myob
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Netsuite
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Anaplan
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs XERO
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Sage 50cloud
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Sage Intacct
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Sap Cash Management
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Spendesk
- Microsoft Dynamics GP vs Zoho Books
Workday Financial
- Workday Financial vs QuickBooks Online
- Workday Financial vs Epicor ERP
- Workday Financial vs DEXT
- Workday Financial vs Cosmolex
- Workday Financial vs Cognos
- Workday Financial vs Classe365
- Workday Financial vs Caseware Working Papers
- Workday Financial vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Workday Financial vs Bill
- Workday Financial vs Basware
- Workday Financial vs Spreadsheet Server
- Workday Financial vs Avidxchange
- Workday Financial vs Avalara
- Workday Financial vs Aplos
- Workday Financial vs Expensify
- Workday Financial vs Financialforce
- Workday Financial vs Fiserv
- Workday Financial vs Freshbooks
- Workday Financial vs Holded
- Workday Financial vs Kashflow
- Workday Financial vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Workday Financial vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Workday Financial vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Workday Financial vs Multiview
- Workday Financial vs Myob
- Workday Financial vs Netsuite
- Workday Financial vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Workday Financial vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Workday Financial vs Anaplan
- Workday Financial vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Workday Financial vs XERO
- Workday Financial vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Workday Financial vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Workday Financial vs Sage 50cloud
- Workday Financial vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Workday Financial vs Sage Intacct
- Workday Financial vs Sap Cash Management
- Workday Financial vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Workday Financial vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Workday Financial vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Workday Financial vs Spendesk
- Workday Financial vs Zoho Books
Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs QuickBooks Online
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Epicor ERP
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs DEXT
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Cosmolex
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Cognos
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Classe365
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Caseware Working Papers
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Bill
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Basware
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Spreadsheet Server
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Avidxchange
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Avalara
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Aplos
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Expensify
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Financialforce
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Fiserv
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Freshbooks
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Holded
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Kashflow
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Workday Financial
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Multiview
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Myob
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Netsuite
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Anaplan
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs XERO
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Sage 50cloud
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Sage Intacct
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Sap Cash Management
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Spendesk
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV vs Zoho Books
Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs QuickBooks Online
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Epicor ERP
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs DEXT
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Cosmolex
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Cognos
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Classe365
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Caseware Working Papers
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Bill
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Basware
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Spreadsheet Server
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Avidxchange
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Avalara
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Aplos
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Expensify
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Financialforce
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Fiserv
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Freshbooks
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Holded
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Kashflow
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Workday Financial
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Multiview
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Myob
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Netsuite
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Anaplan
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs XERO
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Sage 50cloud
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Sage Intacct
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Sap Cash Management
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Spendesk
- Microsoft Dynamics SL vs Zoho Books
Multiview
- Multiview vs QuickBooks Online
- Multiview vs Epicor ERP
- Multiview vs DEXT
- Multiview vs Cosmolex
- Multiview vs Cognos
- Multiview vs Classe365
- Multiview vs Caseware Working Papers
- Multiview vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Multiview vs Bill
- Multiview vs Basware
- Multiview vs Spreadsheet Server
- Multiview vs Avidxchange
- Multiview vs Avalara
- Multiview vs Aplos
- Multiview vs Expensify
- Multiview vs Financialforce
- Multiview vs Fiserv
- Multiview vs Freshbooks
- Multiview vs Holded
- Multiview vs Kashflow
- Multiview vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Multiview vs Workday Financial
- Multiview vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Multiview vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Multiview vs Myob
- Multiview vs Netsuite
- Multiview vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Multiview vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Multiview vs Anaplan
- Multiview vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Multiview vs XERO
- Multiview vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Multiview vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Multiview vs Sage 50cloud
- Multiview vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Multiview vs Sage Intacct
- Multiview vs Sap Cash Management
- Multiview vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Multiview vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Multiview vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Multiview vs Spendesk
- Multiview vs Zoho Books
Myob
- Myob vs QuickBooks Online
- Myob vs Epicor ERP
- Myob vs DEXT
- Myob vs Cosmolex
- Myob vs Cognos
- Myob vs Classe365
- Myob vs Caseware Working Papers
- Myob vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Myob vs Bill
- Myob vs Basware
- Myob vs Spreadsheet Server
- Myob vs Avidxchange
- Myob vs Avalara
- Myob vs Aplos
- Myob vs Expensify
- Myob vs Financialforce
- Myob vs Fiserv
- Myob vs Freshbooks
- Myob vs Holded
- Myob vs Kashflow
- Myob vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Myob vs Workday Financial
- Myob vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Myob vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Myob vs Multiview
- Myob vs Netsuite
- Myob vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Myob vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Myob vs Anaplan
- Myob vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Myob vs XERO
- Myob vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Myob vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Myob vs Sage 50cloud
- Myob vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Myob vs Sage Intacct
- Myob vs Sap Cash Management
- Myob vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Myob vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Myob vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Myob vs Spendesk
- Myob vs Zoho Books
Netsuite
- Netsuite vs QuickBooks Online
- Netsuite vs Epicor ERP
- Netsuite vs DEXT
- Netsuite vs Cosmolex
- Netsuite vs Cognos
- Netsuite vs Classe365
- Netsuite vs Caseware Working Papers
- Netsuite vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Netsuite vs Bill
- Netsuite vs Basware
- Netsuite vs Spreadsheet Server
- Netsuite vs Avidxchange
- Netsuite vs Avalara
- Netsuite vs Aplos
- Netsuite vs Expensify
- Netsuite vs Financialforce
- Netsuite vs Fiserv
- Netsuite vs Freshbooks
- Netsuite vs Holded
- Netsuite vs Kashflow
- Netsuite vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Netsuite vs Workday Financial
- Netsuite vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Netsuite vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Netsuite vs Multiview
- Netsuite vs Myob
- Netsuite vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Netsuite vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Netsuite vs Anaplan
- Netsuite vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Netsuite vs XERO
- Netsuite vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Netsuite vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Netsuite vs Sage 50cloud
- Netsuite vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Netsuite vs Sage Intacct
- Netsuite vs Sap Cash Management
- Netsuite vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Netsuite vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Netsuite vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Netsuite vs Spendesk
- Netsuite vs Zoho Books
Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs QuickBooks Online
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Epicor ERP
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs DEXT
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Cosmolex
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Cognos
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Classe365
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Caseware Working Papers
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Bill
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Basware
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Spreadsheet Server
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Avidxchange
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Avalara
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Aplos
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Expensify
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Financialforce
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Fiserv
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Freshbooks
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Holded
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Kashflow
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Workday Financial
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Multiview
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Myob
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Netsuite
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Anaplan
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs XERO
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Sage 50cloud
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Sage Intacct
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Sap Cash Management
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Spendesk
- Oracle Fusion Financial Management vs Zoho Books
Quickbooks Desktop
- Quickbooks Desktop vs QuickBooks Online
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Epicor ERP
- Quickbooks Desktop vs DEXT
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Cosmolex
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Cognos
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Classe365
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Caseware Working Papers
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Bill
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Basware
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Spreadsheet Server
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Avidxchange
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Avalara
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Aplos
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Expensify
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Financialforce
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Fiserv
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Freshbooks
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Holded
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Kashflow
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Workday Financial
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Multiview
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Myob
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Netsuite
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Anaplan
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Quickbooks Desktop vs XERO
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Sage 50cloud
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Sage Intacct
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Sap Cash Management
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Spendesk
- Quickbooks Desktop vs Zoho Books
Anaplan
- Anaplan vs QuickBooks Online
- Anaplan vs Epicor ERP
- Anaplan vs DEXT
- Anaplan vs Cosmolex
- Anaplan vs Cognos
- Anaplan vs Classe365
- Anaplan vs Caseware Working Papers
- Anaplan vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Anaplan vs Bill
- Anaplan vs Basware
- Anaplan vs Spreadsheet Server
- Anaplan vs Avidxchange
- Anaplan vs Avalara
- Anaplan vs Aplos
- Anaplan vs Expensify
- Anaplan vs Financialforce
- Anaplan vs Fiserv
- Anaplan vs Freshbooks
- Anaplan vs Holded
- Anaplan vs Kashflow
- Anaplan vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Anaplan vs Workday Financial
- Anaplan vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Anaplan vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Anaplan vs Multiview
- Anaplan vs Myob
- Anaplan vs Netsuite
- Anaplan vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Anaplan vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Anaplan vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Anaplan vs XERO
- Anaplan vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Anaplan vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Anaplan vs Sage 50cloud
- Anaplan vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Anaplan vs Sage Intacct
- Anaplan vs Sap Cash Management
- Anaplan vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Anaplan vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Anaplan vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Anaplan vs Spendesk
- Anaplan vs Zoho Books
Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs QuickBooks Online
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Epicor ERP
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs DEXT
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Cosmolex
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Cognos
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Classe365
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Caseware Working Papers
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Bill
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Basware
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Spreadsheet Server
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Avidxchange
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Avalara
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Aplos
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Expensify
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Financialforce
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Fiserv
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Freshbooks
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Holded
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Kashflow
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Workday Financial
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Multiview
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Myob
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Netsuite
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Anaplan
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs XERO
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Sage 50cloud
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Sage Intacct
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Sap Cash Management
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Spendesk
- Quickbooks Online Accountant vs Zoho Books
XERO
- XERO vs QuickBooks Online
- XERO vs Epicor ERP
- XERO vs DEXT
- XERO vs Cosmolex
- XERO vs Cognos
- XERO vs Classe365
- XERO vs Caseware Working Papers
- XERO vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- XERO vs Bill
- XERO vs Basware
- XERO vs Spreadsheet Server
- XERO vs Avidxchange
- XERO vs Avalara
- XERO vs Aplos
- XERO vs Expensify
- XERO vs Financialforce
- XERO vs Fiserv
- XERO vs Freshbooks
- XERO vs Holded
- XERO vs Kashflow
- XERO vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- XERO vs Workday Financial
- XERO vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- XERO vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- XERO vs Multiview
- XERO vs Myob
- XERO vs Netsuite
- XERO vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- XERO vs Quickbooks Desktop
- XERO vs Anaplan
- XERO vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- XERO vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- XERO vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- XERO vs Sage 50cloud
- XERO vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- XERO vs Sage Intacct
- XERO vs Sap Cash Management
- XERO vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- XERO vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- XERO vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- XERO vs Spendesk
- XERO vs Zoho Books
Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs QuickBooks Online
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Epicor ERP
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs DEXT
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Cosmolex
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Cognos
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Classe365
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Caseware Working Papers
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Bill
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Basware
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Spreadsheet Server
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Avidxchange
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Avalara
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Aplos
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Expensify
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Financialforce
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Fiserv
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Freshbooks
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Holded
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Kashflow
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Workday Financial
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Multiview
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Myob
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Netsuite
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Anaplan
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs XERO
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Sage 50cloud
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Sage Intacct
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Sap Cash Management
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Spendesk
- Quickbooks Proadvisor vs Zoho Books
Quickbooks Self Employed
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs QuickBooks Online
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Epicor ERP
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs DEXT
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Cosmolex
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Cognos
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Classe365
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Caseware Working Papers
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Bill
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Basware
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Spreadsheet Server
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Avidxchange
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Avalara
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Aplos
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Expensify
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Financialforce
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Fiserv
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Freshbooks
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Holded
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Kashflow
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Workday Financial
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Multiview
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Myob
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Netsuite
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Anaplan
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs XERO
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Sage 50cloud
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Sage Intacct
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Sap Cash Management
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Spendesk
- Quickbooks Self Employed vs Zoho Books
Sage 50cloud
- Sage 50cloud vs QuickBooks Online
- Sage 50cloud vs Epicor ERP
- Sage 50cloud vs DEXT
- Sage 50cloud vs Cosmolex
- Sage 50cloud vs Cognos
- Sage 50cloud vs Classe365
- Sage 50cloud vs Caseware Working Papers
- Sage 50cloud vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Sage 50cloud vs Bill
- Sage 50cloud vs Basware
- Sage 50cloud vs Spreadsheet Server
- Sage 50cloud vs Avidxchange
- Sage 50cloud vs Avalara
- Sage 50cloud vs Aplos
- Sage 50cloud vs Expensify
- Sage 50cloud vs Financialforce
- Sage 50cloud vs Fiserv
- Sage 50cloud vs Freshbooks
- Sage 50cloud vs Holded
- Sage 50cloud vs Kashflow
- Sage 50cloud vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Sage 50cloud vs Workday Financial
- Sage 50cloud vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Sage 50cloud vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Sage 50cloud vs Multiview
- Sage 50cloud vs Myob
- Sage 50cloud vs Netsuite
- Sage 50cloud vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Sage 50cloud vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Sage 50cloud vs Anaplan
- Sage 50cloud vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Sage 50cloud vs XERO
- Sage 50cloud vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Sage 50cloud vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Sage 50cloud vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Sage 50cloud vs Sage Intacct
- Sage 50cloud vs Sap Cash Management
- Sage 50cloud vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Sage 50cloud vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Sage 50cloud vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Sage 50cloud vs Spendesk
- Sage 50cloud vs Zoho Books
Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs QuickBooks Online
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Epicor ERP
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs DEXT
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Cosmolex
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Cognos
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Classe365
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Caseware Working Papers
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Bill
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Basware
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Spreadsheet Server
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Avidxchange
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Avalara
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Aplos
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Expensify
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Financialforce
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Fiserv
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Freshbooks
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Holded
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Kashflow
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Workday Financial
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Multiview
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Myob
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Netsuite
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Anaplan
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs XERO
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Sage 50cloud
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Sage Intacct
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Sap Cash Management
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Spendesk
- Sage Business Cloud Accounting vs Zoho Books
Sage Intacct
- Sage Intacct vs QuickBooks Online
- Sage Intacct vs Epicor ERP
- Sage Intacct vs DEXT
- Sage Intacct vs Cosmolex
- Sage Intacct vs Cognos
- Sage Intacct vs Classe365
- Sage Intacct vs Caseware Working Papers
- Sage Intacct vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Sage Intacct vs Bill
- Sage Intacct vs Basware
- Sage Intacct vs Spreadsheet Server
- Sage Intacct vs Avidxchange
- Sage Intacct vs Avalara
- Sage Intacct vs Aplos
- Sage Intacct vs Expensify
- Sage Intacct vs Financialforce
- Sage Intacct vs Fiserv
- Sage Intacct vs Freshbooks
- Sage Intacct vs Holded
- Sage Intacct vs Kashflow
- Sage Intacct vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Sage Intacct vs Workday Financial
- Sage Intacct vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Sage Intacct vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Sage Intacct vs Multiview
- Sage Intacct vs Myob
- Sage Intacct vs Netsuite
- Sage Intacct vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Sage Intacct vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Sage Intacct vs Anaplan
- Sage Intacct vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Sage Intacct vs XERO
- Sage Intacct vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Sage Intacct vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Sage Intacct vs Sage 50cloud
- Sage Intacct vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Sage Intacct vs Sap Cash Management
- Sage Intacct vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Sage Intacct vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Sage Intacct vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Sage Intacct vs Spendesk
- Sage Intacct vs Zoho Books
Sap Cash Management
- Sap Cash Management vs QuickBooks Online
- Sap Cash Management vs Epicor ERP
- Sap Cash Management vs DEXT
- Sap Cash Management vs Cosmolex
- Sap Cash Management vs Cognos
- Sap Cash Management vs Classe365
- Sap Cash Management vs Caseware Working Papers
- Sap Cash Management vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Sap Cash Management vs Bill
- Sap Cash Management vs Basware
- Sap Cash Management vs Spreadsheet Server
- Sap Cash Management vs Avidxchange
- Sap Cash Management vs Avalara
- Sap Cash Management vs Aplos
- Sap Cash Management vs Expensify
- Sap Cash Management vs Financialforce
- Sap Cash Management vs Fiserv
- Sap Cash Management vs Freshbooks
- Sap Cash Management vs Holded
- Sap Cash Management vs Kashflow
- Sap Cash Management vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Sap Cash Management vs Workday Financial
- Sap Cash Management vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Sap Cash Management vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Sap Cash Management vs Multiview
- Sap Cash Management vs Myob
- Sap Cash Management vs Netsuite
- Sap Cash Management vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Sap Cash Management vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Sap Cash Management vs Anaplan
- Sap Cash Management vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Sap Cash Management vs XERO
- Sap Cash Management vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Sap Cash Management vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Sap Cash Management vs Sage 50cloud
- Sap Cash Management vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Sap Cash Management vs Sage Intacct
- Sap Cash Management vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Sap Cash Management vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Sap Cash Management vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Sap Cash Management vs Spendesk
- Sap Cash Management vs Zoho Books
Sap Financials Ondemand
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs QuickBooks Online
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Epicor ERP
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs DEXT
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Cosmolex
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Cognos
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Classe365
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Caseware Working Papers
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Bill
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Basware
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Spreadsheet Server
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Avidxchange
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Avalara
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Aplos
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Expensify
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Financialforce
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Fiserv
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Freshbooks
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Holded
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Kashflow
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Workday Financial
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Multiview
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Myob
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Netsuite
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Anaplan
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs XERO
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Sage 50cloud
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Sage Intacct
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Sap Cash Management
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Spendesk
- Sap Financials Ondemand vs Zoho Books
Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs QuickBooks Online
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Epicor ERP
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs DEXT
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Cosmolex
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Cognos
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Classe365
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Caseware Working Papers
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Bill
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Basware
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Spreadsheet Server
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Avidxchange
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Avalara
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Aplos
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Expensify
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Financialforce
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Fiserv
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Freshbooks
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Holded
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Kashflow
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Workday Financial
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Multiview
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Myob
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Netsuite
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Anaplan
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs XERO
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Sage 50cloud
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Sage Intacct
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Sap Cash Management
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Spendesk
- Sap General Ledger Accounting vs Zoho Books
Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs QuickBooks Online
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Epicor ERP
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs DEXT
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Cosmolex
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Cognos
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Classe365
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Caseware Working Papers
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Bill
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Basware
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Spreadsheet Server
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Avidxchange
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Avalara
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Aplos
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Expensify
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Financialforce
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Fiserv
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Freshbooks
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Holded
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Kashflow
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Workday Financial
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Multiview
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Myob
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Netsuite
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Anaplan
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs XERO
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Sage 50cloud
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Sage Intacct
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Sap Cash Management
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Spendesk
- Sap Hana Cloud Platform vs Zoho Books
Spendesk
- Spendesk vs QuickBooks Online
- Spendesk vs Epicor ERP
- Spendesk vs DEXT
- Spendesk vs Cosmolex
- Spendesk vs Cognos
- Spendesk vs Classe365
- Spendesk vs Caseware Working Papers
- Spendesk vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Spendesk vs Bill
- Spendesk vs Basware
- Spendesk vs Spreadsheet Server
- Spendesk vs Avidxchange
- Spendesk vs Avalara
- Spendesk vs Aplos
- Spendesk vs Expensify
- Spendesk vs Financialforce
- Spendesk vs Fiserv
- Spendesk vs Freshbooks
- Spendesk vs Holded
- Spendesk vs Kashflow
- Spendesk vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Spendesk vs Workday Financial
- Spendesk vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Spendesk vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Spendesk vs Multiview
- Spendesk vs Myob
- Spendesk vs Netsuite
- Spendesk vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Spendesk vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Spendesk vs Anaplan
- Spendesk vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Spendesk vs XERO
- Spendesk vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Spendesk vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Spendesk vs Sage 50cloud
- Spendesk vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Spendesk vs Sage Intacct
- Spendesk vs Sap Cash Management
- Spendesk vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Spendesk vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Spendesk vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Spendesk vs Zoho Books
Zoho Books
- Zoho Books vs QuickBooks Online
- Zoho Books vs Epicor ERP
- Zoho Books vs DEXT
- Zoho Books vs Cosmolex
- Zoho Books vs Cognos
- Zoho Books vs Classe365
- Zoho Books vs Caseware Working Papers
- Zoho Books vs Blackbaud Financial Edge Nxt
- Zoho Books vs Bill
- Zoho Books vs Basware
- Zoho Books vs Spreadsheet Server
- Zoho Books vs Avidxchange
- Zoho Books vs Avalara
- Zoho Books vs Aplos
- Zoho Books vs Expensify
- Zoho Books vs Financialforce
- Zoho Books vs Fiserv
- Zoho Books vs Freshbooks
- Zoho Books vs Holded
- Zoho Books vs Kashflow
- Zoho Books vs Microsoft Dynamics GP
- Zoho Books vs Workday Financial
- Zoho Books vs Microsoft Dynamics NAV
- Zoho Books vs Microsoft Dynamics SL
- Zoho Books vs Multiview
- Zoho Books vs Myob
- Zoho Books vs Netsuite
- Zoho Books vs Oracle Fusion Financial Management
- Zoho Books vs Quickbooks Desktop
- Zoho Books vs Anaplan
- Zoho Books vs Quickbooks Online Accountant
- Zoho Books vs XERO
- Zoho Books vs Quickbooks Proadvisor
- Zoho Books vs Quickbooks Self Employed
- Zoho Books vs Sage 50cloud
- Zoho Books vs Sage Business Cloud Accounting
- Zoho Books vs Sage Intacct
- Zoho Books vs Sap Cash Management
- Zoho Books vs Sap Financials Ondemand
- Zoho Books vs Sap General Ledger Accounting
- Zoho Books vs Sap Hana Cloud Platform
- Zoho Books vs Spendesk
“Frequently Asked Questions”
Which is the best accounting software for a small business?
The best accounting software for a small business depends on specific needs, but here are some top-rated options:
- QuickBooks Online: QuickBooks Online is another option that is quite prevalent and wanted among small business users. It is easy to use, has rich features, and is cloud-based. These include invoicing, expenses, taxes, and reports where customers can personalize their appearance. It also supports a wide range of other third-party apps.
- Xero: Xero is scalable, which means that firms with expansionist visions can use it because it allows them to expand when the need arises. It provides ways for preparing or generating invoices, payments, banking, and even reporting financial data. This means that Xero also interacts with over 800 apps, which makes it very flexible.
- FreshBooks: It is suitable for service-oriented and new small businesses as well as freelancers. It consolidated invoicing time tracking features, as well as an expense system that looks minimalistic and has an easy-to-use mobile application for field financial management.
- Zoho Books: Zoho Books is another cheap and basic software that provides basic accounting services such as billing, inventory tracking, and banking. It is part of the Zoho family and is therefore recommended for companies that already use other Zoho solutions.
All of these are ideal for small businesses, and each can be said to be efficient in meeting their needs, depending on the price factor.
Which is a free accounting software for small businesses?
Wave Accounting is among the excellent free accounting software for small businesses.
It offers a wide range of features, including:
- Invoicing
- Expense tracking
- Bank reconciliation
- Financial reporting
- Receipt scanning
Wave is 100% free to use when it comes to performing its primary tasks of accounting, which will make the software perfect for small companies, freelancers, and independent business owners who have no complex accounting concerns.
However, if you need more services related to your business, like payroll credit card processing, among others, they attract extra charges. Some of the other leading free accounting software are ZipBooks and GnuCash. However, Wave has an easy-to-understand flow and offers all the necessary options.
Can I use Excel for financial reporting and as an accounting software?
Of course, you can generate financial reports and use Excel as basic accounting software, but it has its disadvantages compared to the usual accounting software.
Advantages of Using Excel:
- Customization: You can track your business’s finances far beyond the averages and make bespoke financial reports, P&L statements, and cash flow analyses.
- Templates: Different templates are available in Excel for budgeting, invoicing, and tracking finances, and of course, you have the flexibility to make the necessary modifications.
- Cost-effective: First, excel is fairly inexpensive; if you have Microsoft Office, as many people do, Excel is included in the package.
- Data manipulation: Pivots, queries, filters, and miscalculations are well accomplished, particularly in Microsoft Excel.
Limitations of Excel:
- Manual work: Unfortunately, most of the activities need to be performed manually, which increases the probability of errors and time consumption.
- No automation: Excel cannot track or unclassified transactions like accounting software, making financial management slightly more complicated.
- Lack of scalability: Over time, these features can be tedious when dealing with lots of data or several users when running your business.
- Limited compliance features: Excel doesn’t include integral tax compliance, payroll processing, or compatibility features with other financial solutions.
Whereas Excel can be used for financial reports in very small companies or start-ups, QuickBooks or Xero has many advantages in terms of automation, security, and capacity over Excel.
Which accounting software is best for online retail and e-commerce?
For businesses which are operating online, selling products online, the best accounting software solutions should come with features and tools most helpful for inventory sales, payment gateways and integration to e-commerce platforms.
Here are some top choices:
- QuickBooks Online
- Zoho Books
- Shopify Accounting by A2X
- NetSuite
All of these options come with an array of components that address the needs of e-commerce, such as the ability to deal with multiple sales channels, inventory control, and integrated payment processing systems.
Which accounting software is best for non-profit accounting?
When it comes to the non-profit organizations (NPOs) the software should address the issues of donor management and compliance reporting.
Here are some top choices:
- QuickBooks Online for Nonprofits
- Aplos
- Blackbaud Financial Edge NXT
- Sage Intacct
- Zoho Books
The presented solutions are intended to meet NPOs needs and help them to address the questions connected with the management of donations, grants, project financing as well as financial reporting.
Which accounting software is best for big businesses?
Depending on the size of the organization, big business accounting software needs to be packed with more features such as scalability, multi-currency processing, and real-time financial reporting, as well as integration with other enterprise systems.
Some of the top accounting software solutions for large organizations include:
- Oracle NetSuite
- SAP ERP
- Microsoft Dynamic 365
- Sage Intacct
- QuickBooks Enterprise
- Infor CloudSuite
- Xero
These applications are created for the effective management of highly converted financial operations, the integration of cross-continental operations, and real-time analytics for large businesses.
What is better for mid-size businesses, accounting software or ERP?
In the case of mid-size organizations, ERP (enterprise resource planning) systems are usually preferred over accounting software packages.
Here’s why:
- Advanced Features: ERP plans are considerably richer than simple accounting software and may include options such as multicurrency, extended reporting, and analysis.
- Integration: Accounting is a major component of ERP services that also include inventory, human resources, sales, and supply chain management services, which help create a centralized view of the business.
- Scalability: ERP is developed to offer increased complexity and higher volumes of data when an organization is expanding.
What is the difference between accounting software and ERP?
Here are the major differences between the both:
| Basis | ERP Software | Accounting Software |
| Scope | Comprehensive suite covering various business functions like HR, Inventory, CRM, etc. | Focuses primarily on financial management and accounting tasks. |
| Integration | Integrate multiple business processes and departments | Typically integrated with fewer business functions |
| Scalability | Designed to scale with complex and growing business needs. | May be limited in scalability and complexity compared to ERP. |
| Cost | Usually, it costs higher due to its extensive functions and customizable options. | Often more affordable and suitable for small and mid-size organizations. |
Do I need accounting software or ERP?
The presentation here highlights that there are specific areas where accounting software will meet the needs of your business while the ERP system will meet other needs of the business.
Here’s how to decide:
Business Size and Complexity
- Accounting Software: Suitable for those businesses that do not have complicated accounting operations to perform.
- ERP: More suitable for organizations that are large or operate in a multifaceted way that means that they need interconnected systems across different functions.
Functionality Needs
- Accounting Software: Is mostly concerned with matters relating to invoicing, expenses, or preparation of financial statements.
- ERP: It offers full coverage and contains functions such as finance, human resource, supply chain, and customer relationship management.
Integration Requirements
- Accounting Software: May not afford interfaces compatible with other business applications.
- ERP: A large number of business processes are unified and entails the features of a single interface to create a more efficient operation.
Scalability
- Accounting Software: Applicable for companies that have less complicated activities or those that have small size operations.
- ERP: Can address growing complexity and larger data size of the business.
Budget
- Accounting Software: Preliminary decisions generally require less investment than the equivalent in later stages and are usually more easily accomplished.
- ERP: It costs more as compared to it offers more features and endpoints customization, but it is required when clients need all-in-one solutions.
If your business is small or medium-sized and your requirements are not very complex, then you might benefit most from accounting software whereas if your business has more complicated needs and processes, then you are more likely to benefit from an ERP system that will comprise accounting software as well as other application modules.
Can I send invoices and receive payments online in accounting software?
Yes, there are few high quality accounting softwares with integration capabilities which fulfills the requirements like sending invoices and receiving payments online.
Some of the popular accounting software options with these features are:
- QuickBooks Online
- Xero
- FreshBooks
These applications optimize and automate invoices and payments and help with the times and lines within cash flow.
